File
advertisement

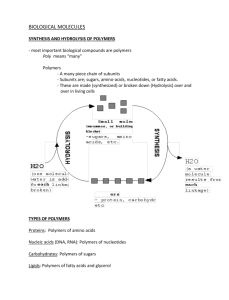
Station One Identifying Macromolecules Worksheet Identify each of the molecules below as one or more of the following: carbohydrate, lipid, monomer of a protein, monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide, polypeptide, saturated fatty acid, unsaturated fatty acid, triglyceride, phospholipid, steroid, or amino acid. Write the term(s) inside the box with the molecule. 1. 2. 3. 4. From: Carnegie Mellon Depart. of Biological Sciences: http://telstar.ote.cmu.edu/biology/Membr anePage/index2.html 5. 6. 9. 10. 13. 7. 8. 11. 14. 12. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Station One Key 1. monomer of protein, amino acid 2. steroid, lipid 3. monomer of protein, amino acid 4. unsaturated fatty acid, lipid, trans 5. Carbohydrate, polysaccharide 6. monomer of protein, amino acid 7. monosaccharide, carbohydrate 8. monosaccharide, carbohydrate 9. monosaccharide, carbohydrate 10. monosaccharide, carbohydrate 11. disaccharide, carbohydrate 12. monomer of protein, amino acid 13. steroid, lipid 14. monosaccharide, carbohydrate 15. unsaturated fatty acid, lipid, cis 16. saturated fatty acid, lipid 17. Lipid, triglyceride 18. Lipid, phospholipid 19. Protein, polypeptide, 3 amino acids 20. Monomer of protein, amino acid Station Two Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids Practice 1. _____________________ Lipid which typically contains 4 carbon rings. 2. _____________________ Scientific name for starch 3. _____________________ Atom that is more numerous in carbohydrates than lipids 4. _____________________ Function or use that both carbohydrates and lipids share 5. _____________________ Primary component of the cell membrane of all cells 6. _____________________ Primary component of cell walls in plant cells 7. _____________________ Glycogen helps to regulate blood sugar or helps animals to maintain this 8. _____________________ Functional group composed of 1 carbon atom, 2 oxygen atoms, and 1 hydrogen atom 9. _____________________ Portion of a phospholipid that dissolves in water 10. _____________________ Fatty acids that are solids at room temperature 11. _____________________ Process which forms polysaccharides and triglycerides 12. _____________________ Atoms that make up carbohydrates and lipids 13. _____________________ Process which disassembles polysaccharides and triglycerides 14. _____________________ Fatty acids which contain multiple double bonds 15. _____________________ Insoluble in water 16. _____________________ Common name for monosaccharide 17. _____________________ Term that describes the fatty acid tail of a phospholipid 18. _____________________ Term that describes two monosaccharides linked by a dehydration synthesis reaction 19. ____________________ Functional group that is present in amino acids, which is made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen 20. ____________________ Monomers of proteins 21. ____________________ Type of bonds that help to form high level protein structures 22. ____________________ Functional group in amino acids which contains nitrogen 23. ____________________ Hydrogen bonding occurs between these in proteins 24. ____________________ Determines the order of amino acids in protein 25. ____________________ Composed of a variable group, amino group, and carboxyl group Station Two: KEY Carbohydrates and Lipids Practice Key 1. Steroid - Lipid which typically contains 4 carbon rings. 2. Polysaccharide or Carbohydrate - Scientific name for starch 3. Oxygen - Atom that is more numerous in carbohydrates than lipids 4. Store energy - Function or use that both carbohydrates and lipids share 5. Phospholipid – Primary component of the cell membrane of all cells 6. Cellulose, Polysaccharide - Primary component of cell walls in plant cells 7. Homeostasis - Glycogen helps to regulate blood sugar or helps animals to maintain this 8. Carboxyl or carboxylic acid - Functional group composed of 1 carbon atom, 2 oxygen atoms, and 1 hydrogen atom 9. Head (polar or hydrophilic region) -Portion of a phospholipid that dissolves in water 10. Saturated - Fatty acids that are solids at room temperature 11. Condensation - Process which forms polysaccharides and triglycerides 12. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen - Atoms that make up carbohydrates and lipids 13. Hydrolysis - Process which disassembles polysaccharides and triglycerides 14. Polyunsaturated - Fatty acids which contain multiple double bonds 15. Lipids- Insoluble in water 16. Sugar - Common name for monosaccharide 17. Hydrophobic or Nonpolar - Term that describes the fatty acid tail of a phospholipid 18. Disaccharide - Term that describes two monosaccharides linked by a dehydration synthesis reaction 19. Carboxyl Group (Carboxylic Acid) -Functional group that is present in amino acids, which is made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen 20. Amino Acid -Monomers of proteins 21. Hydrogen Bonds - Type of bonds that help to form high level protein structures 22. Amine group - Functional group in amino acids which contains nitrogen 23. Oppositely charged amino acids - Hydrogen bonding occurs between these in proteins 24. DNA (initially) or RNA (more directly) - Determines the order of amino acids in protein 25. Amino Acid - Composed of a variable group, amino group, and carboxyl group Station 3 Below are the 4 molecules you should know how to draw. Label each and fill in the missing parts: Label these two molecules and tell what is missing from each. What is are these and what are they missing? Water Use the diagram above to answer these questions. 