gr12nomenclatureisu_answers
advertisement

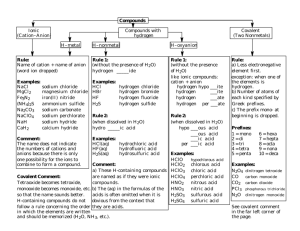
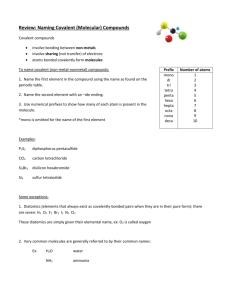
1 SCH 4U Nomenclature Independent Study An excellent knowledge of Chemical Nomenclature is essential for success in grade 12 Chemistry. For your first independent study you will review the nomenclature you learned in grade 11 and write a test. Nomenclature Test Date:___________________________________________ Valence Value The valence value of an element is defined as the numbers of electrons an atom of that element will gain/lose/share when forming a compound. Cross-Over Rule for Writing Formulas STEPS 1. Write down the symbols of the elements in the order given in the name. 2. Write the valences above the elements symbol. 3. Divide the valences by the highest common multiple. 4. Cross-over valences 5. Drop all 1’s and unnecessary brackets sodium chloride magnesium oxide calcium fluoride lithium sulphate aluminum phosphate Na Cl Mg O Ca F Li SO4 Al PO4 1 1 Na Cl 1 1 Na Cl Na1Cl1 NaCl 2 2 Mg O 1 1 Mg O Mg1O1 MgO 2 1 Ca F 2 1 Ca F Ca1F2 CaF2 1 2 Li SO4 1 2 Li SO4 Li2(SO4)1 Li2SO4 3 3 Al PO4 1 1 Al PO4 Al1(PO4)1 AlPO4 Notes: a) You should be able to do all 5 steps in your head when you are finished the unit. b) When naming compounds, the least electronegative element is usually written first. c) Groups of elements such as SO42- and PO43- are referred to as radicals or polyatomic ions. These radicals behave as if they were a single entity and follow the cross over rule in the same manner as other single elements. Brackets are used in the formula only if there are 2 or more of the radical indicated in the formula. Binary Ionic Compounds A binary compound contains 2 elements only. Rules for Binary Ionic Compounds: a) The name of the binary compound always ends in "ide". b) The first mentioned element may have more than one valence and if it does this must be indicated in the name. c) Elements have a valence value determined by their group on the Periodic table unless indicated by the name. I 2 3 4 3 2 1 0 2 A) Binary Compounds where the first element has 1 valence only Use rule “c” and the cross-over rule. Examples: sodium oxide Na2O Exercise: calcium sulfide CaS magnesium bromide MgBr2 For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. calcium nitride __Ca3N2_ silver sulphide _Ag2S___ barium iodide __BaI2__ silicon oxide __SiO2__ zinc silicide __ZnSi__ magnesium chloride _MgCl2__ aluminum carbide ___Al4C3_ sodium fluoride ___NaF__ barium carbide __Ba2C__ aluminum bromide __AlBr3_ potassium bromide ___KBr__ cesium phosphide __Cs3P__ LiCl __lithium chloride___________ K2S ___potassium sulfide_________ BaO __barium oxide_______________ Al2O3 __aluminum oxide____________ B) Binary Compounds with Multivalent Elements Many transition metals and some other elements have multiple valence values and therefore can form multiple compounds with the same non-metal. Due to this it is necessary to indicate the valence of the metal in the name of the compound using either the Stock (IUPAC or Roman Numeral) or Classical (“ous” and “ic”) method. The second element (non-metal) always has a valence equal to the value as determined from its group in the periodic table. Method 1: Stock/IUPAC/Roman Numeral Method This is the currently preferred method as the valence of the first is indicated using the corresponding Roman Numeral in brackets following the name of the first element. Examples: iron(III) chloride FeCl3 tin(IV) iodide SnI4 phosphorus (III) oxide As2O3 mercury(II) oxide HgO Exercise: For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. iron(III) chloride __FeCl3____ arsenic(V) iodide __As2O5____ tin(IV) oxide __SnO2_____ gold(I) telluride __Au2Te____ phosphorus(V) chloride ___PCl5____ sulphur(VI) oxide __SO3______ copper(I) bromide ___CuBr____ bismuth(v) phosphide __Bi3P5____ antimony(V) sulphide __Sb2S5____ mercury(II) chloride __Hgl2____ arsenic(III) oxide __As2O3___ gold(III) chloride __AuCl3____ mercury(I) sulphide __Hg2S_____ copper(II)sulphide __CuS______ Pb3N2 __lead (II) nitride____________ SbF3 __antimony (III) fluoride__________ NiI2 __nickel (II) iodide__________ MnO2 Co2Se3 _cobalt (III) selenide______ BiF5 ___bismuth (V) fluoride___________ SnO2 __tin (IV) oxide______________ ZnO ___zinc oxide____________________ __manganese (IV) oxide___________ 3 Method 2: Classical/"ous' and "ic" Method This method can be used when the multivalent element has 2 possible valences. The name of the element ending with "ous" denotes the lower valence value and the name of the element ending with an "ic" denotes the higher valence values. In some cases, the Latin name for the element is used. iron: gold: copper: tin: lead: cobalt nickel mercury platinum ferrous aurous cuprous stannous plumbous cobaltous nickelous mercurous platinous (valence = 2) (valence = 1) (valence = 1) (valence = 2) (valence = 2) (valence = 2) (valence = 2) (valence = 1) (valence = 2) and and and and and and and and and ferric auric cupric stannic plumbic cobaltic nickelic mercuric platinic (valence = 3) (valence = 3) (valence = 2) (valence = 4) (valence = 4) (valence = 3) (valence = 3) (valence = 2) (valence = 4) *Some elements having more than two valence values or oxidation states use specific values for the "ous" and the "ic". nitrogen manganese arsenic ous = 1 ic = 2 ous = 2 ic = 3 ous = 3 ic = 5 chromium phosphorus bismuth ous = 2 ic = 3 ous = 3 ic = 5 ous = 3 ic = 5 Examples: stannous chloride arsenic phosphide SnCl2 As3P5 phosphorous oxide nitric oxide P2O3 NO Exercise: For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. ferric oxide __Fe2O3________ auric iodide _AuI3__________ phosphoric sulfide ___P2S5________ nitrous phoshpide __N3P__________ cuprous fluoride __CuF_________ stannic oxide __SnO2_________ stannic fluoride __SnF4_________ arsenious nitride __AsN__________ antimonous sulfide __SbS3________ mercuric fluoride __HgF2_________ arsenious bromide __AsBr3________ cuprous nitride __Cu3N_________ nickelic iodide __NiI3_________ auric chloride ___AuCl3_______ chromous oxide __CrO__________ cupric sulfide ___CuS_________ NiI2 _nickelous iodide____ Sb2S5 __antimonic sulfide______ HgBr __mercurous bromide_____ As4C5 ___arsenic carbide_______ CoCl3 ___cobaltic chloride______ Au2S ___aurous sulfide________ As3N5 __arsenic nitride______ PAs ___phosphorous arsenide_ Fe2C __ferrous carbide______ NiP ___nickelic phosphide PbS __plumbous sulfide________ CoF3 ___cobaltic fluoride_____ CuO __cuproc oxide____________ Au2Se3 ___auric selenide______ 4 Formula of Elements Most elements are written as single entities. Example: iron Fe(S) copper Cu(S) The exceptions to this rule are: a) the diatomic gases: H O F B I N Cl hydrogen H2(g) oxygen O2(g) nitrogen N2(g) chlorine Cl2(g) b) two other non-metals: helium He(g) fluorine F2(g) bromine Br2(l) sulphur S8(s) iodine I2(s) phosphorus P4(s) ** The exceptions must be memorized! ** Common Radicals or Polyatomic Ions Radicals or polyatomic ions are groups of atoms that are treated as a single entity when writing formulas and names. The following list of common radicals (polyatomic ions) must be memorized along with their valences. Positive polyatomic ions replace metals in an ionic compound and a negatively charged polyatomic ion goes in place of the nonmetal. If more than 1 of the radical is required in the chemical formula, brackets are placed around the radical’s formula with the subscript outside the bracket. Radical name Formula Valence Radical name Formula Valence 1 hydroxide OH 1 ammonium NH4+ cyanide 1 manganate MnO3- 1 chromate CNCrO42- 2 dichromate Cr2O72- 2 cyanate CNO- 1 thiocyanate SCN- 1 carbonate CO32- 2 nitrate NO3- 1 phosphate PO43- 3 sulfate SO42- 2 fluorate FO3- chlorate ClO3- 1 - Examples: sodium hydroxide lithium cyanide sodium dichromate NaOH LiCN Na2Cr2O7 1 potassium chromate ammonium hydroxide magnesium permanganate K2CrO4 NH4OH Mg(MnO4)2 Exercise: For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. potassium hydroxide _KOH____________ cobalt(II) cyanate __Co(CNO)2________ iron(III) cyanate _Fe(CNO)3_________ zinc hydroxide __Zn(OH)2_________ barium