Quiz # 4 - KFUPM Open Courseware
advertisement

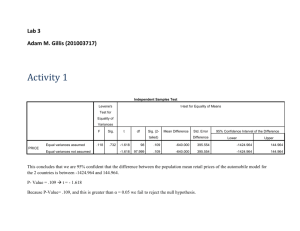
01 01 MKT 345 MARKETING RESEARCH (TERM 071) QUIZ # 4 (TUESDAY, JAN. 15, 2008) - Dr. Alhassan G. Abdul-Muhmin NAME: ______________________________________________ ID # ____________________ NOTE: Each question carries one point 1. Which of the following analysis techniques can you use to investigate the relationship between two variables, both of which are measured at the ratio level? A. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) B. Correlation analysis C. Chi-square analysis (Crosstabulation) 2. You want to investigate the relationship between two variables, one of which is dependent and the other is independent. The dependent variable is an interval-level variable and the independent is a nominal variable. Which of the following techniques can you use? A. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) B. Correlation analysis C. Chi-square analysis (Crosstabulation) The Table below shows results from a frequency analysis of respondents' nationality in a previous MKT 345 class project. There were two possible answers to the question (Saudi and Non-Saudi). Use it to answer the next two questions. NATION Nationality Valid Mis sing Total Saudi Non-Saudi 3 Total System Frequency 124 13 1 138 3 141 Percent 87.9 9.2 .7 97.9 2.1 100.0 Valid Percent 89.9 9.4 .7 100.0 Cumulative Percent 89.9 99.3 100.0 3. What is the sample size used in the analysis? A. 138 B. 141 C. 100 D. It is not possible to tell from the Table 4. What percent of those who answered the question are non-Saudis? A. 13% B. 9.2% C. 9.4% D. 99.3% 5. Which of the following is/are likely to be true regarding the number 3 in the second column (i.e. the number between “Non-Saudi” and "Total")? A. It is the result of an error in the data entry B. It indicates a respondent whose nationality is not one of the two options C. It is the result of an error made by SPSS in computing the frequencies D. Only A and C The Tables below show results of a regression analysis conducted on two of the variables in our class project. Use them to answer the next three questions. Regression Model Summary Model 1 R R Square Adjusted R Square Std. Error of the Estimate .315a .099 .093 1.47519 a. Predictors: (Constant), Overall satisfaction with STC ANOVAb Model 1 Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig. Regression 33.982 1 33.982 15.615 .000a Residual 309.018 142 2.176 Total 343.000 143 a. Predictors: (Constant), Overall satisfaction with STC b. Dependent Variable: Loyalty toward STC Coefficientsa Unstandardized Coefficients Model 1 B Std. Error (Constant) 2.640 .385 Overall satisfaction with STC .329 .083 Standardized Coefficients Beta .315 95% Confidence Interval for B t Sig. Lower Bound Upper Bound 6.850 .000 1.878 3.402 3.952 .000 .164 .493 a. Dependent Variable: Loyalty toward STC 6. What is this type of regression called? A. Multiple regression B. Simple regression C. Dependent variable regression D. Independent variable regression E. Non-linear regression 7. What proportion of variance in the dependent variable is explained by the significant independent variables? A. 100% B. 31.5% C. 9.9% D. 14.7% 8. Using alpha=0.05, what can we conclude about the coefficient for overall satisfaction with STC? A. It is significantly different from zero in the population B. It is significantly different from zero in the sample C. It is NOT significantly different from zero in the population D. It is NOT significantly different from zero in the sample The Tables below show results of independent samples T-Test obtained from analysis of the data from our class project questionnaire using SPSS. Use the Tables to answer the next three questions. (NOTE: According to the scale used in the questionnaire a higher satisfaction score indicates a higher level of satisfaction). T-Test Group Statistics Q24a Landline Monthly Bill Marital Status N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Married 40 163.50 217.498 34.389 Single 56 136.43 167.141 22.335 Independent Samples Test Levene's Test for Equality of Variances Q24a Landline Monthly Bill Equal variances assumed Equal variances not assumed t-test for Equality of Means F Sig. t df Sig. (2tailed) Mean Std. Error Difference Difference .838 .362 .689 94 .492 27.071 .660 7.001 .511 27.071 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference Lower Upper 39.264 -50.888 105.031 41.006 -54.712 108.855 9. Which of the following questions was the analysis conducted to answer? A. Is there is a relationship between marital status and monthly landline phone bill? B. Does monthly landline phone bill affect marital status? C. Both A and B 10. In the second Table, which of the two rows should we use to test for equality of means between the two groups, given α = 0.05? A. The first row, i.e. the one labeled “Equal variances assumed” B. The second row, i.e. the one labeled “Equal variances not assumed” 11. Given α = 0.05, what conclusion can we draw from the t-test for equality of means about the population from which the sample is drawn? A. In the population, there is NO relationship between marital status and monthly landline phone bill. B. In the population, there is a relationship between marital status and monthly landline phone bill; married respondents have significantly higher phone bills than singles. C. In the population, there is a relationship between marital status and monthly landline phone bill; married respondents have significantly lower phone bills than singles. D. It is not possible to draw any conclusions from the results.
![[PowerPoint 2007] presentation file](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005406460_1-7834316c409f9802f7aec3d8538324fb-300x300.png)