1. Oxygen atoms are represented by what color? 2. Hydrogen atoms are represented by what color? 3. How many water molecules are in the diagram? 4. How many oxygen atoms are there? 5. How many hydrogen atoms are there? 6. Where do you find covalent bonds? 7. Does a solid or dotted line represent covalent bonds? 8. Where do we find hydrogen bonds? 9. Does a solid or dotted line represent hydrogen bonds? True or False. Correct the false statements. 10. Water molecules exhibit cohesive properties because they are attracted to each other. This is due to covalent bonding. 11. Water has a low specific heat capacity and can change temperature rapidly. 12. Water is attracted to other things meaning it has adhesive properties. This is due to hydrogen bonding. 13. Water has a high latent heat of vaporization, meaning it takes a lot of heat to evaporate water. 14. Water makes a good solvent because it can dissolve many substances due to its polarity. This is important property aids in the cooling mechanism for humans and other animals. Answer these questions. 15. What type of molecules are soluble in blood? Insoluble? 16. What is lipoprotein and what does it help to transport? 17. Why is blood plasma important? 18. What is hemoglobin in the blood used for? 19. Which would take more time/energy to transport in the blood, oxygen or cholesterol? Why? Station 3 KEY Amino Acid Fatty Acid: Water Key: 1. Black 2. White 3. 6 4. 6 5. 12 6. Between oxygen and hydrogen in the same water molecule 7. Solid line 8. Between oxygen and hydrogen in different water molecule 9. Dotted line 10. False, This is due to hydrogen bonding. 11. False, water has a high specific heat and cannot change temperature rapidly. 12. True 13. True 14. False, This is important to help organisms transport need substances around there body. 15. Polar things such as carbohydrates. Insoluble are lipids or nonpolar substances. 16. Capsule made by body to transports lipids around body since they don’t dissolve in water, ex. Cholesterol 17. Water portion of the blood used to transport things around the body 18. Transport oxygen 19. Cholesterol, because it is a lipid and the body has to make a lipoprotein to transport it. Station 4 Name that Carbohydrate! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. I am an animal carbohydrate used in aerobic respiration. I consist of one ring. I am a disaccharide found in milk. I am a sugar found in plants and I am made of two rings. I am a monosaccharide found in fruit. I am a polysaccharide found in the cell walls of plants. I am a monosaccharide used as a sweetener in foods. I am a malt sugar made of 2 glucose molecules. I am stored in liver and I store energy for animals. I am an energy source for plants and a way for them to store glucose. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Classify these as mono-, di-, or polyGlycogen 6. Glucose Fructose 7. Sucrose Maltose 8. Lactose Starch 9. Galactose Cellulose What goes in the boxes? Fructose Sucrose Sucrase Glucose Water OH H Name that Protein! 1. I speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy, I help digest food in the mouth 2. I help regulate glucose levels in the blood 3. I help with immunity by defending body against pathogens 4. Pigment found in photoreceptors in the retina of our eyes 5. I give animals cells shape and help move chromosomes during mitosis 6. I cause muscle contractions in muscles 7. I help transport oxygen in the blood. 8. I help catalyze reactions in the Calvin cycle 9. Connective tissue in skin, blood vessels, and ligaments, rope-like protein and very abundant in our body Station 4 KEY Key: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Glucose Lactose Sucrose Fructose Cellulose Classify key 1. Poly 2. Mono 3. Di 4. Poly 5. Poly Key: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Enzyme called amylase Insulin Antibodies, immunoglobulins Rhodopsin Tubulin Actin and myosin Hemoglobin Rubisco Collagen 6. 7. 8. 9. Galactose Maltose Glycogen Starch 6. 7. 8. 9. Mono Di Di Mono Station 5 Name that reaction! Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. 4. Building polymers or breaking polymers Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. 4. Building polymers or breaking polymers Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? What type of molecules if this? What are the monomers you see in this molecule? What types of bonds are holding the monomers together? How many monomers are their? Station 5 KEY Name that reaction! Pick the correct answer: 7. Hydrolysis or Condensation 8. Water is reactant, water is a product. 