Y4-Y5-Y6 Block A Unit 2
advertisement
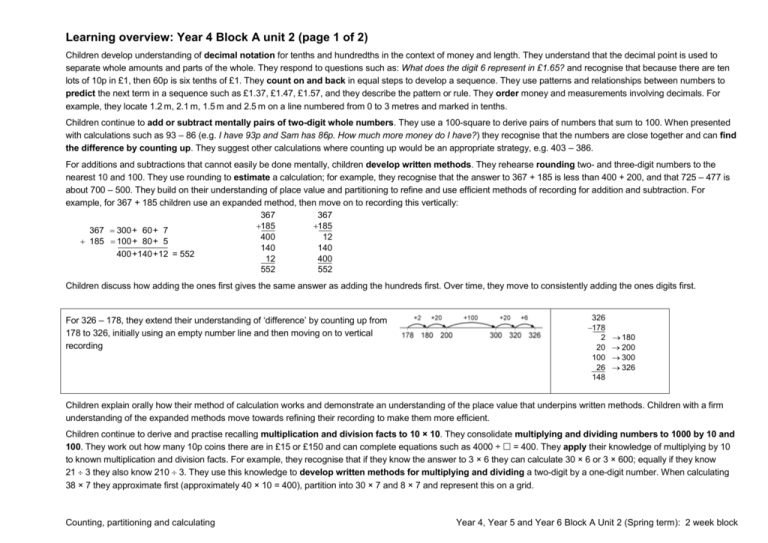
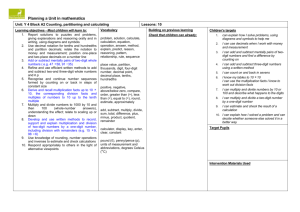
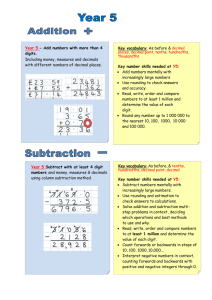
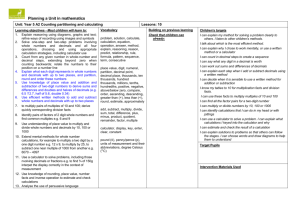
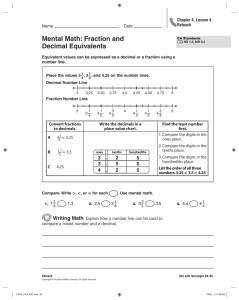
Learning overview: Year 4 Block A unit 2 (page 1 of 2) Children develop understanding of decimal notation for tenths and hundredths in the context of money and length. They understand that the decimal point is used to separate whole amounts and parts of the whole. They respond to questions such as: What does the digit 6 represent in £1.65? and recognise that because there are ten lots of 10p in £1, then 60p is six tenths of £1. They count on and back in equal steps to develop a sequence. They use patterns and relationships between numbers to predict the next term in a sequence such as £1.37, £1.47, £1.57, and they describe the pattern or rule. They order money and measurements involving decimals. For example, they locate 1.2 m, 2.1 m, 1.5 m and 2.5 m on a line numbered from 0 to 3 metres and marked in tenths. Children continue to add or subtract mentally pairs of two-digit whole numbers. They use a 100-square to derive pairs of numbers that sum to 100. When presented with calculations such as 93 – 86 (e.g. I have 93p and Sam has 86p. How much more money do I have?) they recognise that the numbers are close together and can find the difference by counting up. They suggest other calculations where counting up would be an appropriate strategy, e.g. 403 – 386. For additions and subtractions that cannot easily be done mentally, children develop written methods. They rehearse rounding two- and three-digit numbers to the nearest 10 and 100. They use rounding to estimate a calculation; for example, they recognise that the answer to 367 + 185 is less than 400 + 200, and that 725 – 477 is about 700 – 500. They build on their understanding of place value and partitioning to refine and use efficient methods of recording for addition and subtraction. For example, for 367 + 185 children use an expanded method, then move on to recording this vertically: 367 367 185 185 367 300 + 60 + 7 400 12 185 100 + 80 + 5 140 140 400 +140 +12 = 552 12 400 552 552 Children discuss how adding the ones first gives the same answer as adding the hundreds first. Over time, they move to consistently adding the ones digits first. For 326 – 178, they extend their understanding of ‘difference’ by counting up from 178 to 326, initially using an empty number line and then moving on to vertical recording 326 178 2 20 100 26 148 180 200 300 326 Children explain orally how their method of calculation works and demonstrate an understanding of the place value that underpins written methods. Children with a firm understanding of the expanded methods move towards refining their recording to make them more efficient. Children continue to derive and practise recalling multiplication and division facts to 10 × 10. They consolidate multiplying and dividing numbers to 1000 by 10 and 100. They work out how many 10p coins there are in £15 or £150 and can complete equations such as 4000 ÷ = 400. They apply their knowledge of multiplying by 10 to known multiplication and division facts. For example, they recognise that if they know the answer to 3 × 6 they can calculate 30 × 6 or 3 × 600; equally if they know 21 3 they also know 210 3. They use this knowledge to develop written methods for multiplying and dividing a two-digit by a one-digit number. When calculating 38 × 7 they approximate first (approximately 40 × 10 = 400), partition into 30 × 7 and 8 × 7 and represent this on a grid. Counting, partitioning and calculating Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Learning overview: Year 4 Block A unit 2 (page 2 of 2) e.g. 38 × 7 = (30 × 7) + (8 × 7) = 210 + 56 = 266 30 8 7 210 56 266 The number with the most digits is always placed in the left-hand column of the grid so that it is easier to add the partial products. The next step is to move the number being multiplied (38) to an extra row at the top of the grid. Presenting the grid like this helps children to set out and add the partial products 210 and 56. When dividing 64 by 4 children approximate first. They recognise that the answer must lie between 40 ÷ 4 = 10 and 80 ÷ 4 = 20, and use this approximation to do a calculation such as Remainders after division are recorded similarly. 