Ch 16 The Endocrine System
advertisement

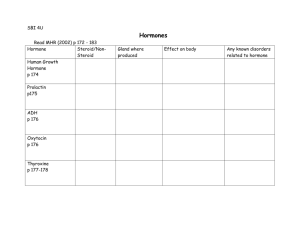
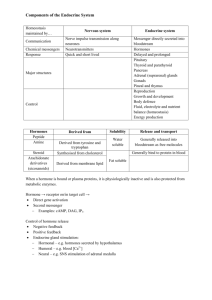
1 Ch 16 The Endocrine System I. Overview- functions to work with nerves to control cellular activity A. Control1. carried2. time of deliveryB. targets 1. 2. 3. C. Major processes under endocrine control 1. reproduction 2. growth/development 3. immune response 4. blood balance a. water b. electrolytes c. nutrients 5. cellular metabolism 6. energy balance D. Glands1. exocrine2. endocrinea. b. glands (fig 16.1) 1. gland with both tissues (exo/endocrine)E. Endocrine tissues1. Adipose cells2. G.I. tract a. gastrinb. CCKF. Autocrine/Paracrine1. autocrineEx: prostaglandins- secreted by smooth muscle smooth muscle contractions 2. paracrine- 2 II. Hormones- Chemical compounds..3 types A. Types 1. amino acid base2. steroida. gonadal hormones b. adrenocortical hormones 3. Eicosanidsa. leukotrinesb. prostaglandinsc. derived1. arachidonic acid B. Mechanisms of Hormone Action 1. hormone effecta. cellular processEx: Epinephrine - B.V. - other cells2. effector changes a. membrane permeabilityb. protein synthesis1. activates/deactivatesc. inducesd. stimulates3. Amino Acid based activation a. amino acid based hormones1. amino acids cannot penetrate plasma membrane b. Amino acids bindc. 2ed Messenger- G protein 1. a membrane2. activated- (guanasine triphosphate)3. adenylate cyclaseEx: hormone binds (1st messenger) (GDPGTP) activation of G-protein Effector (adenylate cyclase) generates cAMP from ATP cAMP activates downstream proteins d. PiP- calcium signal mechanism (see fig 16.2) another example 2ed messenger 3 4. Steroid Hormone based activation (fig 16.3) a. permeability1. activation2. mRNA formation a. protein synthesisEx: steroid hormone enters cell binds to a chaperone in nucleus a hormone/receptor complex is activated binds to strand of chromatin transcription occurs mRNA carries transcripted protein ribosome A new protein is formed C. Target Cell Specificity 1. specifica. ACTH(adrenocorticotropic hormone)b. Thyroxine2. Hormone receptor interaction- 3 factors a. blood levelsb. receptorsc. affinity1. desensitization2. up regulationD. Half-life, Onset, and Duration of Hormone Activity 1. Effect2. Circulation- 2 forms a. freeb. bound1. lipid-soluble3. concentrationa. rate of releaseb. speed1. enzymes2. removeda. waste products4. Half-lifea. shortb. longerc. varies- 4 d. water solublee. lipid solublef. releasedE. Interaction of Hormones 1. PermissivenessEx: need of thyroid hormone to develop the reproductive system 2. SynergismEx: glucagon and epinephrine liver to release glucose = 150% greater Release this way. 3. AntagonismEx: insulin lowers blood glucose ; glucagons increases blood glucose F. Control of Hormone Release (see fig 16.4) In general, negative feedback system of release requires a stimuli… 3 types 1. Humoral stimulia. ions b. sugar c. nutrients…etc.,.. Ex: low blood Ca++ levels parathyroid hormone increases Ca++ -Insulin and aldosterone release too 2. Neuronal stimulia. nerve fibersEx: parasympathetic fibers adrenal medulla release of catacholamines - epinephrine and norepinephrine 3. Hormonal stimulia. hypothalamusIII. Major Endocrine Glands A. Pituitary gland (hypophysis)- mother gland 1. location- sella turcica of… 2. secretes3. description (fig 16.4c)a. infundibulumb. two lobes 1. Posterior pituitary (fig 16.5) a. pituicytesb. neurohormonesc. storaged. neurohypophysis- 5 2. Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)a. composedb. hormones- *see table 16.1 know these 4. Hormones of the Pituitary (anterior)a. two classes of… 1. Tropic hormones (tropins)a. TSH- thyroid stimulating hormone b. ACTH- adrenocorticotropic hormone c. LH- Leutinizing hormone d. FSH- follicle stimulating hormone 2. Non-Tropic Hormones a. GH- growth hormone..HGH- human growth hormone b. PRL- prolactin B. Posterior Pituitary- (hormones made in hypothalamus)1. oxytocin2. ADH- antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin)C. Blood flow and Release (anterior) 1. arteriala. superior hypophysial artery1. primary and secondary capillary plexus a. site2. Veins3. Venule- TSH,FSH,LH,ACTH,GH, and PRL D. Blood flow (posterior) 1. arterial2. veins3. venuleNote: Table 16.1… details of pituitary hormones Know… hormone, regulation of release, target organ, effects 6 B. The Thyroid gland (fig 16.7)1. location2. structurea. isthmus3. blood supply a. superiorb. inferior4. microanatomy a. colloid