hydroxide __Ba(OH)2_________ gallium dichromate __Ga2(Cr2O7)3______ ammonium chloride __NH4Cl___________ potassium chromate __K2CrO4_________ copper(II) chromate __CuCrO4_________ Sn(CN)4 _stannic cyanide_______________ ammonium dichromate __(NH4)2Cr2O7_____ Al(OH)3 __aluminum hydroxide___________ ammonium bromate __NH4BrO3_________ KMnO4 __potassium permangante________ ferrous hydroxide __Fe(OH)2_________ CsCN ___cesium cyanide_______________ nickel(III) cyanide __Ni(CN)3_________ XeF6 __xenon hexafluoride____________ auric bromide __AuBr3___________ Ca(SCN)2 __calcium thiocyanate_________ 5 Acids There are three groups of acids: - binary acids - oxy acids - derived oxy acids 1. Binary Acids This is a very small but common group of acids. The following rules apply to all of the members. 1. All have the prefix “hydro” and end with “ic”. 2. All must contain hydrogen as the first element. 3. Use the normal cross-over-rule to determine the formula. 4. All are dissociated in water and must be so indicated by using (aq) behind the formula. 5. Have no oxygen in their formula Examples: hydrochloric acid HCl(aq) hydrosulfuric acid H2S(aq) hydrocyanic acid HCN(aq) Exercise: For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. hydrobromic acid __HBr(aq) hydrotelluric acid _ H2Te(aq)_ hydrofluoric acid _ HF(aq)_ hydroiodic acid _ HI (aq)__ hydroselenic acid _ H2Se(aq)_ hydrosulfuric acid _ H2S (aq)_ hydrochloric acid __ HCl (aq) hydrophosphoric acid _ H3P(aq) 2. Oxy Acids This is a larger group of acids. They are alike in that they all contain H, O and at least one other non-metal element. All members of this group of acids follow the rules below. 1. The name of the acid ends in “ic”. 2. The name of the associated radical ends in “ate”. 3. The valence value of the associated radical is equal to the number of acidic hydrogens in the acid. The following 6 oxy acids and their associated radicals along with their valences must be memorized. Name of the Acid Formula of the Acid Name of the Formula of the valence value for the associated radical associated radical associated radical chromate C2H3O2- 1 1 acetic acid HC2H3O2 nitric acid HNO3 nitrate NO3- fluoric acid HFO3 fluorate FO3- 1 carbonic acid H2CO3 carbonate CO32- 2 2 3 sulfuric acid H2SO4 sulfate SO42- phosphoric acid H3PO4 phosphate PO43- NOTE: Using the periodic table it is possible to write the names and formulas for a number of other oxy acids using the fact that members of the same chemical family have similar chemical properties. Elements of the same chemical family (group) follow the pattern of the oxy acid immediately above the oxy acid that has been memorized. Example: memorized acid: fluoric acid = HFO3 therefore: chloric acid = HClO3 iodic acid = HIO3 bromic acid = HBrO3 If hydrogens are joined with the radicals learned earlier a few more acids can be formed. chromate = CrO42chromic acid = H2CrO4 cyanate = CNOcyanic acid = HCNO 6 Exercise: On a separate piece of paper complete the following chart for the acids listed. Name of the acid bromic acid manganic acid Formula of the acid telluric acid selenic acid Name of the Formula of the Valence value of the associated radical associated radical associated radical iodic acid cyanic acid silicic acid arsenic acid dichromic acid chromic acid 3. Derived Oxy Acids Theses acids are all derived from the parent oxy acids which you are to memorize. The table below shows the rule to determine the derived oxy acids from the parent acid. When adding or removing oxygen atoms from the parent acid, the number of hydrogens on the acid and the valence of the associated radical remains the same as the parent. Parent Oxy Acid + 1 O Parent Oxy Acid Parent Oxy Acid - 1 O Parent Oxy Acid - 2 O Type of Acid per______ic ic ous hypo_____ous Associated Radical per______ate ate ite hypo_____ite Example perchloric acid HClO4 perchlorate ion ClO4chloric acid HClO3 chlorate ion ClO3chlorous acid HClO2 chlorite ion ClO2hypochlorous acid HClO hypochlorite ion ClO- Exercise: On a separate piece of paper complete the following chart