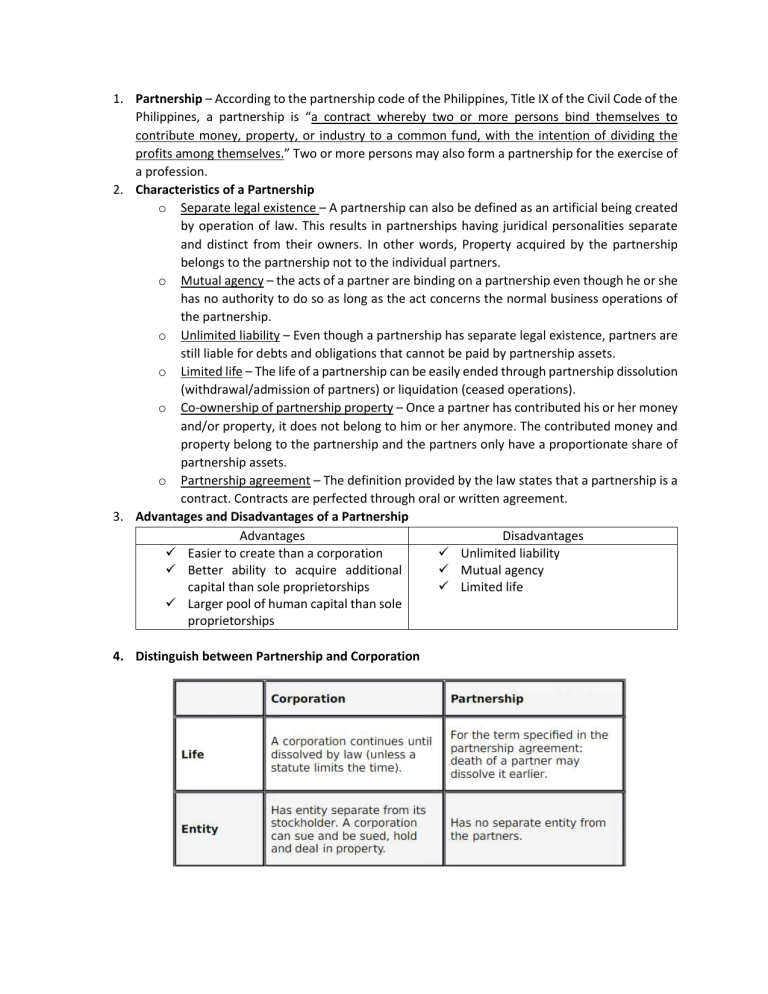
1. Partnership – According to the partnership code of the Philippines, Title IX of the Civil Code of the Philippines, a partnership is “a contract whereby two or more persons bind themselves to contribute money, property, or industry to a common fund, with the intention of dividing the profits among themselves.” Two or more persons may also form a partnership for the exercise of a profession. 2. Characteristics of a Partnership o Separate legal existence – A partnership can also be defined as an artificial being created by operation of law. This results in partnerships having juridical personalities separate and distinct from their owners. In other words, Property acquired by the partnership belongs to the partnership not to the individual partners. o Mutual agency – the acts of a partner are binding on a partnership even though he or she has no authority to do so as long as the act concerns the normal business operations of the partnership. o Unlimited liability – Even though a partnership has separate legal existence, partners are still liable for debts and obligations that cannot be paid by partnership assets. o Limited life – The life of a partnership can be easily ended through partnership dissolution (withdrawal/admission of partners) or liquidation (ceased operations). o Co-ownership of partnership property – Once a partner has contributed his or her money and/or property, it does not belong to him or her anymore. The contributed money and property belong to the partnership and the partners only have a proportionate share of partnership assets. o Partnership agreement – The definition provided by the law states that a partnership is a contract. Contracts are perfected through oral or written agreement. 3. Advantages and Disadvantages of a Partnership Advantages Disadvantages Easier to create than a corporation Unlimited liability Better ability to acquire additional Mutual agency capital than sole proprietorships Limited life Larger pool of human capital than sole proprietorships 4. Distinguish between Partnership and Corporation 5. Classifications of Partnerships and the different kinds of partners o General Partnership - the most basic form of partnership. It does not require forming a business entity with the state. In most cases, partners form their business by signing a partnership agreement. Ownership and profits are usually split evenly among the partners, although they may establish different terms in the partnership agreement. o Limited partnership – Limited partnerships (LPs) are formal business entities authorized by the state. At least one partner has unlimited liability and at least one partner has limited liability. Limited partners – partners having limited liability General partners – partners having unlimited liability o Limited Liability Partnership – a type of partnership that aims to protect innocent partners from the malpractice and wrongdoings of other partners. This kind possesses multiple insurance claims to protect the partners. It’s mostly used by individuals forming a partnership for the practice of a profession (e.g., lawyers, accountants, medical professionals, auditors). o Limited Liability Company – have features of both a corporation and a partnership. Unlike the limited partners in a limited partnership, members of a limited liability company can participate in management without losing the limited liability protection. The owners are called “members” and they enjoy limited liability. 6. Compare Sole Proprietorship and Partnerships Sole Proprietorship Partnerships Owned by a single person Owned by 2 or more individuals The sole proprietor is responsible for The partners are equally responsible all the losses and profits caused. for all the losses and profits caused. Less risk of internal conflict Risk of being held accountable because of other partners’ actions. 7. Know the difference between Capital and Drawing accounts Capital account Capital refers to the money or assets invested into a business by its owners When capital is brought into the business, cash or a non-cash asset account is debited and capital account is credited. inflow of resources increase in the value of both capital as well as assets of the business entity Drawing account Drawings refer to the money withdrawn from a business by its owners for their personal use. When cash or some other asset are withdrawn from the business, drawings account is debited and cash or a non-cash asset account is credited. outflow of resources deduction in the value of both capital and assets of the entity. References: Florendo, J. G. (2016). Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1. Manila: Rex Book Store, Inc. https://www.scribd.com/document/292648395/Corporation-vs-Partnership