sat-grasp
advertisement

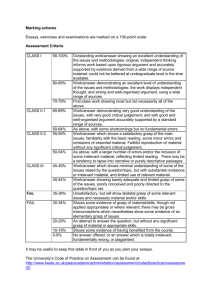
GRASP(1) ======== Joao Marques-Silva <jpms@ecs.soton.ac.uk> NAME ---sat-grasp - CNF satisfiability solver (v2.0) SYNOPSIS -------sat-grasp [ [+|-]D ] [ [+|-]V ] [ +B backtrack-limit ] [ +C conflict-limit ] [ +S database-growth-limit ] [ +T max-runtime ] [ +b backtrack-mode ] [ +d decision-making ] [ +g max-conf-clause-size ] [ +i implicationengine ] [ +m multiple-conflicts ] [ +p preprocess-mode ] [ [+|-]u ] filename DESCRIPTION ----------sat-grasp is a front-end for GRASP (Generic seaRch Algorithm for Satisfiability Problems), which permits reading Conjunctive Normal Form (CNF) formulas in the DIMACS CNF format and allows configuring GRASP. GRASP denotes a configurable algorithm for solving instances of the satisfiability problem (SAT), which implements different techniques for pruning the search space. GRASP can be used as the core search engine for different SAT-based tools or embedded in other application-specific tools. This man page is valid for version 2.0 of GRASP. Among other features, GRASP can realize different Boolean constraint propagation procedures and can implement different forms of dependencydirected backtracking, in both cases exploiting the structure of the problem instance and of the search. If a CNF formula is viewed as a database of clauses, then GRASP solves instances of SAT by adding additional clauses to the clause database in order to prune the amount of search. Different growth rates of the clause database are permitted. In addition, several techniques are used to control how clauses are added to the clause database. Decision making in GRASP is supported by several heuristics, that are chosen with the respective command-line argument. The decision making procedure chosen affects decisively the run times for different instances of SAT. OPTIONS ------------------------------------------------------[+|-]D Run GRASP with (+) and without (-) DEBUG mode (the default). [+|-]V Run GRASP with (+) and without (-) VERBOSE mode (the default). Running with VERBOSE mode provides information on how the search evolves. +B backtrack-limit Defines the maximum number of backtracks that can be used for solving a given instance of SAT. GRASP quits if this number of backtracks is reached. +C conflict-limit Defines the maximum number of conflicts that can be used for solving a given instance of SAT. GRASP quits if this number of conflicts is reached. For non-chronological backtracking option +B should be used, whereas option +C should be used with dynamic backtracking. +T max-runtime Defines the CPU time that can be used for solving a given instance of SAT. GRASP quits if this run time is reached. +S database-growth-limit Identifies a bound on the growth of the clause database. GRASP quits is this bound is reached. +b backtrack-mode Can either be 'C' for chronological backtracking, 'N' for nonchronological backtracking and 'D' for dynamic non-chronological backtracking. With chronological backtracking the size of teh clause database is contant. +d decision-making Choice of decision making procedure. Currently, sat-grasp accepts the following static decision making heuristics: F Fixed order decision making. Initial order of the variables is kept. LCS Prefer variables with the largest combined sum of literals. LIS Prefer variables with the largest individual sum of literals. JW Static implementation of the Jeroslow-Wang heuristic, which gives preference to assignments that simplify the smallest clauses. In addition, sat-grasp accepts the following dynamic decision making heuristics: BOHM Implements Max Bohm's heuristic (from Bohm's technical report). MSMM Customized version of MOM's heuristic (from Freeman's dissertation). MSOS One-sided variation of Jeroslow-Wang heuristic that includes weighted contributions of clauses that can be satisfied. MSTS Two-sided variation of the above heuristic. B2WS Another variation of the above heuristic which gives more weight given to clauses that can be satisfied by a given assignment. DLIS Dynamic LIS (i.e. for each decision assignment apply the LIS heuristic). DLCS Dynamic LCS. Similar to DLIS, but using the LCS heuristic. +g max-conf-clause-size In the presence of conflicts, this option denotes the largest size of identified conflicting clauses. This option guarantees a polynomial growth of the clause database. By default, any clause can be added to the clause database, and so the growth is exponential. +i implication-engine Defines the boolean constraint propagation procedure to apply after each decision assignment is made. By default (or with +i0) Boolean Constraint Propagation (BCP) is used. For the current implementation only the default option is available. +m multiple-conflicts Specifies that multiple conflicts are to be processed each time a conflicting decision assignment is made. This technique allows choos- ing the conflict that prunes the search tree the most. multipleconflicts identifies how multiple conflicts are to analysis options are merged (M) and separate (S). Currently, only merged analysis can be used. +p preprocess-mode Defines the engine to use for preprocessing purposes. [+|-]r Option (=) (the default) allows repacking a conflicting clause in terms of decision assignments whenever the size of that conflicting clause is too large. [+|-]t Option (+) (the default) allows for pruning unnecessary decision assignments. [+|-]u Option (+) (the default) allows the identification of UIPs. UIPs permit discovering structure in implication sequences, which provide stronger pruning conditions. ------------------------------------------------ENVIRONMENT ----------The current implementation of sat-grasp and GRASP does not allow for run time configuration based on environment variables. BUGS ---No oustanding bugs are known as far as the author is aware. In addition, there are no restrictions on the sizes of formulas and/or clauses. Some features provided in version 1.0 have not yet been incorporated in version 2.0. SEE ALSO -------GRASP was developed as the underlying search engine of a software package for the analysis of combinational switching circuits. The primary reference is Joao P. Marques Silva, "Search Algorithms for Satisfiability Problems in Combinational Switching Circuits", Ph. D. Dissertation, EECS Department, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, May 1995. AUTHOR -----Joao Marques-Silva, IST/INESC-ID, Lisbon, Portugal (jpms@inescid.pt). Also, EECS Department, University of Michigan (jpms@eecs.umich.edu). CONTACT ------Joao Marques-Silva, ECS, Univ. Southampton, jpms@ecs.soton.ac.uk