64 4 (40 24) 4 (40 4) (24 4) 10 6 16 The next step is to reduce the method of recording to a column format, but showing the working. Point out the links with the grid method on the left. 64 40 24 24 0 96 7 (70 26) 7 (70 7) (26 7) 10 3 R 5 13 R 5 30 7 210 8 7 56 96 70 26 21 5 (4 10) (4 6) . Answer: 16 (7 10) (7 3) . Answer: 13 R 5 Children use their knowledge of calculations to solve problems and puzzles. Given an equation with missing digits such as 7 + 8 = 1, they find how many different ways they can complete it. They find three consecutive numbers which add up to 39 and then consider what other numbers up to 50 they can make by adding three consecutive numbers. They record the stages in the problem using calculations and/or drawings. They explain what information they selected and why. They evaluate the work of other children and modify their thinking in the light of comments and questions from others. Counting, partitioning and calculating Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Learning overview: Year 5 Block A unit 2 (page 1 of 2) Children secure understanding of the value of each digit in decimals to two places. For example, they use coins (£1, 10p and 1p) or base-10 apparatus (with a ‘flat’ representing one whole) to model the number 2.45, recognising that this number is made up of 2 wholes, 4 tenths and 5 hundredths. They understand the relationship between hundredths, tenths and wholes and use this to answer questions such as: Which of these decimals is equal to 19100? 1.9 10.19 0.19 19.1 How many hundredths are the same as three tenths? Children use images such as bead strings or number lines to help them count in tenths and hundredths from various start numbers. They position decimals on number lines, explaining for example that 2.85 lies halfway between 2.8 and 2.9. They suggest numbers that lie between, say, 13.5 and 13.6. Children create and continue sequences of decimals, e.g. counting up from zero in steps of 0.2 or backwards from 3 in steps of 0.3. They identify the rule for a given sequence and use this to find the next or missing terms, e.g. finding the missing numbers in the sequence: 1.4, , 1.8, 2, 2.2, . They use counting to answer questions such as 0.2 × 6 or 1.8 ÷ 0.3, explaining how they worked out the answer. Children partition decimals using both decimal and fraction notation, for example, recording 6.38 as 6 + 310 + 8100 and as 6 + 0.3 + 0.08. They write a decimal given its parts: e.g. they record the number that is made from 4 wholes, 2 tenths and 7 hundredths as 4.27. They apply their understanding in activities such as: Find the missing number in 17.82 – = 17.22. Play ‘Zap the digit’: In pairs, choose a decimal to enter into a calculator, e.g. 47.25. Take turns to ‘zap’ (remove) a particular digit using subtraction. For example, to ‘zap’ the 2 in 47.25, subtract 0.2 to leave 47.05. Children extend their understanding of multiplying and dividing by 10, 100 or 1000 to decimals. They use digit cards and a place value grid to practise multiplying and dividing numbers by 10, 100 and 1000, e.g. moving each digit two columns to the right to work out that 132 ÷ 100 = 1.32. They recognise that as each digit moves one column to the right, its value becomes 10 times smaller (and the reverse for multiplication). They apply this understanding in a range of activities such as: Find the missing number in 0.42 × = 42. Play ‘Stepping stones’: Work out what operation to enter into a calculator to turn the number in one stepping stone into the number in the next stepping stone. Children extend written methods for addition to include numbers with one and two decimal places. They use their understanding that 10 tenths make one whole and 10 hundredths make one tenth to explain each stage of their calculation, for example, to add 72.8 km and 54.6 km. 72.8 54.6 127.4 8 tenths add 6 tenths makes 14 tenths, or 1 whole and 4 tenths. The 1 whole is ‘carried’ into the units column and the 4 tenths is written in the tenths column. 1 With subtraction of three-digit numbers and decimals, some children may be ready to use more compact methods. The number of steps in the vertical recording of the ‘counting up’ method is reduced. For 326 – 178, they extend their understanding of ‘difference’ by counting up from 178 to 326, initially using an empty number line and then moving on to vertical recording. Counting, partitioning and calculating 326 178 2 20 100 26 148 180 200 300 326 326 178 22 126 148 200 326 4.25 1.83 0.17 2.25 2.42 2.00 4.25 1 Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Learning overview: Year 5 Block A unit 2 (page 2 of 2) The examples below work towards the decomposition method. Example: 563 – 248, adjustment from the tens to the ones, or ‘borrowing ten’ 500 60 3 200 