CHEMISTRY
advertisement
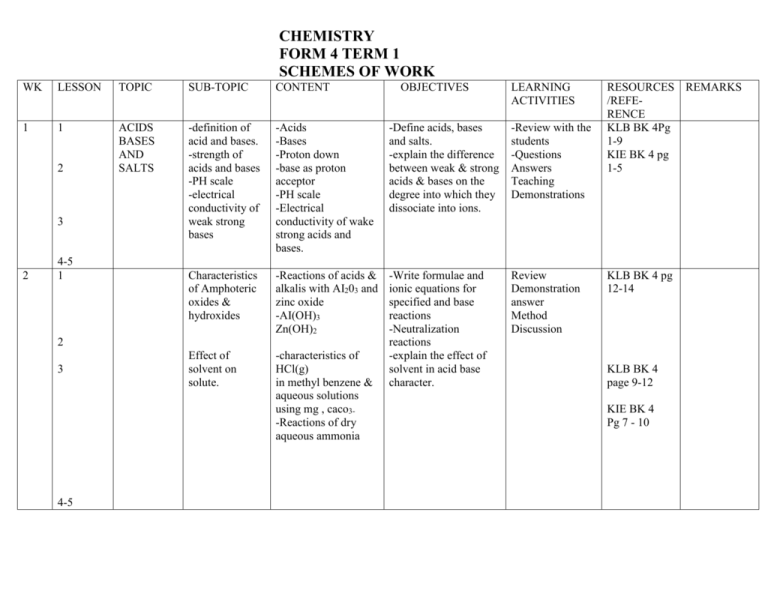
CHEMISTRY FORM 4 TERM 1 SCHEMES OF WORK WK LESSON TOPIC SUB-TOPIC CONTENT 1 1 ACIDS BASES AND SALTS -definition of acid and bases. -strength of acids and bases -PH scale -electrical conductivity of weak strong bases -Acids -Bases -Proton down -base as proton acceptor -PH scale -Electrical conductivity of wake strong acids and bases. -Define acids, bases and salts. -explain the difference between weak & strong acids & bases on the degree into which they dissociate into ions. -Review with the students -Questions Answers Teaching Demonstrations Characteristics of Amphoteric oxides & hydroxides -Reactions of acids & alkalis with AI203 and zinc oxide -AI(OH)3 Zn(OH)2 Review Demonstration answer Method Discussion Effect of solvent on solute. -characteristics of HCl(g) in methyl benzene & aqueous solutions using mg , caco3-Reactions of dry aqueous ammonia -Write formulae and ionic equations for specified and base reactions -Neutralization reactions -explain the effect of solvent in acid base character. 2 3 2 4-5 1 2 3 4-5 OBJECTIVES LEARNING ACTIVITIES RESOURCES REMARKS /REFERENCE KLB BK 4Pg 1-9 KIE BK 4 pg 1-5 KLB BK 4 pg 12-14 KLB BK 4 page 9-12 KIE BK 4 Pg 7 - 10 3 1 SALTS 2 3 SOLUBILITY SOLUBILITY CURVES -solubility curves -fractural crystallization – Extraction of Na2CO3 from L Magandi 1 Water hardness 2 -Removal of water hardness -Types of water hardness -methods of removal of water hardness. 4-5 4 Complex ions -Salts -Precipitate reactions -Reaction of cations i.e Ca 2+,Fe2+,Fe3+,Ba2+ , Zn2+,Al3+,Cu2+ with ammonia solution, clC032-,SO42- SO32-Cu(NH3)42+ Zn(NH3)42+ (Pb(OH)4)2- 3-5 -Advantages & disadvantages of water hardness. Advantages & disadvantages of hard water -Define salt -test for presence of specified anion or cations. -identify precipitates and complexes produced by specified cation – anion reaction. -identify complex ions produced by specified anion-caption reations -Explain the use of solubility curves in salt extraction. -state the types and causes of hardness of water. -state the effect and explains the methods of removal of water hardness. -state the advantages & disadvantages of hard water. -class experiment -questions Answers -discuss solns of the said cations KLB bk 4 PG 14 – 18 Demonstration Discuss KLB BK 4 pg 18-20 KLB BK 4 pg 20-25 KLB BK 4 pg 25-29 5 1 2-3 ENERGY CHANGES IN CHEMICA L& PHYSICAL PROCESSE S -Endothermic and Exothermic reactions - latent heat -Enthalpy notation DH for exothermic endothermic reactionmolar heat Quantitative determination of enthalpies -Formation of HCL from H2 cl2 -formation of CH3Cl from methane & chlorine -Enthalpies -combustion -solution -displacement -neutralization -Energy level diagram -Thermo chemical cycles -heat of solution., DH lattice DH hydration -Energy content of fuels 4-5 6 1 2 3 4 5 7 1 2-3 -simple energy level diagram - Ness’ law 4-5 Common fuels -pollution by common fuels e.g engine -Internal combustion engine pollution -Define exothermic and endothermic reaction using DH notation -Draw energy level diagrams. -Explain fusions and vaporization as evidence of interparticle fumes -Explain energy changes are caused by bond breaking and bond forming in chemical reactions. -Define and explain various types of heat changes. -carry out experiments to determine & enthalpy changes for some reactions KLB BK 4 pg 32-3 9 -Write correct simple thermo chemical equations -state Hess’ law abd carry out related calculations. -Relationship between DH solution, DH salt ,DH hydr -state and explain the factors that influence the choice of fuels. -explain the environmental KLB BK 4 pg 56 – 59 KLB BK 4 pg 40 - 55 60-64 64-67 67-68 effects on fuels. 