for the acids listed. Name of the acid Formula of the acid phosphoric acid phosphorous acid hypophosphorous acid sulfuric acid sulfurous acid nitric acid nitrous acid Name of the Formula of the Valence value of the associated radical associated radical associated radical perbromic acid bromic acid bromous acid hypobromous acid iodic acid iodous acid hypoiodous acid selenic acid selenous acid telluric acid tellurous acid manganic acid permanganic acid Salts The word, salt, is the general term given to a class of compounds which can be formed when an acid and a base neutralize each other. According to this definition then, most of the compounds we dealt with in the section on binary compounds could be considered to be salts formed from a base and a binary acid. In the same manner, we can get salts formed from a base and an oxy acid or derived oxy acid. Examples: sodium sulphate aluminum carbonate cupric nitrite Na2SO4 Al2(CO3)3 Cu(NO2)2 calcium phosphate zinc perchlorate stannous hypoiodite Ca3(PO4)2 Zn(ClO4)2 Sn(IO)2 7 Salts from oxy acids potassium chlorate__KClO3____________ sodium carbonate __Na2CO3__________ sodium nitrate ferric sulfate __Fe2(SO4)3_______ iron(III) acetate ___Fe(C2H3O2)3_______ gold(I) phosphate __Au3PO4__________ aluminum silicate ___Al2(SiO3)3__________ magnesium chlorate __Mg(ClO3)2______________ magnesium phosphate __Mg3(PO4)2______ ammonium nitrate __NH4NO3_______________ aurous sulfate K2CO3 __potassium carbonate__________ ammonium chlorate __NH4ClO3__________ Na3PO4 __sodium phosphate_____________ zinc nitrate Fe(ClO3)2 __iron (II) chlorate (ferrous chlorate) potassium acetate _KC2H3O2_____________ Al(C2H3O2)3 _aluminum acetate_______________ lithium chromate __Li2CrO4_____________ Zn3(PO4)2 _zinc phosphate________________ __NaNO3_____________ __Au2SO4 ____________ __Zn(NO3)2______________ Salts from Derived Oxy Acids aluminum sulfite _Al2(SO3)2________ copper(I) permanganate __CuMnO4____________ cobalt(III) chlorite _Co(ClO2)3______ ammonium hypophosphite __(NH4)3PO2________ tin(IV) hypochlorite __Sn(ClO)4________ mercuric perchlorate __Hg(ClO4)2____ sodium phosphite __Na3PO3__________ magnesium sulfite ___MgSO3__________ aluminum nitrite __Al(NO2)3________ cuprous chlorite __CuClO2_____________ cobalt(II) hypophosphite__Co3PO2)2________ ammonium hypoiodite ___NH4IO____________ stannic perchlorate __Sn(ClO4)4________ gold(III) chromate sodium sulphite __Na2(SO3_________ Ga(BrO4)3 ___gallium perbromate_____ aluminum chlorite __Al(ClO2)3______ Pt(ClO)4 __platinum (IV) hypochlorite__ nickel(III) hypochlorite _Ni(ClO)3_________ Ag2O __silver oxide____ tin(IV) phosphite NH4CNO __ammonium cyanate___ _Sn3(PO3)4_________ __Au2(CrO4)3_________ Acid Radicals and Acid Salts 1. Acid Radicals In certain circumstances the oxy acids with multiple acidic hydrogens are able to lose the hydrogens one at a time. This results in radicals with acidic hydrogens still attached which are referred to as acid radicals. Step 1: H3PO4 H+ + H2PO4Step 2: H2PO4- H+ + HPO42- Step 3: HPO42- H+ + PO43Radical PO43HPO42H2PO4- Name phosphate monohydrogenphosphate dihydrogenphosphate Valence 3 2 1 Notes: a) Valence = # of hydrogen removed from the acid OR valence of non-acid radical-# of H’s still attached b) Mono may be left off a monohydrogen acid radical c) For oxy acids with 2 acidic hydrogens (diprotic acids), the prefix “bi” may be used in place of monohydrogen (eg. HCO3- = bicarbonate or monohydrogen carbonate) 8 For the following give the formula and valence value of the radicals listed: phosphite __PO33-____ monohydrogensulphate __HSO4-__ __1__ monohydrogenphosphite _HPO32-_____ _2__ suphite __SO32-____ __2__ dihydrogenphosphite __H2PO3-___ __1__ monohydrogensulphite __ HSO3-____ __1__ hypophosphite __ PO23-____ __3__ carbonate __ CO32-____ __2__ monohydrogenhypophosphite __ HPO22-___ __2__ monohydrogencarbonate __ HCO3-___ __1__ dihydrogenhypophosphite __ H2PO2-___ __1__ chromate ___ CrO42-___ __2__ sulphate ___SO42-___ __2__ monohydrogechromate ___HCrO4-__ 2. Acid Salts The acid radicals are treated just