EOCT STUDY GUIDE-3 TEST GRADES
advertisement

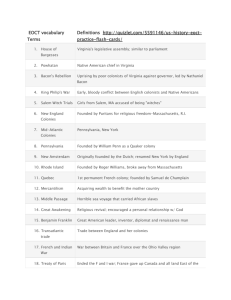
EOCT Vocab *Put the correct letter to the LEFT of the number Standard 1-European settlement in North America 17th century 1. Virginia Company A. Virginia’s legislative assembly; similar to parliament 2. House of Burgesses B. Founded by William Penn as a Quaker colony 3. Powhatan C. 1st permanent French colony; founded by Samuel de Champlain 4. Bacon’s Rebellion D. Originally founded by the Dutch; renamed New York by England 5. King Philip’s War E. Pennsylvania, New York 6. Salem Witch Trials F. Founded by Puritans for religious freedom-Massachusetts, R.I. 7. New England Colonies G. Founded by Roger Williams, broke away from Massachusetts 8. Mid-Atlantic Colonies H. Uprising by poor colonists of Va. Against governor, led by Bacon 9. Pennsylvania I. English business company that sent people to America for goods 10. New Amsterdam J. Early, bloody conflict b/w English colonist and Native Americans 11. Rhode Island K. Girls from Salem, MA accused of being “witches” 12. Quebec L. Native American chief in Virginia Standard 2-Development of society and economy of British North America 13. mercantilism A. Acquiring wealth to benefit the mother country 14. Middle Passage B. Great American leader, inventor, diplomat and renaissance man 15. Great Awakening C. Horrible sea voyage that carried African slaves 16. Benjamin Franklin D. Religious revival; encouraged a personal relationship w/ God 17. Transatlantic trade E. Trade b/w England and her colonies. Standard 3-Causes of the American Revolution 18. French and Indian War A. Ended the F and I war; France gave up Canada/ all land E of Miss 19. Treaty of Paris 1763 B. British tax on all paper products (documents etc.) 20. Proclamation of 1763 C. Closed the port of Boston as punishment for Boston Tea Party 21. Stamp Act D. Led by Sam Adams, protested unfair British rule 22. Intolerable Acts E. American patriot; wrote an influential pamphlet protesting Britain 23. Sons of Liberty F. British law; said colonists could not settle beyond the Appalachians 24. Thomas Paine/Common Sense G. War b/w Britain and France over the Ohio Valley region Standard 4-American Revolution 25. Declaration of Independence A. America’s leader during the Revolution; 1 st president 26. John Locke B. Writer of Declaration of Ind; influenced by John Locke 27. Thomas Jefferson C. Philosopher who believed in natural rights, criticized kings 28. George Washington D. Final battle of American Rev; support from France 29. Yorktown E. Ended American Rev; America officially gained independence 30. Treaty of Paris 1783 F. America’s most important document; declaring independence Standard 5-US Constitution 31. Articles of Confederation A. Protest of farmer’s who couldn’t pay their war debts 32. Federalists B. Fist 10 amendments to Constitution; emphasizes personal freedoms 33. Anti-Federalists C. America’s 1st laws; was too weak b/c govt had no power to tax etc. 34. Great Compromise D. Settled disputes b/w states w/ large and small populations 35. Bill of Rights E. Supporters of strong central govt and rule by elite; led by Hamilton 36. Shay’s Rebellion F. Supporters of states power; farmers; led by Jefferson 37. Whiskey Rebellion G. Rebellion of farmers protesting tax on whiskey 38. Checks and Balances H. Legislative (Congress), Executive (President), Judicial (Courts) 39. Separation of Powers (3 branches of govt) I.Written by Hamilton, Madison; supports Constitution 40. The Federalist J. System where 1 branch can’t dominate another Standard 6-Territorial Expansion and Population Growth 41. NW Ordinance A. Doubled the size of US; purchased by Thomas Jefferson 42. Louisiana Purchase B. Britain and US; fought over freedom of the sea, impressment 43. Lewis and Clark Expedition C. Encouraged Westward expansion and creation of new states 44. War of 1812 D. Explored undiscovered western USA 45. Monroe Doctrine E. Outlawed interference in American affairs/Western Hemisphere Standard 7-Economic Growth and impact in the first half of the 19th century 46. Industrial Revolution A. Promoted stronger president, participation of “common man”, 47. Eli Whitney named after Andrew Jackson; includes “spoils system” 48. Manifest Destiny B. America’s right to expand westward 49. Elizabeth Cady Stanton C. Inventor of cotton gin and interchangeable parts 50. Seneca Falls Convention D. Power driven machines replaced hand labor 51. Jacksonian Democracy E. Leader for women’s rights/suffrage F. America’s 1st women’s rights convention Standard 8-North-South Divisions and Westward Expansion 52. Nat Turner A. Leading white abolitionist, created