Microscopy: History, Usage, and Utility
advertisement

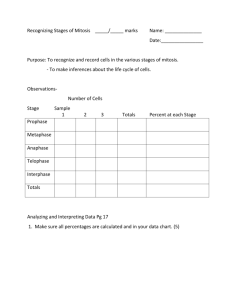
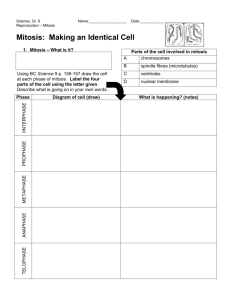
Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis Mitosis and Apoptosis in Metazoan Development Readings: Human Biology, pp. 364-367 & 385-389 Reserve: Cell Suicide in Health and Disease, Scientific American, Dec. 1996. 1. Introduction A. B. C. Animal Types i. Protozoa ii. Metazoa Metazoan Organization i. Cells ii. Tissues iv. Organs v. Organ Systems vi. Organism Metazoan Developmental Process i. Fertilization Zygote ii. Zygote Embryo iii. Embryonic Development a. Processes required for Development to Occur Process Developmental Stage Cleavage Morula Morphogenesis Blastula Differentiation Gasturla Growth Size Increase Page 1 Neurula Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis 2. Introduction to the Cell Cycle A. B. C. Functions of Cell Division • Growth • Replace Tissues • Wound Healing • Fight Infection • Maintain Surface to Volume Ratio Terms i. Chromatin ii. Diploid Number – 46 iii. Haploid Number - 23 DNA Forms i. Chromatin ii. Chromosomes a. Unduplicated b. Duplicated • Sister Chromatids • Centromere • Centrioles in Centrosomes Page 2 Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis 3. Stages of the Cell Cycle A. Interphase Page 3 Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis B. Interphase Stages i. G1 ii. S iii. G2 iv. a. Chromosomes condense b. Nuclear Envelope Disappears c. Spindle Forms Cells that do not Divide a. C. Cell Division i. ii. 4. G0 Mitosis Cytokinesis Mitosis (nuclear division – not cell division) and Cytokinesis Page 4 Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis A. Prophase i. Early Prophase • • • ii. Late Prophase • • C. D. Centrioles Migrate Nuclear Envelope Fragments Chromosomes Visible Spindle Forms between the moving centrosomes Centromeres attach to spindle fibers Metaphase i. Early Metaphase ii. Late Metaphase Anaphase Page 5 Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis • E. Cytokinesis Begins Telophase i. Spindle Disappears ii. New Nuclear Envelopes Forms iii. Chromatin Forms Again. iv. Cytokinesis Continues • 5. Cleavage Furrow Mitotic Control A. Why is Control Important Page 6 Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis • B. 6. Non-random * Uncontrolled Mitosis * Too Little Mitosis Means of Control i. Crowding ii. Hormones iii. Growth Factors Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) A. Compare and Contrast Necrosis and Apoptosis i. Necrosis a. b. ii. Causes • Mechanical Injury • Ischemia • Toxic Chemical Exposure Results • Swelling of Cells • Cell Rupture • Inflammation Apoptosis (Programmed Cell Death) a. Characteristics Page 7 Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis B. • Genetically Controlled Process • Neat and Tidy Process • Inflammation Never Occurs • Cells Play an Active Role in Their Death Initiation of Apoptosis i. For Proper Development a. Tadpole Development Page 8 Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis ii. iii. C. b. Human Hand Development c. At the Start of Menstruation d. Immunological Development e. Nervous System Development Removal of Damaged Cells a. Prevent Cancer Development b. Prevent Developmental Birth Defects Removal of virally Infected Cells Characteristics of the Apoptotic Process i. Shrinkage of Cell ii. Activation of Caspase Cascade of Reactions a. D. Caspases iii. Bleb Production iv. Phagocytosis Initiation of Apoptosis i. Intrinsic Factors a. Causes • Increased Levels of Toxins and/or Oxidants • Damaged DNA (that can not be repaired) Page 9 Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis ii. Extrinsic Factors a. E. When Apoptosis Fails to Work i. ii. 7. “Death Receptors” Apoptosis and Viral Infections a. Human Papaloma Virus Cervical Cancer b. Epstein-Barr Virus Mononucleosis Lyphomas Apoptosis and Cancers a. Some Leukemia b. Melanoma (Skin Cancer [worst]) Conclusion – Mitosis and Apoptosis are equally important for proper human development and maintenance. And precise homeostatic controls govern both processes. An upset in either one may result in a state of disease and death. A. Balance Page 10 Human Biology Student Outline – Mitosis and Apoptosis B. Development C. Maintenance of Health Page 11