like any other radical. Examples: calcium dihydrogenhypophosphite Ca(H2PO2)2 potassium monohydrogen carbonate KHCO3 aluminum bisulphite sodium hydrogensulfate Al(HSO3)3 NaHSO4 __3__ __1__ Exercise: For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. sodium monohydrogenphosphate _Na2HPO4_ ferric monohydrogensulphate _Fe(HSO4)3__ magnesium dihydrogenphosphate __Mg(H2PO4)2__ ammonium hydrogencarbonate _NH4HCO3__ aluminum dihydrogenphosphite __Al(H2PO3)3__ chromium(III) hydrogensulphite _Cr(HSO3)3_ chromium(III) hydrogenphosphite _Cr2(HPO3)3_ nickel(II) monohydrogensilicate _Ni(HSiO3)2_ cupric monohydrogenarsenate __CuHAsO4__ cadmium monohydrogenselenate _Cd(HSeO4)2_ stannic dihydrogenhypophosphite __Sn(H2PO3)4__ potassium monohydrogenselenite _KHSeO3_ K2HPO3 _potassium hydrogenphosphite_ Bi2(HPO3)5 _bismuth (V) hydrogen phosphite_ Ba(HSO3)2 Pb(H 2PO2)2 _lead (II) dihydrogenhypophosphite_ _barium bisulfite_ Hydrates Hydrates are crystals containing a given number of water molecules within their structure. When naming a hydrate Greek prefixes in front of the word hydrate are used to indicate the number of water molecules into the crystal. In the chemical formula the number of water molecules is separated from the formula of the compound by a dot “∙” Examples: copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate CuSO4 ∙ 5H2O chlorine octahydrate Cl2 ∙ 8H2O Exercise: For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. calcium sulfate dihydrate _CaSO4 2 H2O_ chromium(III) nitrate nonahydrate Cr(NO3)3 9 H2O magnesium sulfite heptahydrate _MgSO3 7H2O_ cobalt(II) perchlorate pentahydrate Co(ClO4)3 5 H2O sodium carbonate decahydrate Na2CO3 10 H2O aluminum oxide monohydrate ferric chloride hexahydrate calcium nitrate trihydrate cadmium bromide tetrahydrate barium chloride dihydrate BaCl2 2 H2O _Al2O3 H2O_ aluminum nitrate monohydrate Al(NO3)3 H2O _FeCl3 6 H2O_ bromine decahydrate Br2 10 H2O iodine tetrahydrate _I2 4 H2O__ Ca(NO3)2 3 H2O _CdBr2 4 H2O_ copper(II) bromate hexahydrate Cu(BrO3)2 6 H2O 9 Peroxides These are binary oxides, which contain an extra oxygen atom. Rules: 1. Write the formula of the regular oxide. 2. Add on one extra oxygen atom. 3. Do not at this stage cancel any of the subscripts. Na2O Na2O2 H2O H2O2 CaO CaO2 Exercise: For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. zinc peroxide ___ ZnO2_______ potassium peroxide ___ K2O2_________ calcium peroxide ___ CaO2_________ strontium peroxide ____ SrO2__________ cesium peroxide ___ H2O2_________ hydrogen peroxide ____ H2O2____________ copper(II) peroxide ____ CuO2____________ barium peroxide ____ BaO2____________ magnesium peroxide ___ MgO2____________ aluminum peroxide ____ Al2O3___________ Thio Compounds The prefix “thio” in the name indicates that an oxygen atom has been replaced by a sulphur atom. Examples: potassium sulphate K2SO4 potassium thiosulphate K2S2O3 sodium carbonate Na2CO3 sodium thiocarbonate Na2SCO2 potassium cyanate KCNO potassium thiocyanate KSCN Exercise: For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. ammonium thiocyanate _(NH4)2SCO2_______ potassium thiosulfate ____K2S2O3___________ sodium monohydrogenthiosulphate _NaHS2O3__ aluminum thiocarbonate __Al2(SCO2)3________ CaS2O2 AlSPO3 __calcium thiocarbonite______ __aluminum thiophosphate______ Molecular Compounds These compounds contain 2 non-metals and are named using Greek prefixes. This method does not use the valence values. The Greek prefix is placed in front of the element name to indicate how many atoms of the element to place in the formula. If there is only 1 atom of the first element, mono is not used on the name of the first element. Prefixes 1 = mono 2 = di 3 = tri 4 = tetra 5 = penta 6 = hexa 7 = hepta 8 = octa 9 = nona 10 = deca Examples: diphosphorus pentoxide P2O5 arsenic trichloride AsCl3 carbon monoxide CO xenon tetrafluoride XeF4 Exercise: For all exercises you will give the name if formula provided and the formula if the name is provided. xenon hexafluoride ___XeF6_____ silicon dioxide ___SiO2_______ sulfur dioxide ___SO2________ carbon tetrachloride ___CCl4_______ sulphur trioxide __SO3___________ lead dioxide ___PbO2________ carbon dioxide __CO2___________ manganese dioxide ___MnO2________ carbon disulphide ___CS2_________ nitrogen dioxide ___NO2_______ dinitrogen tetroxide __N2O4______ diphosphorus trisulfide __P2S3_______ 10 carbon tetrachloride ___CCl4______ ICl __iodine monochloride____________ lead dioxide ___PbO2________ SeCl2 ___selenium dichloride_________ dichlorine monoxide ___Cl2O_________ ICl7 ___iodine heptachloride___________ ___P2S5____ NF3 ___nitrogen trifluoride____________ ____krypton difluoride_____________ P2S5 ___ diphosphorus pentasulphide _ diphosphorus pentasulphide KrF2 PRACTICE, PRACTICE, PRACTICE sulphur ____S8 (s)___________ lead (IV) nitride __Pb3N4__________ plumbous peroxide ___PbO2__________ cupric chloride ___CuCl2________ calcium iodite ___Ca(IO3)2_______ stannous iodide ___SnI2_______ sulfur dioxide ___SO2________ aluminum nitride __AlN_______ boron hypoarsenite __BAsO2______ antimonous bromide __SbBr3________ neon ___Ne (g)___________ tin (IV) sulfide ___SnS2___________ platinum (IV) thiocarbonite ___Pt(SCO)2_________ silver oxide __Ag2O____________ calcium cyanide heptahydrate ___Ca(CN)2 7 H2O___ calcium phosphide __Ca3P2__________ cuprous permanganate ___CuMnO4______ iron (II) sulfide ___FeS__________ chromous acid __H2CrO3____ arsenic phosphide __AsP___________ cyanic acid __HCNO________ mercury (II) nitride __Hg3N2___________ iodine monochloride ___ICl________ tin (IV) fluoride ___SnF4__________ stannic dihydrogen hypophosphite __Sn(H2PO2)4____ sodium hydride ___NaH_____________ auric peroxide ___Au2O4______ sodium monohydrogen phosphate __Na2HPO4______ ammonium selenide ___(NH4)2Se_____ barium hydroxide __Ba(OH)2_________ titanium ___Ti (s)______ sodium bicarbonate __NaHCO3__________ ferrous thiosilicate __FeSSiO2___ perchloric acid ___HClO4__________ cadmium bisulphate ___Cd(HSO4)2_______ nitrous acid __HNO2______ lithium phosphide ___Li3P____ calcium peroxide ___ CaO2 __________ bromine __Br2 (l) ________ plumbous oxide ____PbO____________ potassium oxide _K2O____ potassium chloride ____KCl___________ barium sulfide __BaS_________ hydrogen iodide ___HI_____________ magnesium fluoride __MgF2_______ antimonous phosphide ___SbP_____________ mercurous bromide __Hg2Br2________ silver sulfide ___Ag2S____________ zinc hydride __ZnH2________ mercuric oxide ___Hg2O___________ ferric sulfide __Fe2S3__________ phosphorus (III) chloride ___PCl3___________ arsenic (V) oxide ___As2O5_________ ferrous oxide ___FeO__________ 11 magnesium peroxide ____MgO2__________ silver hypoarsenite __Ag3AsO2__ zinc chromate dehydrate ___ZnCrO4 10 H2O__ copper (II) sulphate pentahydrate _CuSO4 5 H2O_ phosphoric acid ____H3PO4______ cyanic acid ___HCNO_ chromic cyanide ____Cr(CN)3______ sulfur dioxide _____SO2________ sodium thiosulfate hexahydrate _Na2S2O2 6 H2O_ potassium permanganate ____KMnO4_______ iron (III) carbonate _Fe2(CO3)3_ zinc chloride ____ZnCl2________ magnesium phosphide __Mg3P2_______ diarsenic pentasulfide ____As2S5_______ fluorine ___F2(g)____________ hypophosphorous acid ____H3PO2_______ chlorous acid __HClO2____ potassium hydroxide _____KOH_________ dicarbon tetrahydride __C2H4_____ iron (III) cyanate ___Fe(CNO)3______ hydrosulfuric acid ___H2S (aq)_________ barium chromate ____BaCrO4______ stannous tungstenate __SnWO4____ ammonium thiocyanate ____NH4SCN______ magnesium peroxide ___MgO2______ potassium dichromate ____K2Cr2O7_____ ammonium hydrogenhypophosphite _(NH4)2HPO2__ mercuric tellurite ____HgTeO3______ tetracarbon decahydride __C4H10_____ platinum (IV) silicate ____Pt(SiO3)2_______ nickelic perbromate __Ni(BrO4)3________ cobaltous thioselenite _____CoSSeO2_____ chlorine dihydrate __Cl2 2 H2O________ tricarbon octahydride _____C3H8_____ copper (II) hypoarsenite ___Cu3(AsO2)2____ thiocyanic acid ____HSCN______ dichromic acid __H2Cr2O7_____ silver hypophosphite ___Ag3PO2_____ aurous hydroxide ___AuOH__________ bromine ___Br2(l) ________ barium bithiocarbonate ___Ba(HSCO2)2_____ silicon