9. Building polymers or breaking polymers 10. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 11. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 12. What are the reactants and products? 2 amino acids-> dipeptide + water Pick the correct answer: 7. Hydrolysis or Condensation 8. Water is reactant, water is a product. 9. Building polymers or breaking polymers 10. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 11. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 12. What are the reactants and products?glycerol and 3 fatty acids -> triglyceride + 3 water Pick the correct answer: 7. Hydrolysis or Condensation 8. Water is reactant, water is a product. 9. Building polymers or breaking polymers 10. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 11. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 12. What are the reactants and products? 2 monosacc- -> disacc. + 2 water Pick the correct answer: 7. Hydrolysis or Condensation 8. Water is reactant, water is a product. 9. Building polymers or breaking polymers 10. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 11. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 12. What are the reactants and products?2 amino acids-> dipeptide + water Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. 4. Building polymers or breaking polymers Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Glycerol and 3 fatty acid > triglyceride + 3 water Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? 2 amino acids -> dipeptide + water Pick the correct answer: 1. Hydrolysis or Condensation 2. Water is reactant, water is a product. 3. Building polymers or breaking polymers 4. Bond: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 5. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 6. What are the reactants and products? Dipeptide + water-> 2 amino acids Pick the correct answer: 7. Hydrolysis or Condensation 8. Water is reactant, water is a product. 9. Building polymers or breaking polymers 10. Bond formed: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 11. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 12. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 7. Hydrolysis or Condensation 8. Water is reactant, water is a product. 9. Building polymers or breaking polymers 10. Bond formed: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 11. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 12. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 7. Hydrolysis or Condensation 8. Water is reactant, water is a product. 9. Building polymers or breaking polymers 10. Bond formed: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 11. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 12. What are the reactants and products? Pick the correct answer: 7. Hydrolysis or Condensation 8. Water is reactant, water is a product. 9. Building polymers or breaking polymers 10. Bond formed: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 11. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 12. What are the reactants and products? Triglyceride + 3water -> glycerol and 3 fatty acids Pick the correct answer: 7. Hydrolysis or Condensation 8. Water is reactant, water is a product. 9. Building polymers or breaking polymers 10. Bond formed: glycosidic, peptide, or ester 11. Carbohydrates, lipid, proteins? 12. What are the reactants and products? What type of molecules if this? polypeptide What are the monomers you see in this molecule? Amino acids What types of bonds are holding the monomers together? Peptide bonds How many monomers are their?six Station 6 1. Label all the parts of the enzyme reaction above. 2. Is this an anabolic or catabolic reaction? 3. Compare the enzyme before and after the reaction. 4. What is the optimum temperature for this enzyme? pH? 5. What happens to the enzyme at 45 degrees? 6. What happens to the enzyme at a pH of 10? 7. Describe why the enzyme activity plateaus once a certain substrate concentration is reached? 8. Does this enzyme work best in an acidic or basic environment? Insert these into the correct box - With enzyme - Without enzyme - Reactants - Products - Activation energy without enzyme - Activation energy with enzyme Answers these questions: 1. Why does the rate of a reaction increase when heated? 2. If the temperature gets to high what happens? Why? 3. What is denaturation of enzymes and can it be reversed? 4. What is optimum pH for an enzyme? 5. Why does the reaction rate increase when substrate concentration is first increased? 6. What are some advantages to immobilization of enzymes in industry? Station 6 KEY Substrate Product Active site Enzyme 1. Label all the parts of the enzyme reaction above. A 2. Is this an anabolic or catabolic reaction? catabolic 3. Compare the enzyme before and after the reaction. It is unchanged 4. What is the optimum temperature for this enzyme? 