8 1 2-3 4&5 9 1 2&4 5 REACTION -Reaction rates RATES & REVERSIBLE REACTION -Quantitative S treatment factors affecting the rate of a reaction. -methods used to measure ratio of chemical reaction Reversible reactions -effect if different factors on position of equation -uses in industrial processes eg contact e Heber presses -Definition -collision theory -Quantitative treatment on effect of concentration , temp, s.Area light, catalyst -Experiments eg. Cuco3 + HCl -Na2S203& HCl mg & HCl -H202 & catalyst. -Equilibrium asa state of balance eg. In -acid – alkaline -chlorate dichromate hydrated CuSO4 Le Chamber principal -Define rate of a reaction. -explain the term activation energy -Describe some methods used to measure rates of reaction. -explain the effects of different factors on reaction rates. -illustrate reaction rates graphically 73- -state examples of simple reversible reaction. Explain chemical equilibrium as a state of balance. -Explain the effect of different factors on position of equilibrium as a state if balance. -Explain the effect of different factors on position of equilibrium. KLB BK 4 Pg 91-104 pg 82-91 -73-82 10 1 2-3 ELECTRO- Red ox CHEMISTR reactions Y -oxidation numbers -displacement reactions of metals 4-5 Displacement reactions in halogens 11 12 1 Electrochemical -cal cell -Quantitive treatment of the electron flow in zn/ zn3+ // Cu2+ /Cu -standard electrode potentials -Dry cells /Accumulators fuel cells Electron transfer – Determination of oxidation No -Redox reactions using Fe2+ , Fe3+ with H202 -Displacement reactions -Reducing power M/M2+ Oxidizing power of halogens and cl, Br and I only. -explain redox reactions in terms of gain or loss of e-identify changes in O.N during redox reactions -write balanced redox equations. KLB BK 4 Pg 123141 Reactions of metal/metal cation. -Explain an electrochemical cell in terms of electron transfer -Draw cell diagrams and write the cell notation. -Explain the construction and working of an electrochemical cell. -Compare oxidizing and reducing power of ions for displacement reactions. -calculate the EMF of the cell given standard potentials KLB BK 4 Pg 123-141 13 1 2 3 4 5 -Electrolysis-factors affecting electrolysis -preferential discharge in ions during electrolysis -Quantitative treatment of electrolysis -Faradays first law of electrolysis -Numerical computations -Applications of electrolysis -preferential discharge of ions during electrolysis. -ionic equation for reaction taking place at electrodes. -Factors affecting electrolysis. -Application of electrolysis. -Extraction of metals., -Manufacture of NaOH, Cl2,H2. -Electrolysis of brine. -Refining of copper. -Electroplating -state and explain the factors that affect preferential discharge of ions during electrolysis. -Relate the quantity of electricity passed to amount of substances liberated at electrodes. -describe some applications of electrolysis. KLB BK 4 Pg 141-154 Pg 154-155 Pg. 155-160 Pg 160-164 CHEMISTRY FORM 4 TERM 2 SCHEMES OF WORK WK LESSON TOPIC SUB-TOPIC CONTENT 1 1 METALS Methods of extraction -electrolytic production of sodium and aluminium and zinc -Chief ores of sodium and aluminium -electrolytic method of extraction -Electrolytic extraction of zinc Extraction of metals by reduction method. E.g iron, zinc, lead and copper. -Extraction of iron copper. Zinc and lead from their ores. Properties of metals -physical properties -chemical properties e.g mpt,Bpt thermal & electrical conductivity -density malleability -Reaction with water, cl2, dil. HCl -Brass -Bronze -Steel 2 1 2-5 3 1 2 3-5 4 1-2 Uses of metals and their alloys Pollution effect OBJECTIVES -Name the chief ore of some metals e.g Na and Al -Describe and