Energy and Machines Notes
advertisement

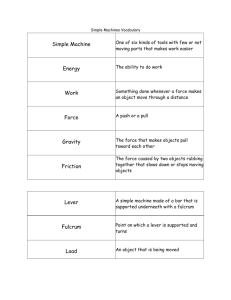
Energy and Machines Notes Topic one What is a machine? A machine is any device, simple or complicated, that uses energy to perform a useful task or function. A screw driver is an example of a machine. Energy is defined as the capacity to do work, or transfer heat. Work is defined as the result of a force being exerted on an object and the object moving in the general direction of the force. Two condition required for work to be done are (1) a force is exerted on the object, and (2) the object moves for a distance in the general direction of the force. Force is measured in Newtons. Therefore work is measured in Newtons (N). Imagine the situations described. One group of people have lifted a rock from the ground to the bed of the truck, while another group struggles to move a car stuck in the mud (they do not move the car). Which of these groups is actually accomplishing work? The group that actually lifts the rock into the flat bed of the truck has performed work. If you look at the conditions required in the previous question is states that there must be movement in the general direction of the force. There is no movement with the people pushing on the car that is stuck, therefore there is no work accomplished. 1 SYSTEMS AND SUBSYSTEMS Are all machines complicated? No. All machines are made up of the SIX most basic machines, which are... 1. Ramp 2. Lever 3. Pulley 4. wheel-and-axle 5. Wedge 6. Screw A complicated machine can be thought of as a system. Its working parts make up the subsystems of the machine. Another name for the simple machine called the inclined plane is Ramp Another description for the simple machine called the pulley is the Rotating wheel with a groove When you pull on a wagon or push on a car that is stuck in the mud you are exerting a force on that object. This force that you exert is called the effort force . A fact that holds true at all times is that the earth's gravity will always exert 10 newtons of force on every 1 Kg of mass. A force exerted by gravity on a block of wood that is .38 Kg or 380 grams (REMEMBER THAT 1 Kg= 10 N) is equal to 3.8 newtons. 2 There is a strong advantage to combining the two different types of simple machines. The overall effort needed to complete a task is significantly reduced. 3 TOPIC TWO - EASING THE TASK WITH LEVERS Archimedes is "quoted" as saying, "Give me a lever long enough and a placeto stand and I will move the earth." So what is a lever system? The Greek scientist Archimedes once claimed that if he had a point of support, he'd be able to move the world. He was referring to the lever's amazing ability to make heavy lifting easier A ramp or a pulley can reduce the force you need to exert (Effort force). a Lever is another effort-reducing device. What types of jobs can a lever help you complete? 1. Hitting a baseball. 2. Opening a bottle of pop. A lever is an effort-reducing simple machine. Below are three different tools that incorporate the idea of a lever into their design. 1. A pair of pliers. 2. A golf club. 3. A pair of scissors. A fulcrum is the point that supports the lever and upon which it turns, or pivots. There are three classes of lever. They are determined by the position of the fulcrum, effort force, and load. 4 1. Class 1 Lever - When a lever’s fulcrum is between the load and the effort force. This lever can also be called the Children's lever. Think about a fun park toy that kids play on. Ex. - A TEETER-TOTTER In a first class lever the fulcrum is between the effort and resistance, where the lever exerts a force. 5 2. Class 2 Lever - When a lever’s fulcrum is at one end, the load in the middle and the effort force at the opposite end from the fulcrum. You could also call this the gardener’s lever. Ex. - A wheelbarrow In a second-class lever the resistance is between the fulcrum and effort. For such levers, if the effort arm is longer than the resistance arm, less effort over a certain distance exerts a greater force over a shorter distance. 3. Class 3 Lever - When a lever’s effort force is between the fulcrum and the load. This could also be called the sportsman's lever. Racquet sports such as tennis, badminton, and fishing require the use of a rod shaped tool. The fulcrum is at the wrist and the effort force is throughout the length of the rod and the load is on the very end. Ex. - An arm lifting a book. Kicking a soccer ball. 6 In a third-class lever the effort is between the fulcrum and the resistance. More effort is required to move less weight, but the speed and distance moved are increased SO WHAT THREE IMPORTANT FACTS HAVE YOU'VE LEARNED ABOUT LEVERS? 1. There are three types of levers 2. They are formed by varying the arrangement of three things: the load, the fulcrum. and the effort force. 3. The arrangement of these three things depends on the lever’s function. 7 TOPIC THREE - THE WHEEL AND AXLE Imagine trying to open a door without a doorknob! Another simple machine at work here and it is called a wheel and axle. This simple machine is used to overcome a large force by applying a smaller effort force, this is called a FORCE ADVANTAGE. But, there are instances where a wheel and axle is used to increase speed, which is called SPEED ADVANTAGE. One example of speed advantage is found on a 21 speed mountain bike. TOPIC FOUR - COMPLETING YOUR SURVEY OF SIMPLE MACHINES What four types of simple machines have we just looked at? 1. The ramp 2. The pulley 3. The lever 4. the wheel-and-axle What is the differences between a wedge and an inclined plane? A wedge is similar to an inclined plane, except that a wedge normally moves into an object (for example, an axe head cuts into a block of wood), while an inclined plane stays still and objects move along it. What is the sixth type of simple machine? The screw. 