37 pH? 7 5. What happens to the enzyme at 45 degrees? denatured 6. What happens to the enzyme at a pH of 10? denatured 7. Describe why the enzyme activity plateaus once a certain substrate concentration is reached? All enzymes are working and can not go any faster 8. Does this enzyme work best in an acidic or basic environment? Neither, neutral Insert these into the correct box - With enzyme - Without enzyme - Reactants - Products - Activation energy without enzyme - Activation energy with enzyme Answers these questions: 9. Why does the rate of a reaction increase when heated? Because kinetic energy increases causing the substrates and enzymes to contact each other more. 10. If the temperature gets to high what happens? Why? Enzyme is denatured because the shape of the enzyme is destroyed. It can never be used again. 11. What is denaturation of enzymes and can it be reversed? Shape damaged on the enzyme. Cannot be reversed 12. What is optimum pH for an enzyme? pH where it works best 13. Why does the reaction rate increase when substrate concentration is first increased? Kinetic energy increases 14. What are some advantages to immobilization of enzymes in industry? Enzyme can be separated easily, and then it can be recycled. Stability can be preserved so that temp. and pH stay constant. Station 7 Answer the questions below: 1. What are the 4 most frequently occurring elements in organisms? Why are carbon atoms important to the functions of all organisms? What is an example of an inorganic compound? 2. What causes water to be polar? What are some properties of water that are important to functions of living organism? (basically, list ways that water benefits living organisms?) 3. Categorize the following carbohydrates as mono-di- or polysaccharides: Sucrose-, glucose-, maltose-, lactose-, cellulose-, starch-, glycogen-, galactose-, fructose-. What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose? Be able to identify the molecular drawings of a triglyceride, a glycerol/fatty acid, amino acid, ribose, cholesterol. 4. Draw and annotate the graphs that show the effect of pH, temperature, and substrate concentration on enzyme activity. State which factors denature enzymes. 5. What is metabolism? Draw a cis-polyunsaturated fatty acid (can be any length). How does the structure of a fatty acid impact health? Which fat is likely to have a negative impact on health? 6. What is the significance of the experiments of the following scientists?: -Friedrich Wohler: 7. What is a proteome? 8. Create a T chart comparing Catabolism- and Anabolism- Include specific examples of organic compounds for each reaction. 9. Compare how carbohydrates and lipids stack up against each other in terms of energy. Station 7 1. What are the 4 most frequently occurring elements in organisms? Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen (CHON), listed in order from most to least abundant in organisms.Why are carbon atoms important to the functions of all organisms? Carbon atoms can form 4 covalent bonds with other molecules, allowing for the formation of very stable compounds. What is an example of an inorganic compound? H20, 02, C02, CH4 2. What causes water to be polar? What has unequal charges. (O is slightly negative and both Hydrogens are slightly positive. What are some properties of water that are important to functions of living organism? Understand how evaporation works, capillary action, surface tension, adhesion & cohesion, etc. (basically, list ways that water benefits living organisms?) 3. Categorize the following carbohydrates as mono-di- or polysaccharides: Sucrose-Di, glucose-mono, maltose-di, lactose-di, cellulose-poly, starch-poly, glycogen-poly, galactose-mono, fructose-mono. What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose? A-town down. Alpha glucose has a OH group on the first carbon that points down. Betas are best. Beta glucose has a OH group on the first carbon that points up. See pic below: Be able to identify the molecular drawings of a triglyceride, a glycerol/fatty acid, amino acid, ribose, cholesterol. See notes and prior quizzes. 4. Draw and annotate the graphs that show the effect of pH, temperature, and substrate concentration on enzyme activity. State which factors denature enzymes. See notes and text for explanation. Temp and pH denature 5. What is metabolism? All the biological processes catalyzed by enzymes in an organism Draw a cis-polyunsaturated fatty acid (can be any length). How does the structure of a fatty acid impact health? Saturated fats are more unhealthy than unsaturated fats because they lack double bonds, and have more hydrogen atoms in their fatty acid chains, making them harder for the body to digest and use. Which fat is likely to have a negative impact on health? Trans fat 6. What is the significance of the experiments of the following scientists?: -Friedrich Wohler: disproved the theory of vitalism by creating urea in the lab from inorganic compounds 7. What is a proteome? 8. Create a T chart comparing Catabolism-complex to simple, breaks down compounds, disaccharide to monosaccharide, or polypeptide to amino acid,etc. uses water, hydrolysis, uses enzymes. and Anabolism- simple to complex, building compounds, monosaccharide to disaccharide, etc, releases water, condensation reaction, uses enzymes, . Include specific examples of organic compounds for each reaction. 9.