abolitionist newspaper “Liberator 53. William Lloyd Garrison B. US vs. Mexico; US gained California, Arizona, N. Mex 54. Frederick Douglas C. Ex-slave abolitionist; created “North Star” abolitionist paper 55. Missouri Compromise D. California would be free; fugitive slave act enforced stronger 56. Wilmot Proviso E. Main would be free, Missouri slave; slavery banned north of 36/30 57. Mexican War F. Led a violent slave revolt 58. Compromise of 1850 G. Failed proposal that all land gained from Mexican War be free Standard 9-Causes of the Civil War 59. John Brown A. Confederate (Southern) General 60. Kansas-Nebraska Act B. Union (Northern) General 61. Abraham Lincoln C. Turning battle b/c it cut the South in 2; North controlled Miss river 62. Gettysburg Address D. Abolitionist who led a slave raid on Harper’s Ferry; died a martyr 63. Vicksburg E. Lincoln’s law that freed all slaves in Confederate states 64. Gettysburg F. Based on agriculture; slaves 65. Emancipation Proclamation G. Based on factories; industrialism 66. North’s economy H. Said all slaves are property; not citizens. US couldn’t prohibit slavery 67. South’s economy I. Lincoln’s speech honoring the dead soldiers fighting for a great cause 68. Robert E. Lee J. US president during Civil War; one of greatest ever 69. U.S. Grant K. Allowed popular sovereignty (states right to choose b/w slavery) 70. Dred Scott Case L. Worst battle; Confederates no longer tried to invade the North after this Standard 10-Reconstruction 71. Presidential Reconstruction 72. Radical Republican Reconstruction 73. Freedman’s Bureau 74. “Civil Rights” Amendments 75. 13th Amendment 76. 14th Amendment 77. 15th Amendment A. Tried to punish the South after Civil War; get revenge B. No revenge on the South; lenient policy C. 13 th-15th Amendments D. Sought to help former slaves; poor whites E. Gave anyone born in America equal citizenship F. Outlawed slavery G. Voting rights for ALL males regardless of color Standard 11-Growth of Big Business and Technology after Reconstruction 78. John D. Rockefeller A. R.R. from east to west coast 79. Andrew Carnegie B. Founder of Standard Oil 80. Transcontinental R.R C. America’s greatest inventor-lightbulb, phonograph, motion picture 81. Thomas Edison D. Founder of Carnegie Steel 82. Robber Baron E. Rich businessman who put other companies out of business 83. Chinese F. One company dominates the industry 84. Trust G. Worked on R.R’s on west coast Standard 12-American Industrial Growth 85. Ellis Island A. Leader of Dakota Sioux Indians; defeated Custer at Little Bighorn 86. Wounded Knee B. Location of immigrant inspection in N.Y. 87. Sitting Bull C. Location of Indian massacre by US troops 88. Samuel Gompers D. Labor leader; head of AFL (American Federation of Labor) Standard 13-Progressive Era 89. Upton Sinclair A. Journalists who exposed corruption 90. Muckrakers B. “Separate but Equal”/unfair laws 91. Jane Addams C. Established “separate but equal” laws 92. Jim Crow laws D. Muckraker who wrote “The Jungle” exposing meat packing plants 93. Plessy vs. Ferguson E. Great US president who est national parks and conservation 94. Theodore Roosevelt F. Reformer who est Hull House for the poor Standard 14-America’s growing relationship with the world 95. Spanish-American War A. Allowed ships to pass from Atlantic to Pacific oceans 96. Panama Canal B. War w/ Spain;US gained Puerto Rico, Philippines, Cuba 97. Roosevelt Corollary C. US has the right to intervene in Latin American affairs 98. Chinese Exclusion Act D. Banned all Chinese immigrants Standard 15-US involvement in WW1 99. Neutrality A. German unrestricted sub warfare; Zimmerman note 100. Why US declared war B. Mass movement of blacks to the north looking for work 101. League of Nations C. international peacekeeping organization; US failed to join 102. 14 points D. US policy at outbreak of WW1 103. Great Migration E. Gave women the right to vote (suffrage) 104. 18th Amendment F. Wilson’s plan for international peace 105. 