global economics
advertisement

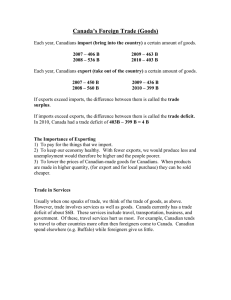
GLOBAL ECONOMICS Global Interdependence –people and nations all over the world depend upon one another for many goods and services Developed countries – nations with a high standard of living and high per captia GDP (ex. US, Canada, & Japan) Developing countries – low average income and has low human capital (ex. Ethiopia, Somalia, Sri Lanka) Globalization – individuals and nations working internationally across barriers of distance, culture, and technology Foreign aid – money, food, military assistance given to less developed countries Exchange rate – price of one nation’s currency in terms of another nation’s currency Child labor – using children to work long hours in unsafe factories and mills denying them an education and endangering them Human rights – universal rights such as right to life, liberty and fair treatment United Nations – purpose is to maintain international peace and seek solutions to global problems International Trade – major force in world today – exchange of services and goods between different nations Foreign trade – international trade among nations Import – goods purchased from other countries Export – goods sold to other countries Tariffs – tax on imported goods Favorable balance of trade – exports are greater than imports Unfavorable balance of trade (trade deficit) – imports are worth more than its exports Free trade – unhindered flow of services between countries – no trade barriers Protective tariffs – when nations try to protect their industries by placing tariffs on imports Comparative advantage – the ability to produce a good at a lower cost than another country can International Economic Organizations – exist to help set trade policy and monitor trade Treaty – a contract binding two or more states under international law North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) – a trade treaty among US, Canada, and Mexico World Trade Organization (WTO) – deals with rules and practices of trade among nations International Monetary Fund (IMF) - monitors global financial system through foreign exchange rates and balances of trade International Monetary Fund (IMF) - monitors global financial system through foreign exchange rates and balances of trade World Bank – lends money to developing countries and expects loans to be repaid European Union – confederation of 25 European countries who cooperate politically Multinational conglomerate – large international company who have offices, factories, or branch plants in multiple countries