40 8 50 13 500 60 3 200 40 8 300 10 5 5 13 56 3 24 8 315 Discuss how 60 + 3 can be partitioned into 50 + 13. The subtraction of the ones becomes ‘thirteen minus eight’, a known fact. Example: 563 – 271, adjustment from the hundreds to the tens, or ‘borrowing one hundred’ 500 60 3 200 70 1 400 160 500 60 3 200 70 1 200 90 2 4 16 5 63 2 71 2 92 Discuss how 500 + 60 can be partitioned into 400 + 160. The subtraction of the tens becomes ‘160 minus 70’, an application of subtraction of multiples of ten. Children continue to rehearse their recall of multiplication and division facts and use these facts and their knowledge of place value to multiply and divide multiples of 10 and 100. They use jottings to record, support or explain mental multiplication and division of TU by U, forging links to the written methods that they are developing and refining. Example: 38 × 7 :38 × 7 = (30 × 7) + (8 × 7) = 210 + 56 = 266 30 8 7 210 56 266 The number with the most digits is placed in the left-hand column of the grid so that it is easier to add the partial products. The next step is to move the number being multiplied (38) to an extra row at the top of the grid. Presenting the grid like this helps children to set out and add the partial products 210 and 56. 30 7 210 8 7 56 The next step is to represent the method of recording to a column format, but showing the working. Point out the links with the grid method. 38 7 210 56 266 Children should describe what they do by referring to the actual values of the digits in the columns (e.g. the first step in 38 × 7 is ‘thirty multiplied by seven’, not ‘three times seven’, although the relationship to 3 × 7 should be stressed). Children use the multiplication and division facts that they know to find factors of numbers, for example, determining that 35 has a factor pair of 7 and 5, so 350 has a factor pair of 70 and 5 or 7 and 50. They use their knowledge of factors for special cases of multiplication and division calculations. For example, to multiply 15 by 6, they work out 15 × 3 × 2 = 45 × 2 = 90, and to divide 72 by 6 they halve it to get 36, then divide by 3. They find common multiples, investigating questions such as: What is the smallest whole number that is divisible by 5 and by 3? Tell me a number that is both a multiple of 4 and a multiple of 6. Are there any other possibilities? Children solve a range of one- and two-step word problems, choosing whether to use mental, written or calculator methods. They record their method in a clear and logical way, using jottings and diagrams where appropriate. They compare their methods with others, recognising where another method is more efficient than the one that they chose. They solve inverse operation problems such as 3.42 + = 10, and word problems such as: Emma saves £3.50 each week. How much has she saved after 16 weeks? I buy presents costing £9.63, £5.27 and £3.72. How much change do I have from £20? One bag of sugar weighs 2.2 pounds. How much will 10 bags of sugar weigh? Zak saves half of his pocket money each month. In one year he saves £51. How much pocket money does he get each month? Counting, partitioning and calculating Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Learning overview: Year 6 Block A unit 2 Children use decimal notation for tenths, hundredths and thousandths. They partition numbers with up to three decimal places. They state the value of the digit 4 in the number 13.648 and recognise that you add 2 tenths to the number 5.235 to make 5.435. They replace the digit 6 with a 0 by subtracting 0.6 from 13.648 on a calculator. Children count in steps of 0.1, 0.01 and 0.001, e.g. 2.4, 2.41. 2.42, 2.43, …, 2.49, 2.5. They order numbers with up to three decimal places and position them on a number line. For example, they locate 0.111 on this line. Children round decimal numbers to the nearest whole number and to the nearest tenth; for example, they round a set of given lengths to the nearest centimetre or millimetre. They use rounding to estimate the answer to calculations such as 17.15 – 8.9, by using the approximation 17 – 9 = 8. They calculate mentally problems such as: A length of ribbon is 2.4 m long. I need to cut it into three equal pieces. What is the length of each piece? The dimensions of my garden are 6.7 m by 6 m. What is its area? Children find the unknown number in an equation such as 0.215 + = 0.275, using their knowledge of place value and using an inverse operation to check. They explain their reasoning: ‘I compared the two numbers and realised that the difference between them was 6 hundredths, so I added 0.06 to 0.215 to check.’ Before they use a written method to add and subtract decimal numbers, children estimate the answer. For example, they calculate 13.86 + 9.481 or 0.236 – 0.154, and use rounding to check that their answer is approximately 23 or 0.08. 13.86 9.481 23.341 11 1 0.236 0.154 0.046 0.036 0.082 11 0.2 0.236 or 0.236 0.154 0.082 1 Children discuss the efficiency of their written methods. They consider different calculations and choose the appropriate method: an efficient written method, a mental method (with jottings if necessary), or a calculator. They use their calculators to solve ‘missing-number’ problems, using their knowledge of inverse operations: 4.2 = × 7 500 ÷ = 25 × 5.1 = 34.17 What number multiplied by itself gives 400? Children solve multi-step problems, including some with negative numbers or decimals, explaining and evaluating their choices, and approximating first: By midday the temperature rose to 8 °C. By midnight it dropped to –4 °C. What was the temperature difference between midday and midnight? The temperature regained half of its drop (from midday to midnight) by 6:00 am the following morning. What was the temperature at 6:00 am? Two adults and two children go to a cinema. Adult tickets are £5.85 and children’s tickets are £2.85. How much change will they get from a £20 note? Children record stages of solving the problems, explaining clearly the calculations that they have done. They compare and evaluate different methods, discussing the appropriateness and efficiency of their chosen method. Counting, partitioning and calculating Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Counting, partitioning and calculating Year 4 objectives Use decimal notation for tenths and hundredths and partition decimals; relate the notation to money and measurement; position one-place and two-place decimals on a number line I can use decimals when I work with money and measurement Recognise and continue number sequences formed by counting on or back in steps of constant size Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block 1999 links Year 5 objectives Year 4 28 and Year 5 29 Year 4 16 Explain what each digit represents in whole numbers and decimals with up to two places, and partition, round and order these numbers I can say what any digit in a decimal is worth Count from any given number in whole-number and decimal steps, extending beyond zero when counting backwards; relate the numbers to their position on a number line I can count on and back in sevens I can count in decimal steps to create a sequence Refine and use efficient written methods to add and subtract two- and three-digit whole numbers and £.p I can add and subtract three-digit numbers using a written method Add or subtract mentally pairs of two-digit whole numbers (e.g. 47 + 58, 91 – 35) I can add and subtract mentally pairs of two-digit numbers and find a difference by counting on Develop and use written methods to record, support and explain multiplication and division of two-digit numbers by a one-digit number, including division with remainders (e.g. 15 × 9, 98 ÷ 6) I can multiply and divide a two-digit number by a one-digit number Multiply and divide numbers to 1000 by 10 and then 100 (whole-number answers), understanding the effect; relate to scaling up or down Year 4 48, 50 Year 4 40, 42, 44, 46 Year 4 6 Use efficient written methods to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places I can explain each step when I add or subtract decimals using a written method I can decide when it is sensible to use a written method for addition or subtraction Use knowledge of place value and addition and subtraction of two-digit numbers to derive sums and differences and doubles and halves of decimals (e.g. 6.5 ± 2.7, half of 5.6, double 0.34) Derive and recall multiplication facts up to 10 × 10, the corresponding division facts and multiples of numbers to 10 up to the tenth multiple I can identify calculations that I can do in my head or with jottings Use understanding of place value to multiply and divide whole numbers and decimals by 10, 100 or 1000 I can multiply or divide numbers by 10, 100 or 1000 I know my tables to 10 10 I can use the multiplication facts I know to work out division facts Year 4 18 and Year 5 19, 59 Year 5 3, 29 Recall quickly multiplication facts up to 10 × 10 and use them to multiply pairs of multiples of 10 and 100; derive quickly corresponding division facts I know my tables to 10 for multiplication facts and division facts. I can use these facts to multiply multiples of 10 and 