Document
advertisement

General WH questions
1.What is a Data Warehousing?
Data Warehouse is a repository of integrated information, available for queries and analysis.
Data and information are extracted from heterogeneous sources as they are generated....This
makes it much easier and more efficient to run queries over data that originally came from
different sources.
Typical relational databases are designed for on-line transactional processing (OLTP) and do
not meet the requirements for effective on-line analytical processing (OLAP). As a result, data
warehouses are designed differently than traditional relational databases.
2.What are Data Marts
Data Mart is a segment of a data warehouse that can provide data for reporting and analysis
on a section, unit, department or operation in the company, e.g. sales, payroll, production.
ER diagram is a entity relantionship diagram that provides the entities along with attributes.
Data Marts are designed to help manager make strategic decisions about their business. Data
Marts are subset of the corporate-wide data that is of value to a specific group of users.
There are two types of Data Marts:
1.Independent data marts – sources from data captured form OLTP system, external
providers or from data generated locally within a particular department or geographic area.
2.Dependent data mart – sources directly form enterprise data warehouses.
3.What is ER Diagram
ER - Stands for entitity relationship diagrams. It is the first step in the design of data model
which will later lead to a physical database design of possible a OLTP or OLAP database
4. What is a Star Schema
A relational database schema organized around a central table (fact table) joined to a few
smaller tables (dimension tables) using foreign key references. The fact table contains raw
numeric items that represent relevant business facts (price, discount values, number of units
sold, dollar value, etc.)
5.What is Dimensional Modelling
It's a process or technique of designing a database model.
In Dimensional Modeling, Data is stored in two kinds of tables: Fact Tables and Dimension
tables.
Fact Table contains fact data e.g. sales, revenue, profit etc.....
Dimension table contains dimensional data such as Product Id, product name, product
description etc.....
Dimensional Modelling is a design concept used by many data warehouse desginers to build
thier datawarehouse. In this design model all the data is stored in two types of tables - Facts
table and Dimension table. Fact table contains the facts/measurements of the business and
the dimension table contains the context of measuremnets ie, the dimensions on which the
facts are calculated.
6. What Snow Flake Schema
Snowflake schemas normalize dimensions to eliminate redundancy. That is, the dimension
data has been grouped into multiple tables instead of one large table. For example, a product
dimension table in a star schema might be normalized into a products table, a
product_category table, and a product_manufacturer table in a snowflake schema. While this
saves space, it increases the number of dimension tables and requires more foreign key joins.
The result is more complex queries and reduced query performance.
Snowflake Schema, each dimension has a primary dimension table, to which one or more
additional dimensions can join. The primary dimension table is the only table that can join to
the fact table.
1
General WH questions
7. What are the Different methods of loading Dimension tables
Conventional Load:
Before loading the data, all the Table constraints will be checked against the data.
Direct load:(Faster Loading)
All the Constraints will be disabled. Data will be loaded directly.Later the data will be checked
against the table constraints and the bad data won't be indexed.
8.What are Aggregate tables
These are the tables which contain aggregated / summarized data. E.g Yearly, monthly sales
information. These tables will be used to reduce the query execution time.
Aggregate tables contain redundant data that is summarized from other data in the warehouse
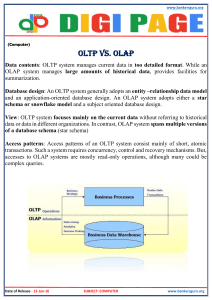
9.What is the Difference between OLTP and OLAP
Main Differences between OLTP and OLAP are:1. User and System Orientation
OLTP: customer-oriented, used for data analysis and querying by clerks, clients and IT
professionals.
OLAP: market-oriented, used for data analysis by knowledge workers( managers, executives,
analysis).
2. Data Contents
OLTP: manages current data, very detail-oriented.
OLAP: manages large amounts of historical data, provides facilities for summarization and
aggregation, stores information at different levels of granularity to support decision making
process.
3. Database Design
OLTP: adopts an entity relationship(ER) model and an application-oriented database design.
OLAP: adopts star, snowflake or fact constellation model and a subject-oriented database
design.
4. View
OLTP: focuses on the current data within an enterprise or department.
OLAP: spans multiple versions of a database schema due to the evolutionary process of an
organization; integrates information from many organizational locations and data stores
OLTP
Current data
Short database transactions
Online update/insert/delete
Normalization is promoted
High volume transactions
Transaction recovery is necessary
OLAP
Current and historical data
Long database transactions
Batch update/insert/delete
Denormalization is promoted
Low volume transactions
Transaction recovery is not necessary
10. What is ETL
ETL stands for extraction, transformation and loading.
ETL provide developers with an interface for designing source-to-target mappings,
ransformation and job control parameter.
· Extraction
Take data from an external source and move it to the warehouse pre-processor database.
· Transformation
Transform data task allows point-to-point generating, modifying and transforming data.
· Loading
Load data task adds records to a database table in a warehouse.
11. What are the vaious ETL tools in the Market
Informatica Datastage AbInitio
12. What are the various Reporting tools in the Market
2
General WH questions
Cognos BusinessObjects MicroStrategies Actuate
13.What is Fact table
A table in a data warehouse whose entries describe data in a fact table. Dimension tables
contain the data from which dimensions are created.
A fact table in dataware house is it describes the transaction data.It contains characterstics
and keyfigures.
A Fact table is a collection of facts and foriegn key relations to the dimensions.
14. What is a dimension table
Answer posted by Riaz Ahmad on 2005-06-09 14:45:26: A dimensional table is a collection of
hierarchies and categories along which the user can drill down and drill up. it contains only the
textual attributes.
A dimesion table in datawarehouse is one which contains primary key and attributes.we called
primary key as DIMID's or SKIDs
15. What is a lookup table
A lookup table is nothing but a 'lookup' it give values to referenced table (it is a reference), it
is used at the run time, it saves joins and space in terms of transformations. Example, a
lookup table called states, provide actual state name ('Texas')
when we want to get related value from some other table based on particular value... suppose
in one table A we have two columns emp_id,name and in other table B we have emp_id
adress in target table we want to have mp_id,name,address we will take source as table A and
look up table as B by matching EMp_id we will get the result as three
columns...emp_id,name,address When a value for the column in the target table is looked up
from another table apart from the source tables, that table is called the lookup table.
16. What is a general purpose scheduling tool
The basic purpose of the scheduling tool in a DW Application is to stream line the flow of data
from Source To Target at specific time or based on some condition.
17. What are modeling tools available in the Market
Modeling Tool Vendor
ERWin Computer Associates
ER/Studio Embarcadero
Power Designer Sybase
Oracle Designer Oracle
18. What is real time data-warehousing
Real-time data warehousing is a combination of two things: 1) real-time activity and 2) data
warehousing. Real-time activity is activity that is happening right now. The activity could be
anything such as the sale of widgets. Once the activity is complete, there is data about it.
Data warehousing captures business activity data. Real-time data warehousing captures
business activity data as it occurs. As soon as the business activity is complete and there is
data about it, the completed activity data flows into the data warehouse and becomes
available instantly. In other words, real-time data warehousing is a framework for deriving
information from data as the data becomes available.
A real time data warehouse provide live data for DSS (may not be 100% up to that moment,
some latency will be there). