Week
advertisement
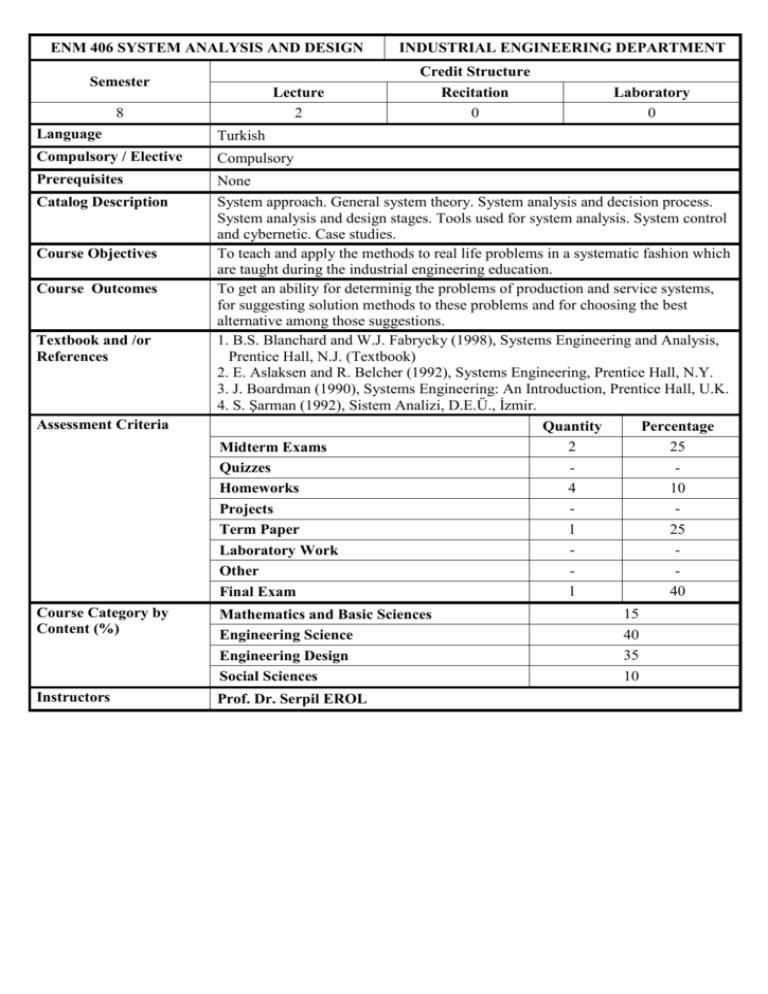
ENM 406 SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Semester Lecture 2 8 INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Credit Structure Recitation 0 Laboratory 0 Language Turkish Compulsory / Elective Compulsory Prerequisites None System approach. General system theory. System analysis and decision process. System analysis and design stages. Tools used for system analysis. System control and cybernetic. Case studies. To teach and apply the methods to real life problems in a systematic fashion which are taught during the industrial engineering education. To get an ability for determinig the problems of production and service systems, for suggesting solution methods to these problems and for choosing the best alternative among those suggestions. 1. B.S. Blanchard and W.J. Fabrycky (1998), Systems Engineering and Analysis, Prentice Hall, N.J. (Textbook) 2. E. Aslaksen and R. Belcher (1992), Systems Engineering, Prentice Hall, N.Y. 3. J. Boardman (1990), Systems Engineering: An Introduction, Prentice Hall, U.K. 4. S. Şarman (1992), Sistem Analizi, D.E.Ü., İzmir. Quantity Percentage 2 25 Midterm Exams Quizzes 4 10 Homeworks Projects 1 25 Term Paper Laboratory Work Other 1 40 Final Exam Catalog Description Course Objectives Course Outcomes Textbook and /or References Assessment Criteria Course Category by Content (%) Mathematics and Basic Sciences Engineering Science Engineering Design Social Sciences Instructors Prof. Dr. Serpil EROL 15 40 35 10 COURSE PLAN Week Topics 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 INTRODUCTION: System approach and other related concepts. GENERAL SYSTEM THEORY AND ITS HISTORY: The general system theory, General system thought, System definition, Classification, Characteristics and their comparison. DECISION MAKING PROCESS AND SYSTEM ANALYSIS: The relationship between system analysis and decision making process, The methods applied during decision process. MODELLING FOR SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND REQUIRED TOOLS: The importance of the modelling for system analysis, Model definition and classification, Tools used for system analysis. STAGES OF SYSTEM ANALYSIS: Stages of system analysis, Models built at these stages and their solution methods, Points to be focussed during system analysis studies. SYSTEM FUNCTIONALITY AND CYBERNETIC: System control, The importance of the control for system functionality, Cybernetic. SYSTEM DESIGN: New system design, Design types, Design stages, Application methods of new system design. MIDTERM EXAM I SYSTEM ANALYSIS CASE STUDIES: Case studies in system analysis. SYSTEM ANALYSIS CASE STUDIES: Case studies in system analysis. SYSTEM ANALYSIS CASE STUDIES: Case studies in system analysis. SYSTEM DESIGN CASE STUDIES: Alternative design applications for an analysed system. SYSTEM DESIGN CASE STUDIES: Choosing the best design for the system among alternative designs. MIDTERM EXAM II RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE COURSE AND DEPARTMENT CURRICULUM Program Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 2 3 An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering X An ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data X An ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs X An ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams X An ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems X An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility X An ability for effective written and oral communication in Turkish and English X The broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a X global and societal context A recognition of the need for, and ability to engage in life-long learning X A knowledge of contemporary issues X An ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for X engineering practice Contribution of the course : 1:None 2:Partially 3:Completely Prepared by : Prof. Dr. Serpil EROL........................................... Date : 13 / 01 / 2003