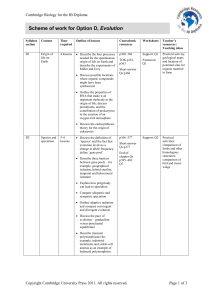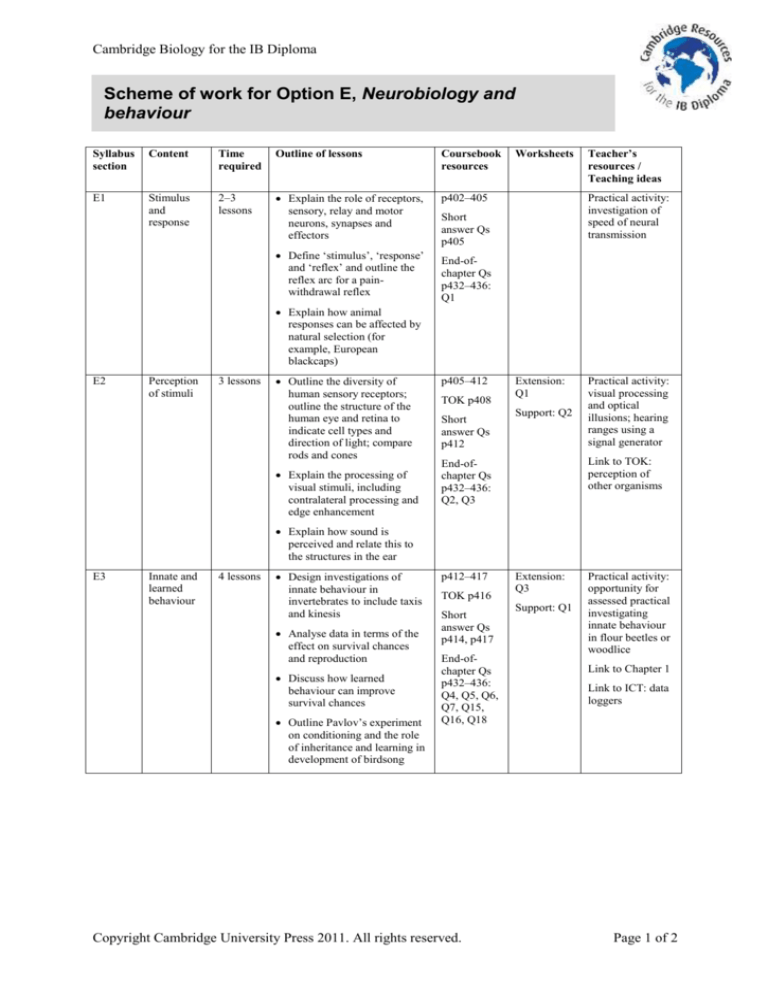
Cambridge Biology for the IB Diploma
Scheme of work for Option E, Neurobiology and
behaviour
Syllabus
section
Content
Time
required
Outline of lessons
Coursebook
resources
E1
Stimulus
and
response
2–3
lessons
Explain the role of receptors,
sensory, relay and motor
neurons, synapses and
effectors
p402–405
Define ‘stimulus’, ‘response’
and ‘reflex’ and outline the
reflex arc for a painwithdrawal reflex
Worksheets
Teacher’s
resources /
Teaching ideas
Practical activity:
investigation of
speed of neural
transmission
Short
answer Qs
p405
End-ofchapter Qs
p432–436:
Q1
Explain how animal
responses can be affected by
natural selection (for
example, European
blackcaps)
E2
Perception
of stimuli
3 lessons
Outline the diversity of
human sensory receptors;
outline the structure of the
human eye and retina to
indicate cell types and
direction of light; compare
rods and cones
Explain the processing of
visual stimuli, including
contralateral processing and
edge enhancement
p405–412
TOK p408
Short
answer Qs
p412
Extension:
Q1
Support: Q2
Practical activity:
visual processing
and optical
illusions; hearing
ranges using a
signal generator
Link to TOK:
perception of
other organisms
End-ofchapter Qs
p432–436:
Q2, Q3
Explain how sound is
perceived and relate this to
the structures in the ear
E3
Innate and
learned
behaviour
4 lessons
Design investigations of
innate behaviour in
invertebrates to include taxis
and kinesis
Analyse data in terms of the
effect on survival chances
and reproduction
Discuss how learned
behaviour can improve
survival chances
Outline Pavlov’s experiment
on conditioning and the role
of inheritance and learning in
development of birdsong
p412–417
TOK p416
Short
answer Qs
p414, p417
End-ofchapter Qs
p432–436:
Q4, Q5, Q6,
Q7, Q15,
Q16, Q18
Copyright Cambridge University Press 2011. All rights reserved.
Extension:
Q3
Support: Q1
Practical activity:
opportunity for
assessed practical
investigating
innate behaviour
in flour beetles or
woodlice
Link to Chapter 1
Link to ICT: data
loggers
Page 1 of 2
Cambridge Biology for the IB Diploma
E4
Neurotransmitters
and
synapses
4–5
lessons
Explain how decision making
in the CNS results from the
interaction of excitatory and
inhibitory synapses
Explain how psychoactive
drugs increase or decrease
postsynaptic transmission
and affect the brain and
personality; give three
examples of excitatory and
inhibitory drugs
p418–422
Support: Q3
Short
answer Qs
p422
End-ofchapter Qs
p432–436:
Q8, Q9, Q10
Practical activity:
personal research
project on the
mode of action of
psychoactive
substances
Link to Aspects of
internationalism:
drug use and
misuse
Explain the effects of THC
and cocaine at synapses,
including the effects on mood
and behaviour
Discuss the causes of
addiction including genetic
and social factors, and
dopamine secretion
E5 (HL)
The human
brain
4 lessons
Identify the parts of the brain
and their functions; explain
how experiments, lesions and
FMRI have been used in
identifying functions of
specific parts of the brain
Explain sympathetic and
parasympathetic control of
the heart, the iris and blood
flow to the gut
p422–427
Short
answer Qs
p427
Extension:
Q2
Link to TOK:
brain death and its
definition
End-ofchapter Qs
p432–436:
Q11, Q12,
Q13
Explain the pupil reflex and
how it is used in determining
‘brain death’
Outline how pain is
perceived and how
endorphins act as painkillers
E6 (HL)
Further
studies of
behaviour
3 lessons
Describe the organisation of
the honey bee colony and that
of one other social animal;
outline how natural selection
may act in social organisms
p428–432
Discuss the evolution of
altruistic behaviour
End-ofchapter Qs
p432–436:
Q14, Q17
Outline the foraging
behaviour of the bluegill fish
and one other example of
optimization of food intake
Short
answer Qs
p432
Practical activity:
video footage of
altruism in
animals
Link to ICT:
social lives of
bees
Explain how mate selection
can lead to exaggerated traits;
outline two examples of the
value of rhythmic behaviour
patterns
Note: 1 lesson = approximately 40 minutes
Copyright Cambridge University Press 2011. All rights reserved.
Page 2 of 2