100 Identify pairs of factors of two-digit whole numbers and find common multiples (e.g. for 6 and 9) Use decimal notation for tenths, hundredths and thousandths; partition, round and order decimals with up to three places, and position them on the number line I can use decimals with up to three places and order them on a number line. I can round decimals to the nearest whole number or the nearest tenth 1999 links Year 6 13, 29, 31 Year 7 42, 44 Year 5 17 Year 5 49, 51 Use efficient written methods to add and subtract integers and decimals, to multiply and divide integers and decimals by a one-digit integer, and to multiply two-digit and three-digit integers by a two-digit integer I can add, subtract, multiply and divide whole numbers and decimals using efficient written methods Year 6 49, 51, 57, 67, 69 Year 5 39, 45, 47 Extend mental methods for whole-number calculations, for example to multiply a two-digit by a one-digit number (e.g. 12 × 9), to multiply by 25 (e.g. 16 × 25), to subtract one nearmultiple of 1000 from another (e.g. 6070 – 4097) I can multiply and divide numbers by 10 or 100 and describe what happens to the digits Year 6 objectives I can work out sums and differences of decimals Year 4 56,66, 68 1999 links Year 5 41, 43 61, 63, 65 Calculate mentally with integers and decimals: U.t ± U.t, TU × U, TU ÷ U, U.t × U, U.t ÷ U I can add, subtract, multiply and divide whole numbers and decimals in my head Year 6 45, 47, 65 Year 6 7 Year 5 59, 65 Year 5 21 I can use tables facts to work out other facts with decimals Year 5 73 Use knowledge of place value and multiplication facts to 10 × 10 to derive related multiplication and division facts involving decimals (e.g. 0.8 × 7, 4.8 ÷ 6) Year 6 61, 63, 65 I can find all the factor pairs for a two-digit number Use knowledge of rounding, number operations and inverses to estimate and check calculations I can estimate and check the result of a calculation Counting, partitioning and calculating Year 4 72 Use knowledge of rounding, place value, number facts and inverse operations to estimate and check calculations I can estimate and check the result of a calculation Use approximations, inverse operations and tests of divisibility to estimate and check results Year 6 19, 73 I can estimate and check the result of a calculation Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Year 4 linked objectives are located in block A unit 1 Use a calculator to solve problems, including those involving decimals or fractions (e.g. to find 34 of 150 g); interpret the display correctly in the context of measurement Year 5 71 I can use a calculator to solve a problem. I can explain what calculations I keyed into the calculator and why Focus of using and applying Report solutions to puzzles and problems, giving explanations and reasoning orally and in writing, using diagrams and symbols I can explain how I solve problems, using diagrams and symbols to help me Year 4 76 Focus of using and applying Explain reasoning using diagrams, graphs and text; refine ways of recording using images and symbols I can explain my method for solving a problem clearly to others. I listen to other children's methods. I talk about which is the most efficient method Solve one-step and two-step problems involving whole numbers and decimals and all four operations, choosing and using appropriate calculation strategies, including calculator use I can explain why I chose to work mentally, or use a written method or a calculator Year 4 76 Use a calculator to solve problems involving multi-step calculations I can use a calculator to solve problems involving more than one step Focus of using and applying Explain reasoning and conclusions, using words, symbols or diagrams as appropriate I can explain my reasoning and conclusions, using symbols to represent unknown numbers Solve multi-step problems, and problems involving fractions, decimals and percentages; choose and use appropriate calculation strategies at each stage, including calculator use I can solve problems involving more than one step Focus on speaking and listening: Focus on speaking and listening: Focus on speaking and listening: Respond appropriately to others in the light of alternative viewpoints I can explain how I solved a problem and can decide whether someone else solved it in a better way Analyse the use of persuasive language I can explain solutions to problems so that others can follow the stages. I can choose words and draw diagrams to help them to understand Year 6 71 Year 6 77 Year 6 57, 75,83, 85, 87, 89, 101 Participate in a whole-class