12 U Organic Chemistry Worksheet # 3 – Organic Functional Group
advertisement

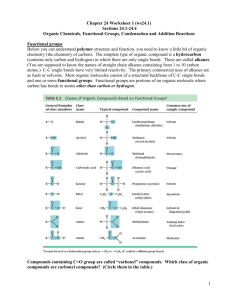
12 U Organic Chemistry Worksheet # 3 – Organic Functional Group Nomenclature 1. Draw the following alcohols a) heptan-2-ol b) 3-methylhexan-1-ol c) cyclopropanol d) 2,4,6-trichlorooctan-2-ol e) pentan-1,4-diol f) benzene-1,3-diol g) but-2-ene-1-ol h) 4-methylpent-2-yne-1-ol i) 3,4-dimethylcycloheptan-1-ol 2. Name the following alcohols H3C CH2 a) H3C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH OH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH OH b) CH3 CH3 c) HO OH Cl CH2 OH H3C CH2 CH2 CH CH CH2 CH2 CH HC OH CH CH3 CH3 CH2 e) CH2 OH H2C d) CH3 f) CH2 OH C HC CH HC CH CH2 CH3 H3C CH2 HC h) H3C CH g) C CH2 C OH CH3 CH3 C C CH3 CH3 OH HC CH2 CH2 CH3 i) 3. Explain why the propane that is used as a fuel in a BBQ is gas at room temperature, but 2-propanol used as rubbing alcohol is a liquid at room temperature. 4. Draw the following ethers a) 1-propoxypentane b) 2-ethoxybutane c) 1-methoxy-4-chlorohexane d) 3-butoxy-2,4-dimethyloctane e) 2-propoxy-4-phenylheptane f) 1-ethoxycyclopentane 5. Name the following ethers CH3 CH H3C O CH3 CH CH CH2 a) H3C O CH2 H3C CH3 CH2 b) CH2 CH CH3 CH3 H2C O c) CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 H3C CH3 CH2 CH3 H3C HC CH2 O H3C CH2 CH2 CH2 O CH2 O CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 H2C CH CH2 CH2 CH3 d) CH2 CH3 e) H3C f) 6. Why is ether no longer used as an anesthetic? Explain using your knowledge of its state and structure. 7. Draw the following aldehydes and ketones a) hexanal b) heptan-3-one c) 3-methyloctanal d) 2,2-dimethylhexan-3-one e) 2,4,6-trichloroheptanal f) 4-phenyloctan-2-one g) 2-methylcyclohexanone h) 4-hydroxyhexanal i) penta-1,4-dione 8. Name the following aldehydes and ketones H3C H3C CH2 O CH3 CH C CH2 CH2 a) b) H3C O CH2 CH2 H3C CH CH2 O C CH3 HC CH2 HC CH3 c) CH3 CH3 H2C C O H3C CH2 CH3 CH H3C CH O CH3 Cl CH HC H2C C e) O O d) CH CH2 CH CH3 f) CH3 g) C CH CH3 Br 9. Explain why no numeral is needed as a prefix in the naming of butanal and butanone. 10. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of predicted solubility, and give reasons for your answers: butanal, butane, butanol. 11. Draw the following carboxylic acids a) butanoic acid b) 2-methylpentanoic acid c) 3,5-dimethylheptanoic acid d) 5-hydroxyhexanoic acid e) 2,3,4-trichlorobutanoic acid f) 2-bromoethanoic acid 12. Name the following carboxylic acids H3C OH CH2 a) H3C CH2 CH2 H3C C CH2 CH2 CH3 O b) C CH3 OH O C CH OH c) HO CH2 CH2 C CH2 O HO CH3 C CH2 O F H3C H3C HC O CH CH2 C C F d) O OH C H3C CH3 C CH2 CH3 OH e) CH2 f) 13. The labels have fallen off three bottles. Bottle A contains a gas, bottle B contains a liquid, and bottle C contains a solid. The labels indicate that the compounds have the same number of carbon atoms, one being an alkane, one an alcohol, and the other a carboxylic acid. Suggest the identity of the contents of each bottle, and give reasons for your explanation. 14. Draw the following esters a) ethyl butanoate b) pentyl propanoate c) propyl 3-ethylhexanoate d) methyl 4-phenylpentanoate e) 2,3-dimethylpentyl ethanoate f) butyl 3-hydroxyheptanoate 15. Name the following esters O O CH2 C H3C CH2 CH2 O CH3 a) H3C CH2 CH2 O CH2 H3C CH2 CH3 O O C C O O C CH3 CH3 CH3 d) O CH2 e) H3C CH2 CH2 C H3C CH2 CH2 O CH3 OH c) CH3 CH3 C C CH C b) O H3C O C CH2 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 CH3 CH3 f) 16. In what way is the functional group of an ester different from that of a carboxylic acid? How does this difference account for any differences in properties? 17. Describe the steps used to name an ester. 18. Draw the following amines a) butan-1-amine b) pentan-2-amine c) propan-1,2-diamine d) N-ethyl-hexan-2-amine e) N,N-dimethyl-pentan-3-amine f) N-methyl-N-propyl-ethanamine 19. Name the following amines H3C H3C a) CH3 CH3 CH CH CH NH2 CH3 CH2 H2C H2C Cl Cl CH2 CH2 CH CH3 b) NH2 CH2 CH HC c) H2N NH2 CH2 H3C CH3 CH d) H2N CH2 CH2 CH3 CH CH2 N NH2 CH2 H3C e) CH3 f) H3C NH CH2 CH3 CH2 20. Explain why amines generally have lower boiling points than alcohols of comparable molar mass. 21. Why are secondary and tertiary amines less soluble than primary amines of similar molecular size? 22. In some cuisines, fish recipes include lemon garnish or a vinegar sauce such as sweet and sour sauce. Suggest a reason why these common culinary techniques might be used. 23. Draw the following amides a) N-ethylbutanamide b) N-propylpentanamide c) N-methyl-3-methylhexanamide d) N-2,3-dichlorobutylpropanamide e) N,N-diethyl-2-methylbutanamide f) N-pentyl-3-hydroxypentanamide 24. Name the following amides O O CH2 H3C CH2 a) H3C C CH2 CH2 NH C CH2 CH3 H3C N C CH3 CH2 H3C CH3 b) CH2 NH CH2 C CH3 c) O CH3 O O H3C H3C CH2 d) H3C CH2 CH2 C CH2 C NH CH2 CH N CH3 CH3 CH2 HC CH3 CH2 CH2 CH NH O e) f) 25. Describe the steps used to name an amide. 26. Which functional groups can you expect to turn litmus paper red? Blue? 27. Which functional groups would form hydrogen bonds with neighbouring molecules? 28. Draw as many structural isomers with the formula C4H10O as possible. Cl CH3