explain general method used in extraction of metals from their ores. -select & describe suitable method for extraction of some metals from the ores. -Name the chief ore from which metal is extracted. -Describe and explain general method used in extract of the metals by reduction process. -Describe and explain physical and chemical properties of some metals -state and explain various uses of these metals and their alloys. LEARNING ACTIVITIES RESOURCES REMARKS /REFERENCE KLB Chem Bk 4 pg 168-173 KLB Chem Bk 4 pg 173-183 KLB Chem Bk 183- 194 KLB Chem Bk 194-197 3-5 5 1 2 of the industrial -duralumin production of uses of – Na, Al,& the metals on Zn, Fe and Cu the environment ORGANIC ALKANOLI CHEMISTR properties Y 3 4 5 6 1 2 ALKANOIC ACIDS (Carboxylic acids) 3 4 5 7 1 2 3 4 Detergents -soapy detergents -preparation -mode of action of soap in cleansing. -Describe the effect of the industrial production processes of the metals on the environment. -General formula -Name and draw the -Nomenclature structures of simple -preparations alkanols. -hydrolysis of alkenes -Describe the -fermentation preparation & explain -physical properties -- the physical & -chemical properties chemical properties of -uses alkanols. -state the main features of the homologous series. -state & explain uses of some alkanols. -General formulae - Name & draw the -Nomenclature structure of simple -Preparation almanac acids. oxidation of alcohols. -Describe the -physical prop. preparation & explain -hydrogen’s bonding the physical & in organic acid. chemical properties of -chemical reactions carboxylic acids. esterification -Homologous series – Uses of carboxylic acids ester(up[ to 2 carbons only -soapy detergent -lab preparation Hydrolysis of fats. -mode of action . -water hardness -pollution effort -manufacture. -Describe the preparation properties & uses of detergents -explain effect of hard water or detergents -pg 203-206 KLB Chem Bk 197 -198 KLB Chem Bk 203-218 210-212 -212-213 – 218 -318-219 KL:B BBK 4 Pg. 219 - 227 KL:B BBK 4 Pg. 227 - 238 8 5 1 2 3 4 9 5 1&2 RADIO ACTIVITY 3 4 5 10 1 -soapless detergents Polymers. -name of some naturally polymers & fibres -Synthetic polymer & fibres-synthetic rubber -advantages & disadvantages of synthetic polymers & fibres Uses of polymers & fibres -Stability of isotopes. -Radioactivity radiations. - Radioactive decay -Half life -Nuclear reactions -mode of action -pollution effect -Name some natural fibres and polymers. -cellulose rubber & valences -Name synthetic polymers e.g P.V.C Polythene,. Nylon, Perspex -uses of polymers -stability of isotopes . Radiations & B & P radiations Characteristics -half life calculators. -change in the nucleus due to a, B & y decay Nucleus fission & fusion -Applications -As some of the energy -List some natural synthetic polymers fibres and state their uses. -Describe the prep. Properties and uses of some synthetic polymers. -Identify the structure of the polymer given the monomer. -state advantages & disadvantages of synthetic materials over natural fibres in terms of structure & properties. KL:B BBK 4 Pg. 238- 243 -Define radioactivity half-life radi0 isotope and nuclides -state types of radioactivity. -Name particles emitted during decay and state the properties . -Carry out simple calculations involving half-life. -Write balanced nucleus reactions. -Distinguish between nuclear fusion & fusion -state uses of some readioi9sotopes. KL:B BBK 4 Pg. 249 257 KL:B BBK 4 Pg 257-263 -Pollution effect of radioactivity. -Quantitative treatment -in chemistry -in medicane carbon dating in agriculture -Dangers of radius (isotopes) environmental pollution Chernobyl disaster -state dangers associated with radio activity.`






