UNDERSTANDING THE OUTLINE OF A LECTURE
advertisement

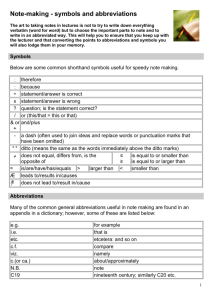
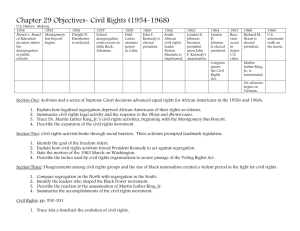
eade LISTENING: SESSION THREE UNIVERSITY LECTURES: Listening and notetaking PART ONE What is a university lecture? What are the objectives of a lecture? What makes lectures difficult to follow? What is the role of a student during a lecture? What additional problems might arise when listening to a lecture that is not in your native language? Lecture Note-Taking Notes provide a record of the lecture content. Effective notes should help you to learn and remember the ideas and facts presented. For each class you will need a different note-taking system. Here are some of the most commonly used methods. I. The Outline: 1) reflects the structure of the lecture. 2) major points farthest to the left. 3) each more specific point to the right. 4) levels of importance will be indicated by distance away from the major point. . Example Extrasensory perception definition: means of perceiving without use of sense organs. three kinds: telepathy: sending messages clairvoyance: forecasting the future psycho-kinesis: perceiving events external to situation current status: no current research to support or refute few psychologists say impossible 1 eade II. The Mapping Method: 1) a graphic representation of the content of a lecture 2) relates each fact or idea to every other fact or idea Example – III. The Charting Method 1) a table with columns and headings 2) info is added in the relevant column Example – Chart format for a history class: Which of these systems do you usually adopt? For which types of lecture? Do you have other methods? 2 eade Note-taking Practice: Omission, abbreviations and symbols When taking notes, we omit many of the unessential words, and use abbreviations and symbols. What parts of speech are usually omitted? Why? What do these abbreviations stand for: e.g i.e. govt asap mos. hr info etc wt ht b/c re esp max yr c What do these symbols mean? & < % w/ > $ ~ @ = x / ° ? The History of Desegregation In the 1950s, school segregation was widely accepted throughout the United States and was a requirement of law in most southern states. In the table below, the text on the left reports how de-segregation came about. It is written in discursive style with full sentences. How are the notes on the right different? What elements have been omitted? What symbols and abbreviations are used? Now you take notes on the rest of the text. Original In 1955 Rosa Parks, a 43 year old black seamstress, was arrested in Montgomery, Alabama, for refusing to give up her bus seat to a white man. Civil Rights leaders, Dr. Martin Luther King, organized the Montgomery Bus Boycott. Eight months later, the Supreme Court ruled, based on the school segregation cases, that bus segregation violated the constitution. Note-form 1955- Rosa Parks, 43, black seamstress, arrested Montgomery AL, b/c refused seat to white man MLK organized Mont Bus Boycott 8 mos >, Supreme Court ruling: school segregation violated constitution In 1957 Little Rock Central High School 1957in Arkansas was to begin desegregation, and black and white students were supposed to attend the same school. On September 3 when nine black students tried to enter the school, they were prevented from doing so by National 3 eade Guardsmen acting on the orders of the Arkansas state governor. On September 20, judge Davies granted an injunction against Governor Faubus and three days later the group of nine students returned to Central High School but were prevented from attending school by a mob of 1,000 townspeople. Finally, President Eisenhower ordered 1,000 paratroopers and 10,000 National Guardsmen to Little Rock, and on September 25, Central High School was desegregated. Imagine you have to give a brief oral summary of the major events leading up to desegregation. Which column would you find most helpful during your summary? Practice: Give a brief oral summary of this text to your partner. Remember to fill in the missing elements as you speak. Then listen to your partner’s summary 4