tetrahydride ___SiH4_______ hydrogen chloride ____HCl_________ cesium arsenite dihydrate __Cs3AsO3 2 H2O__ sulfuric acid ___H2SO4_______ manganic hydroxide __Mn(OH)3__ chromous cyanate ___Cr(CNO)2______ arsenious oxide ___As2O3____ magnesium thiophosphate ____Mg3(SPO3)2_____ silver chlorate __AgClO3____ ferrous iodide ____FeI2___ calcium perbromate ___Ca(BrO4)2____ barium dichromate ____BaCr2O7_______ barium phosphide ___Ba3P2___ phosphorus ___P4(s) _______ nickel (II) cyanide ___Ni(CN)2___ periodic acid __HIO4_______ beryllium phosphate ___Be3(PO4)2____ tetraphosphorus decaoxide ____P4O10_____ cadmium sulfite ___CdSO2______ hydrotelluric acid ____H2Te(aq)____ boron tribromide ___BBr3____ ammonium bitungstenate ____NH4HWO4____ silicon carbide ____SiC________ iron (III) peroxide ____Fe2O4_____ mercuric hydroxide ____Hg(OH)2_______ neon ___Ne(g)_________ cupric perchlorate _____Cu(ClO4)2______ 12 gold (III) selenate _Au2(SeO4)3__ cupric acetate __Cu(C2H3O2)2___ stannic phosphide __Sn3P4___ acetic acid ___HC2H3O2___ arsenic (V) oxide __As2O5___ ammonium phosphate dehydrate (NH4)3PO4 10 H2O sulfur trioxide __SO3_____ aurous chromate ___Au2CrO4___ hydrogen cyanide __HCN__________ ferrous hydroxide ___Fe(OH)2___ lithium hypoiodite __LiIO2________ stannic bromide ___SnBr4_____ magnesium thiosilicate __MgSSiO2______ plumbous thiocyanate ___Pb(SCN)2____ zinc phosphide ___Zn3P2________ oxygen ___O2(g)________ aluminum peroxide ___Al2O4________ arsenic trihydride __AsH3________ lithium sulfate ___Li2SO4_____ ammonium dihydrogenphosphate _NH4H2PO4____ magnesium hypochlorite ___Mg(ClO)2______ phosphorus pentachloride __PCl5______ manganese dioxide ___MnO2________ silver nitrate __AgNO3________ strontium nitrate ___Sr(NO3)2______ calcium chlorite __Ca(ClO2)2______ lead (IV) iodite ___Pb(IO2)4_______ manganese (III) dichromate ___Mn2(Cr2O7)3___ zirconium chloride ____ZrCl2_______ potassium permanganate ___KMnO4_ cobalt (III) hypobromite ___Co(BrO)3______ silicon dioxide __SiO2___________ chromium (III) oxide ____Cr2O3________ palladium (IV) nitrite __Pd3N4_______ iodine monofluoride ___IF___________ diboron hexahydride __B2H6_____________ ammonium perbromate ___NH4BrO4_______ sulfur ___S8 (s)__________ carbon disulphide ___CS2__________ helium __He(g)___________ aluminum hydroxide __Al(OH)3__________ uranium hexafluoride __UF6_________ beryllium sulfite ___BeSO3_________ antimonic sulfate ___Sb2(SO4)5_______ lead (II) dihydrogenphosphite ___Pb(H2PO3)2_____ phosphorus pentachloride ___PCl5______ chromic hydrogenhypophosphite __Cr(HPO2)2__ sulfur hexafluoride __SF6_____ iron (III) dihydrogenhypophosphite __Fe(H2PO2)3____ tin (II) cyanide ___Sn(CN)2_________ potassium hydrogenarsenite __K2AsO3___ phosphorus ___P4(s)__________ mercury (II) bisulfate ___Hg(HSO4)2______ chlorine ___Cl2(g)___________ zinc monohydrogentellurite ___Zn(HTeO3)2_____ cesium manganite __CsMnO2__________ sodium bicarbonate ___NaHCO3_____ ammonium chromite __(NH4)2CrO3______ cobalt (III) bromite ___Co(BrO2)3____ calcium tungstenate ___CaWo4________ aluminum hydride ___AlH3______ silver acetate hexahydrate __AgC2H3O2 6 H2O_ vanadium (V) oxide ___V2O5_______ potassium peroxide ___K2O2__ carbon tetraiodide __CI4___ sodium thiocarbonate __Na2SCO2__ mercurous peroxide __Hg2O2______ lithium dithiosulfite __Li2S3O_____ 13 PbS2O2 _lead(II) thiosulfite__ Ag2S __silver sulfide___ MgO2 __magnesium peroxide______ Fe(OH)2 _iron (II) hydroxide (or ferrous)____ Al2(SO2)3 __aluminum sulfite _____ N2O4 __dinitrogen tetroxide_ Au(MnO3)3 _gold (III) mangante (or auric)_ K2S2O _potassium thiohyposulfite__ BrCl5 __bromine pentachloride_ HMnO4 (aq) __permanganic acid___ Ba(FO)2 __barium hypofluorite_ H2SiO3 (aq) __silicic acid_____ ZnHAsO5 _zinc hydrogenperarsenate_ CaS2O2 __calcium thiosulfite___ Co(NO3)3 _cobalt (III) nitrate (or cobaltic)_ N2O4 ____ dinitrogen tetroxide ____ HgSCO mercury (II) thiocarbonite (or mercuric) Au(IO4)3 _gold (III) periodate (or auric)___ H2S (aq) _hydrosulfuric acid_ PbO3 _lead (IV) peroxide (or plumbic)_ SrCl2∙8 H2O _strontium chloride octahydrate_ Mg(MnO3)2 _magnesium mangante_ H2S (aq) _hydrosulfuric acid_ MnP manganese (III) phosphide (or manganic) Cr(H2PO3)3 chromium(III) dihydrogenphosphite (or chromic) Fe(H2PO3)3 iron (III) dihydrogenhypophosphite (or ferric) K2O2 __potassium peroxide__ PCl5 ___phosphorus pentachloride____ Al(ClO4)3 __aluminum perchlorate___ Rb2SSiO2 _rubidium thiosilicate_ Ga2(SiO3)3 __gallium silicate__ Ra3P2 · 7 H2O _radium phosphide heptahydrate___ P2S3 _diphosphorus trisulfide__ NH4OH __ammonium hydroxide_ HNO3 (aq) __nitric acid____ HCN (aq) _hydrocyanic acid__ FeCr2O7 __iron (II) dichromate (or ferrous)_ Ni3(SPO2)2 _nickel (II) thiophosphite (or nickelous) CuSO4∙5H2O copper(II)sulfate pentahydrate (or cuprous) H2TeO2 (aq) __hypotellurous acid__ H2SeO3 (aq) __selenous acid_____ Cu2Se _copper (I) selenide (or cupric)___ CaCr2O7 __calcium dicjromate__ Ga(OH)3 _gallium hydroxide_ P2O5 _diphosphorus pentoxide____ B2H6 _diboron hexahydride_ BaF2 _barium fluoride__ Cr(BrO)3 chromium (III) hypobromite (or chromic) MnO2 _manganese (IV) oxide___ H2CrO3 (aq) __chromous acid__ Al2O4 _aluminum peroxide____ Pb(ClO)2 __lead (II) hypochlorite (or plumbous)_ HI (aq) __hydroiodic acid_____ H2Se(aq) __hydroselenic acid_ Au2(HAsO2)3·9 H2O gold(III) hydrogenhypoarsenite nonahydrate (or auric) CaMoO4 _calcium molybdenate_ SO3 ___sulfur trioxide__________ C4H8 _tetracarbon octahydride_ Li2SCO2 _lithium thiocarbonate__ ZnSeO2 _zinc hyposelenite_ Sr3N2 · 3 H2O _strontium nitride trihydrate_ BaF2 _barium fluoride__ (NH4)2SiO2 _ammonium silicite_ H2Te(aq) _hydrotelluric acid___ H2Te (aq) _hydrotelluric acid_ Co2(HPO2)3∙4 H2O cobalt (III) hydrogenhypophosphite Cr(CNO)3 _chromium (III) cyanate (or chromic)_ HIO4 (aq) _periodic acid____ tetrahydrate 14 NaBr __sodium bromide__ SnCl4 __tin (IV) chloride (or stannic)__ Ca(C2H3O2)2 __calcium acetate_______ Cu2O _copper P2O5 __diphosphorus pentoxide_____ CuSO4 _copper (II) sulfate (or cupric)_ Ti(SO4)2 __titanium (IV) sulphate__ Ag2S __silver sulfide__ FePO4 _iron (III) phospahte_ CsI __cesium iodide__ K3N __potassium nitride_ Al2S3 __aluminum sulfide__ SO2 __sulfur dioxide_______ Ni(NO3)2 __nickel (II) nitrate (or nickelous)_ CuOH _copper (I) hydroxide___ CoPO4 __cobalt (III) phosphate (or cobaltic)_ Zn(NO2)2 __zinc nitrite____ MnSO3 _manganese (II) sulfite (or manganous) V2S3 _vandium (III) sulfide____ Fe(ClO4)3 _iron (III) perchlorate (or ferric)_ NaOH __sodium hydroxide______ GaCl3 _gallium chloride_ H2SO3 __sulfurous acid_________ Cr2O3 _chromium (III) oxide (or chromic)_ H2S ___dihydrogen monosulfide_____ KNO2 __potassium nitrite__ H3PO4 ___phosphoric acid________ Rb2CrO4 _rubidium chromate__ NH3 __nitrogen trihydride (ammonia)___ (NH4)2HPO4 __ammonium hydrogenphosphate__ HCN __hydrogen cyanide______ Cs2CO3 _cesium carbonate__ Ca(OH)2 ___calcium hydroxide_______ Li2HPO4 __lithium hydrogenphosphate_ Fe(OH)3 __iron (III) hydroxide___ Mg(HCO3)2 __magnesium bicarboante_ H3P __trihydrogen monophosphide_____ Ca(ClO3)2 _calcium chlorate__ Na2CO3 __sodium carbonate________ Sr(MnO4)2 __strontium permanganate__ P2O5 __diphosphorus pentoxide__ SCI3 _sulfur trichloride__ NH3 __ nitrogen trihydride (ammonia)__ Fe(C2H3O2)3 _iron (III) acetate (or ferric)_ FeSO4 __iron (III) sulfate (or ferrous)______ Ag2SO3 __silver sulfite___ SiO2 __silicon dioxide____ Hg2Cl2 __mercury (I) chloride (or mercurous)_ GaCl3 __gallium chloride____ TiO2 _titanium (IV) oxide___ CoBr2 ___cobalt (II) bromide (or coblatous)_ NH4HSO4 B2H4 _diboron tetrahydride__ P2O5 ___diphosphorus pentoxide__ CO ___carbon monoxide___ NO2 __nitrogen dioxide___ P4 ___phosphorus___________ SO3 ___sulfur trioxide___________ NH4Cl ___ammonium chloride____________ CCl4 ___carbon tetrachloride__ Al2O3 ____aluminum oxide__________ Ag2Cr2O7 __silver dichromate__ KBr ___potassium bromide_______ CuSiO2 __copper (II) silicate (or cupric)____ K2S ___potassium sulfide________ AsBr5 _arsenic (V) bromide (or arsenic)__ SnI2 ____tin (II) iodide_(or stannous)___ Sb3N5 _antimony (V) nitride (or antimonic)__ (I) oxide (or cuprous)___ ammonium bisulfate (or hydrogensulfate)