19th Amendment G. Outlawed alcohol (prohibition) Standard 16-Key developments after WW1 106. Red Scare A. Flowering of Africa American art/achievement (Langston Hughes etc) 107. Henry Ford B. America’s main form of entertainment during the 20’s-30’s 108. radio/movies C. Fear of communism in America 109. Harlem Renaissance D. Inventor of Model T automobile and mass production/assembly line Standard 17-Great Depression 110. Causes of GD A. Makeshift shacks that sufferers from the depression lived 111. Dust Bowl B. Overproduction, underconsumption, stock mkt speculation 112. Hoovervilles C. Stock Market Crash 113. October 29, 1929/”Black Tuesday” D. Caused by over farming Standard 18-FDR’s New Deal 114. New Deal A. FDR’s failed plan to pack the court w/ hand picked judges 115. TVA B. FDR’s “eyes and Ears”; she was a great inspiration to millions 116. Social Security Act C. FDR’s series of programs to end the Depression 117. Wagner Act D. Tennessee Valley Authority-built dams and power plants 118. Neutrality Act E. Gave insurance/benefits to retired persons over age 65 119. Eleanor Roosevelt F. Protected the rights of workers/union members 120. “Court Packing” plan G. Made it illegal to sell weapons or make loans to nations at war Standard 19-WW2 121. A. Philip Randolph A. Turning point battle in the Pacific against Japan 122. Pearl Harbor B. Where Japanese Americans were placed after Pearl Harbor attack 123. Lend-Lease program C. Code-name of atomic bomb project 124. Internment camps D. Proposed to march on Washington for civil rights for blacks in America 125. Battle of Midway E. Rationing, war bonds, factories, women working in factories 126. D-Day F. December 7, 1941; Japanese attack on America; reason for US entry 127. War mobilization in the US G. US policy to lend weapons to Allied nations 128. Manhattan Project H. Largest Allied invasion force in history; goal to regain France Standard 20-Cold War impact on the US 129. Marshall Plan A. Policy to help any country fight against communism 130. Truman Doctrine B. Led communist “witch hunts”; accused many innocent Americans 131. Korean War C. US plan to rebuild Europe by donating billions of dollars 132. Joseph McCarthy D. Near nuclear war with Cuba/Russia; Cuban nukes pointed at US 133. Bay of Pigs E. War fought in Vietnam; US helped S. Vietnam vs. communist N. Vietnam 134. Cuban Missile Crisis F. Failed US attempt to overthrow Castro; disaster for US 135. Vietnam War G. N vs. S Korea; ended in a stalemate at the 38th parallel 136. Tet Offensive H. Largest N. Vietnamese (Vietcong) invasion of the war 137. Containment I. US policy to stop the spread of communism Standard 21-Technological development and economic growth in US 1945-1970 138. Baby Boom A. Mass produced homes/planned communities for cheap 139. Levittown B. National network of highways connecting US cities 140. Interstate Highway Act C. Huge growth of population after WW2 141. Sputnik D. First satellite in space launched by Russia 142. Impact of T.V. E. Influenced American viewers to politics, civil rights etc. Standard 22-Civil Rights 1945-1970 143. Brown vs. Board A. “I have a dream”, “Letter from Birmingham jail” 144. MLK’s influential speeches B. Outlawed discrimination based on race, gender, religion 143. Civil Rights Act 1964 C. Outlawed literacy tests for voting 144. Voting Rights Act 1965 D. Outlawed segregation in schools; overturned Plessy vs. Ferguson 145. Truman E. President who integrated he army; huge step for civil rights mvmnt Standard 23-political developments b/w 1945-1970 145. Warren Court A. Law that police must read suspects their constitutional rights upon arrest 146. Great Society B. Became famous for landmark decisions such as Brown vs. Board, Miranda etc 147. Miranda Rights C. LBJ’s program to end poverty/discrimination-(Medicare, Welfare, Civil Rights Act 1964) Standard 24-Social change movements of the 1960’s 148. SCLC A. National Organization for Women; women’ s rights group 149. NOW B. Environmentalist who wrote “Silent Spring” criticizing pesticides/pollution 150. Cesar Chavez/UFW C. Southern Christian Leadership Conference 151. Rachel Carson D. Leader for Hispanic Civil Rights/United Farm Workers Movement 152. Richard Nixon E. Conservative movement president; wanted to reform Great Society programs Standard 25-Changes in politics since 1968 153. Watergate Scandal A. Gave women right to choose if they want abortion; Supreme Court decision 154. Roe vs. Wade B. Commited by Nixon’s administration; goal was to cover attempted burglary 155. Camp David Accords C. Reagan’s economic policy; tax cuts, arms build up, budget cuts 156. Iran Hostage Crisis D. North American Free Trade Agreement; est by Clinton administration 157. Reaganomics E. Peace agreement b/w Israel and Egypt at led by Jimmy Carter @ Camp David 158. Collapse of USSR F. Lasted 444 days; US hostages finally released by Iranian radicals 159. NAFTA G. Reagan’s biggest success in foreign policy; Berlin Wall torn down 160. Clinton’s impeachment H. Opened trade with China; led by Richard Nixon 161.Opening of China I. Terrorist attacks on US soil (World Trade Center, Pentagon) 162.2000 presidential election J. Second president to suffer impeachment for perjury/obstruction of justice 163. 9/11 attacks K. Bush vs. Gore, very controversial-Bush won (lost popular vote, won electoral vote)