filled folliclesFn- production of thyroid hormone b. surrounded (fig 16.7b)Fn- produce calcitonin c. follicle cells5. Thyroid Hormonea. thyroxine (T4)1. secretedb. tri-iodothyronine (thyronine T3)1. derivedc. tyrosine amino acidsd. differences1. T42. T3e. Effects1. exceptions-adult brain, spleen, testes, uterus, thyroid 2. Glucose Oxidationa. b. c. calorigenic effect1. adrenergic controlled3. other effectsa. tissue growth b. skeletal/nervous development c. maturation/growth d. reproduction see table 16.2 for systems effected, effects, hyper and hypo secretions 7 F. Synthesis1. response2. TSH3. T3 and T4 a. colloid lumenG. Steps of synthesis …see fig 16.8 1. Thyroglobin a. transported colloid 2. Iodinea. oxidizedb. active formc. I1 converted to I2 3. Iodine Transporta. Iodine couples with tyrosine amino acid and forms… thyroglobulin colloid 4. MIT (T1) and DIT (T2) are formed… a. one iodine attaches MIT monoiodinetyrosine b. two iodine attaches DIT diiodinetyrosine c. enzymes link… 1. two DIT’s 2. MIT and DIT 5. Colloid endocytosis6. Cleavagea. some T3 is converted from T4 H. Transport/reg T3 T4 1. transporteda. TBG’sb. produced2. binding affinitya. enzymesb. intracellular binding3. control- increased T4 or decreased a. TSHb. TSH inhibition 1. somatostatin 2. increased glucocorticoids 3. sex hormones4. High blood- 8 6. Calcitonin- a polypeptide hormone… a. produced1. parafollicular cells b. function1. inhibition2. stimulates3. activation4. childhoodB. The Parathyroid Gland (fig 16.10) 1. location2. morphology3. microscopy- (fig 16.10b) a. oxyphil cellsb. chief cells4. PTH (parathyroid hormone) a. typeb. function1. responds2. targets 3 organs a. boneb. kidneysc. intestines3. stimulatesa. calcitrolC. The Adrenal Gland (suprarenal) 1. occurs2. locationa. supra renal glands3. constructiona. innerb. outer4. Adrenal Cortex- steroid hormones (corticosteroids) A. layers- 3 zones (layers) 1. zona glomerulosaa. mineralocorticoids2. zona fasciculataa. glucocorticoids3. zona reticularisa. gonadocorticoids- 9 B. Corticosteroids 1. Mineralocorticoidsa. Na/K b. aldosterone1. transcription2. kidney tubules3. reabsorptionc. overall effects1. Ions K, H, HCO3,and CL d. secretion control1. rising K+ blood levels2. lower Na+ blood levels3. inhibition of aldosteronee. Other mechanisms of control 1. Renin-angiotensin mechanisma. stimulus1. plasma osmolarityb. juxtaglomerular apparatus1. rennina. angiotensinogenb. angiostensin IIc. main effect… TO INCREASE BLOOD PRESSURE 2. ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) a. Extreme stress1. CRH (corticotrophin releasing hormone)2. net effect… 3. Arterial natriuretic peptide (ANP) a. secreted1. rise in blood pressure b. effect1. blocks2. decreases… c. hypersecretion1. aldosteronisma. hypertension + edemab. excretion1. unresponsive… 2. muscle… 2. hyposecretion 10 2. Glucocorticoids a. purpose1. blood… 2. blood… b. hormones 1. cortisol- ( hydrocortisone)2. cortisone 3. corticosterone c. regulation d. Cortisole1. release… a. ACTH2. inhibition3. levels a. highestb. lowest4. STRESS 5. Excess levels… a. depressb. inhibit1. depressc. effects 1. 2. 3. 6. Drugs: glucocorticoid drugs for chronic inflammation (arthritis) allergic responses…all can upset a delicate hormonal balance. 3. Gonadocorticoids- (sex hormones) a. secretedb. androgens1. androstenedione 2. dehydroepiandrosterone (DEHA) 3. convertedc. productiond. Fn 1. puberty2. women a. b. 11 5. The Adrenal Medulla A. Chromaffin cells 1. location2. composition3. synthesizea. epinephrine and norepinephrine Sequence: tyrosine dopamine norepinephrine epinephrine Function: fight or flight response effects are on cardiovascular ststem D. Pancreas A. type of gland1. edocrine and exocrine B. Cells 1. Acinar cellsa. digestive juice2. Islets cells (islets of langerhans) a. alpha cellsb. beta cellsC. Hormones 1. Glucagon a. releaseb. target1. glycogen 2. synthesisa. gluconeogenesis 2. Insulin- syn from _____________ just before it is needed. a. sugar levelsb. influencesc. inhibitsE. The GonadsA. Female1. estrogen2. progesteroneB. Male1. testosterone- 12 F. The Pineal Gland A. locationB. cells1. calcium saltsC. Endocrine function1. Melatonina. serotoninb. concentrations1. highest2. lowestc. animalsd. childrene. Biological clock (suprachiasmatic nucleus) f. Fn- G. The Thymus A. locationB. infancy/childhoodC. endocrine1. thymoproteins 2. thymic factor 3. thymosins D. Fn- normal development of T-lymphocytes… immune system 13 14 15 16