debate using the conventions and language of debate I can take part in a whole-class debate Year 4 Building on previous learning • add or subtract mentally combinations of one- and two-digit numbers Check that children can already: • derive number pairs that total 100 • identify the calculation needed to solve a word problem • use informal written methods to add and subtract two- and three-digit numbers • explain and record their methods and solutions to problems and calculations • estimate sums and differences of two- or three-digit numbers • read, write, partition and order whole numbers to 1000 • recall multiplication and division facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 10 times-tables • use £.p notation • multiply one- and two-digit numbers by 10 and 100 • understand and use the < and > signs • use informal written methods to multiply and divide two-digit numbers • round two- or three-digit numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 • round remainders up or down, depending on the context • recall addition and subtraction facts for each number to 20 Year 4 vocabulary for this unit Additional Year 5 vocabulary for this unit problem, solution, calculate, calculation, equation, operation, answer, method, explain, predict, reason, formula, term, consecutive reasoning, pattern, relationship, rule, sequence numeral, decimal place, ten thousands, place value, partition, thousands, digit, four-digit number, decimal point, decimal place, tenths, hundredths hundred thousands, millions, positive, negative, integer, thousandths, convert, dividend, add, subtract, multiply, divide, sum, total, difference, plus, minus, product, quotient, remainder above/below zero, compare, order, ascending, divisor, descending, greater than (>), less than (<), calculator, display, key, enter, clear, round, estimate, approximately constant factor, multiple units of measurement and their abbreviations calculator, display, key, enter, clear, constant pound (£), penny/pence (p), units of measurement and abbreviations, degrees Celsius (°C) Counting, partitioning and calculating Additional Year 6 vocabulary for this unit strategy, represent Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Block E unit 3 Counting, partitioning and calculating Block D unit 3 Block C unit 3 Block B unit 3 Use knowledge of rounding, number operations and inverses to estimate and check calculations Develop and use written methods to record, support and explain multiplication and division of two-digit numbers by a one-digit number, including division with remainders (e.g. 15 × 9, 98 ÷ 6) Use a calculator to carry out one-step and two-step calculations involving all four operations; recognise negative numbers in the display, correct mistaken entries and interpret the display correctly in the context of money Block A unit 3 Multiply and divide numbers to 1000 by 10 and then 100 (wholenumber answers), understanding the effect; relate to scaling up or down Identify the doubles of two-digit numbers; use these to calculate doubles of multiples of 10 and 100 and derive the corresponding halves Refine and use efficient written methods to add and subtract two-digit and three-digit whole numbers and £.p Derive and recall multiplication facts up to 10 × 10, the corresponding division facts and multiples of numbers to 10 up to the tenth multiple Block E unit 2 Block D unit 2 Add or subtract mentally pairs of two-digit whole numbers (e.g. 47 + 58, 91 – 35) Block C unit 2 Use decimal notation for tenths and hundredths and partition decimals; relate the notation to money and measurement; position one-place and two-place decimals on a number line Use knowledge of addition and subtraction facts and place value to derive sums and differences of pairs of multiples of 10, 100 or 1000 Block B unit 2 Block A unit 2 Block E unit 1 Recognise and continue number sequences formed by counting on or back in steps of constant size Block D unit 1 Partition, round and order four-digit whole numbers; use positive and negative numbers in context and position them on a number line; state inequalities using the symbols < and > (e.g. –3 > –5, –1 < +1) Block C unit 1 Solve one-step and two-step problems involving numbers, money or measures, including time; choose and carry out appropriate calculations, using calculator methods where appropriate Block B unit 1 Block A unit 1 Year 4 Block A Report solutions to puzzles and problems, giving explanations and reasoning orally and in writing, using diagrams and symbols Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Block E unit 