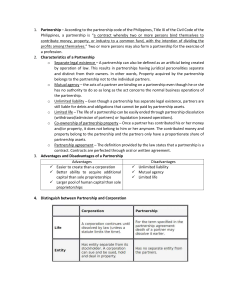
2015-2016 Chapter 8 Economic Organizer
advertisement
COURSE OUTLINE Unit 1: Fundamentals of Economics Economics and Choice Chapter 1:The Economic Way of Thinking Chapter 2: Economic Systems Chapter 3: The American Free Enterprise Unit 2: Microeconomics Market Economies at Work Chapter 4: Demand Chapter 5: Supply Chapter 6: Demand, Supply, and Prices Chapter 7: Market Structures Unit 3: Types of Business Organizations Chapter 8: Types of Business Organizations Unit 4: Macroeconomics Money and Banking Chapter 10: Money and Banking Unit 5: Measuring and Monitoring Economic Performance Chapter 12: Economic Indicators and Measurements Chapter 13: Facing Economic Challenges Unit 6: The Role of Government in the Economy Chapter 14: Government Revenue and Spending Chapter 15: Using Fiscal Policy Unit 7: The Global Economy Chapter 16: The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy Chapter 17: International Trade Unit 8: Personal Finance Chapter 11: Personal Finance & Financial Markets CP Economics Organizer Chapter 8: Business Organizations The Big Picture: Sole Proprietorships. A sole proprietorship is a business organization owned and controlled by one person. The advantages are: ease of starting up or closing; freedom and control for the owner; few rules and regulations; and the owner’s exclusive right to profits. The disadvantages are; limited access to funds; limited life, so the business ends if the owner leaves; and by far the most serious, unlimited liability, which puts the owner’s personal assets at risk. Partnerships. A partnership is a business co-owned by two or more people who agree on how responsibilities, profits, and losses will be divided. In a general partnership, partners share management duties, profits and losses. In a limited partnership, at least one partner does not run the business and is liable only for the funds he or she invested. All such partnerships must have at least one general partner who runs the business and is liable for all debts. In a limited liability partnership, all partners are limited and responsible only for the amount they invested as well as any losses brought about by their mistakes. The advantages of partnerships are ease of start-up, few regulations, greater access to resources, shared decision making, and opportunities to specialize. The disadvantages are unlimited liability (except in partnerships designed to prevent that), the potential for conflict among members, and limited life. Corporations. A corporation is a business owned by shareholders who receive profits but have limited liability for losses. The advantages are access to resources, limited liability, and unlimited life. The disadvantages are expensive and time consuming start up, heavy regulation, double taxation (personal incomes as well as company profits are taxed), and loss of control for owners. Corporations often merge to form new companies, such as multinational corporations with businesses in several countries. Unit Pacing: ____– Sole Proprietorships & Partnerships Homework ____– Read p. 226-235 ____—Read p. 238-242 ____ – Corporations ____—Video Analysis: Walmart 3 & 4 ____-- RETEACHING ACTIVITIES: Sections 1 & 2 ____—Chapter 8 Vocabulary Quiz & TEST Key Terms and Phrases: (Reading Assignments) ____– Study Ch. 7 Vocabulary Quiz & TEST 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Sole Proprietorship Zoning law Liability Collateral Longevity Partnership General partnership 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Corporate charter Profit Interest Corporations Articles of incorporation Limited partnerships Start-ups ____-- Unit Benchmark #3 TEST Essentials Questions: GPS 1. What is the difference between a proprietorship and a partnership? 2. Explain the how corporations are different and similar to partnership. 1. SSEMI4a Course Website: http://www.gocats.org