8 TOPIC FIVE - EXAMINING MECHANICAL DEVICES Mechanical devices are usually made up of large numbers of such simple machines . Do systems always need to have a constant energy supply? NO. Some systems have their energy supplied by outside sources, and only require energy when the device is in use. What is the main subsystem of a stapler? The main subsystem of a stapler uses a lever. 9 TOPIC SIX - USING GEARS What is a GEAR WHEEL? A gear wheel is a wheel with precisely manufactured, identical teeth around its edge. What does a gear wheel do? A gear wheel is used to transfer rotary motion and force from one part of a machine to another part. What does the term mesh mean in simpler terms? Mesh means to interlock neatly. A smaller gear is called a pinion. The gear that supplies the energy is called the driving gear. The gear to which the force is directed is called the driven gear. MULTIPLYING GEARS AND REDUCING GEARS A large gear driving a smaller gear decreases torque and increases speed in the driven gear A small gear driving a larger gear increases torque and reduces speed in the driven gear What is a reducing gear? When the driving gear has fewer teeth than the driven 10 gear, the driven gear then rotates more slowly than the driving gear. Such gears are called reducing gears, because they reduce turning speed. A car or bicycle in low gear uses reducing gears. When the driving and the driven gears are the same size these gears are known as parallel gears . Do parallel gears both move in the same direction when moving? (HINT: Do both move in a clockwise direction when moved?) Explain. NO. When the driving wheel spins in a clockwise direction it moves the driven gear in a counter-clockwise direction. GEARS IN A BICYCLE Machines use gears to change forces. The bicycle is the most efficient machine ever invented for converting human muscle power into motion. Bicycles use gears and levers to connect the muscle power from your legs to turning the rear wheel. The connection is made with a chain so that the gear ratio between the crank and the freewheel can be changed while the bicycle is moving. Modern bicycles have between one and 24 different 11 speeds. Each speed corresponds to a different gear ratio. Why are some gears easier to pedal than others? Why do some gears allow you to go faster than others? What are sprockets? The gears that are actually toothed discs. Where is the front sprocket located? The front sprocket is attacked to the pedal crank (where your foot is located) Where is the rear sprocket located? The back sprocket is attached to the hub (axis) of the rear crank - the middle of the back wheel. When would you use first gear? When you're trying to go up a very steep hill. You turn the pedal like crazy and you do not move very fast or far for your effort, but you do not exert a great deal of effort throughout the climb either. 12 TOPIC SEVEN - SOURCES OF ENERGY TO RUN MACHINES What is one form of energy used in machines, besides the power of our human bodies? Chemical energy. Mostly all energy originates as Solar energy, from out Sun. Some energy is geothermal, which supplies tube worms and other subterranean and oceanic life. SOME FORMS OF ENERGY What is thermal energy? The total energy of all the particles in a material or object. What is potential energy? Potential energy is actually stored energy. “AVAILABLE ENERGY.” What is kinetic energy? Energy of motion is Kinetic Energy. What is elastic potential energy? Elastic Potential energy is the energy stored in a wound up spring. What is mechanical energy? Mechanical energy is a type of energy we associate with mechanical devices. It can be kinetic (when the parts of the device are moving) or potential (when a grandfather clocks pendulum is at the top of its swing, its energy is potential energy). 13 What does an energy converter do? It converts energy from one form to another. For example, solar powered energy can be converted to electrical energy. THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY What is the law of conservation of energy? Although energy may change its form, it is never “created” and never “destroyed.” Scientists say that energy in a system is “conserved.” this means that energy is neither created nor destroyed, but transformed (changed from one form to another). 14 TOPIC EIGHT - ENERGY USE AND EFFICIENCY How many devices will you use today that will do work for you, provide you with heat or light, or entertain you? Most of these devices use electrical energy to produce some other form of energy. Some devices use the chemical energy of fuels such as natural gas, wood, or gasoline. If you were given a gasoline engine in a car that produced only 15 Kj of useful mechanical output energy for every 60 Kj of chemical input, its efficiency would be......? What percentage does this number represent? 15 Kj/60Kj = 0.25 this means that the efficiency of the engine is 25%. The energy that is not put to useful work is wasted. Are incandescent light bulbs efficient? NO. The majority of the energy is lost as heat. MEASURING EFFICIENCY Efficiency is equal to (energy produced by the device) divided by (energy used to operate the device) and this number is then multiplied by 100%. Ex. The above engine is only 25% efficient. How can you figure out the efficiency of many household devices? 15 You look for the special label on them with an “energy use” rating called the Energuide number. This number tells you how much electrical energy the device will use, on average, in a month. The efficiencies of Some Heat Engines Heat Engine Efficiency Airplane engine 10 % Steam locomotive 10 % Automobile engine 22 % Steam turbine 30 % Diesel engine 35 % 16 17 18 19