SPH 4U Physics Grade 12 Course Outline
advertisement
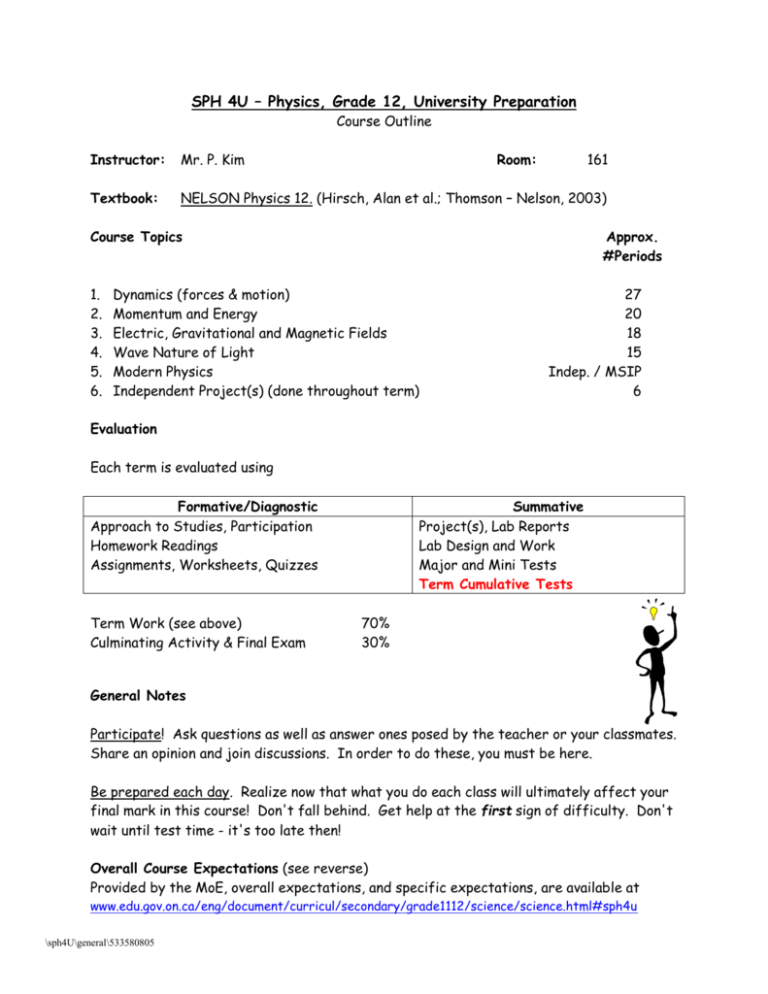
SPH 4U – Physics, Grade 12, University Preparation Course Outline Instructor: Mr. P. Kim Room: 161 Textbook: NELSON Physics 12. (Hirsch, Alan et al.; Thomson – Nelson, 2003) Course Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Approx. #Periods Dynamics (forces & motion) Momentum and Energy Electric, Gravitational and Magnetic Fields Wave Nature of Light Modern Physics Independent Project(s) (done throughout term) 27 20 18 15 Indep. / MSIP 6 Evaluation Each term is evaluated using Formative/Diagnostic Approach to Studies, Participation Homework Readings Assignments, Worksheets, Quizzes Term Work (see above) Culminating Activity & Final Exam Summative Project(s), Lab Reports Lab Design and Work Major and Mini Tests Term Cumulative Tests 70% 30% General Notes Participate! Ask questions as well as answer ones posed by the teacher or your classmates. Share an opinion and join discussions. In order to do these, you must be here. Be prepared each day. Realize now that what you do each class will ultimately affect your final mark in this course! Don't fall behind. Get help at the first sign of difficulty. Don't wait until test time - it's too late then! Overall Course Expectations (see reverse) Provided by the MoE, overall expectations, and specific expectations, are available at www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/document/curricul/secondary/grade1112/science/science.html#sph4u \sph4U\general\533580805 Scientific Investigation & Career Exploration demonstrate scientific investigation skills (related to both inquiry and research) in the four areas of skills (initiating and planning, performing and recording, analysing and interpreting, and communicating); identify and describe careers related to the fields of science under study, and describe the contributions of scientists, including Canadians, to those fields. Forces and Motion analyse technological devices that apply the principles of the dynamics of motion, and assess the technologies’ social and environmental impact; investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, forces involved in uniform circular motion and motion in a plane, and solve related problems; demonstrate an understanding of the forces involved in uniform circular and planar motion Momentum & Energy analyse, and propose ways to improve, technologies or procedures that apply principles related to energy and momentum, and assess the social and environmental impact of these technologies or procedures; investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, through laboratory inquiry or computer simulation, the relationship between the laws of conservation of energy and conservation of momentum, and solve related problems; demonstrate an understanding of work, energy, momentum, and the laws of conservation of energy and conservation of momentum, in one and two dimensions. Electric, Gravitational and Magnetic Fields analyse the operation of technologies that use gravitational, electric, or magnetic fields, and assess the technologies’ social and environmental impact; investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields, and solve related problems; demonstrate an understanding of the concepts, properties, principles, and laws related to gravitational, electric, and magnetic fields and their interactions with matter. Wave Nature of Light analyse technologies that use the wave nature of light, and assess their impact on society and the environment; investigate, in qualitative and quantitative terms, the properties of waves and light, and solve related problems; demonstrate an understanding of the properties of waves and light in relation to diffraction, refraction, interference, and polarization. Modern Physics analyse, with reference to quantum mechanics and relativity, how the introduction of new conceptual models and theories can influence and/or change scientific thought and lead to the development of new technologies; investigate special relativity and quantum mechanics, and solve related problems; demonstrate an understanding of the evidence that supports the basic concepts of quantum mechanics and Einstein’s theory of special relativity. \sph4U\general\533580805