3 Block D unit 3 Block C unit 3 Block B unit 3 Block A unit 3 Block E unit 2 Block D unit 2 Block C unit 2 Block B unit 2 Block A unit 2 Block E unit 1 Block D unit 1 Block C unit 1 Block B unit 1 Block A unit 1 Year 5 Block A Explain reasoning using diagrams, graphs and text; refine ways of recording using images and symbols Solve one-step and two-step problems involving whole numbers and decimals and all four operations, choosing and using appropriate calculation strategies, including calculator use Count from any given number in whole-number and decimal steps, extending beyond zero when counting backwards; relate the numbers to their position on a number line Explain what each digit represents in whole numbers and decimals with up to two places, and partition, round and order these numbers Use knowledge of place value and addition and subtraction of twodigit numbers to derive sums and differences and doubles and halves of decimals (e.g. 6.5 ± 2.7, half of 5.6, double 0.34) Use efficient written methods to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places Recall quickly multiplication facts up to 10 × 10 and use them to multiply pairs of multiples of 10 and 100; derive quickly corresponding division facts Identify pairs of factors of two-digit whole numbers and find common multiples (e.g. for 6 and 9) Use understanding of place value to multiply and divide whole numbers and decimals by 10, 100 or 1000 Extend mental methods for whole-number calculations, for example to multiply a two-digit by a one-digit number (e.g. 12 × 9), to multiply by 25 (e.g. 16 × 25), to subtract one near multiple of 1000 from another (e.g. 6070 – 4097) Use knowledge of rounding, place value, number facts and inverse operations to estimate and check calculations Counting, partitioning and calculating Use a calculator to solve problems, including those involving decimals or fractions (e.g. to find 3¤4 of 150 g); interpret the display correctly in the context of measurement Refine and use efficient written methods to multiply and divide HTU × U, TU × TU, U.t × U and HTU ÷ U Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Block E unit 3 Block D unit 3 Block C unit 3 Block B unit 3 Block A unit 3 Block E unit 2 Block D unit 2 Block C unit 2 Block B unit 2 Calculate mentally with integers and decimals: U.t ± U.t, TU × U, TU ÷ U, U.t × U, U.t ÷ U Block A unit 2 Use knowledge of place value and multiplication facts to 10 × 10 to derive related multiplication and division facts involving decimals (e.g. 0.8 × 7, 4.8 ÷ 6) Block E unit 1 Use decimal notation for tenths, hundredths and thousandths; partition, round and order decimals with up to three places, and position them on the number line Block D unit 1 Solve multi-step problems, and problems involving fractions, decimals and percentages; choose and use appropriate calculation strategies at each stage, including calculator use Find the difference between a positive and a negative integer, or two negative integers, in context Block C unit 1 Block B unit 1 Block A unit 1 Year 6 Block A Explain reasoning and conclusions, using words, symbols or diagrams as appropriate Use efficient written methods to add and subtract integers and decimals, to multiply and divide integers and decimals by a one-digit integer, and to multiply two-digit and three-digit integers by a two-digit integer Use a calculator to solve problems involving multi-step calculations Use approximations, inverse operations and tests of divisibility to estimate and check results Counting, partitioning and calculating Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Week Mental/Oral (rehearse, recall, 1 refine, reason, revisit, read) Objectives Activity Main Activity Objectives Key vocabulary Plenary Direct teaching Key questions Activities - (considering lower, middle & higher achievers) Indicate organisation & support. Resources (incl ICT) Review, reflect. Key questions Mon Tues Wed Thur Fri Assessment & future action Counting, partitioning and calculating Homework Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block Week Mental/Oral (rehearse, recall, 2 refine, reason, revisit, read) Objectives Activity Main Activity Objectives Key vocabulary Plenary Direct teaching Key questions Activities - (considering lower, middle & higher achievers) Indicate organisation & support. Resources (incl ICT) Review, reflect. Key questions Mon Tues Wed Thur Fri Assessment & future action Counting, partitioning and calculating Homework Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6 Block A Unit 2 (Spring term): 2 week block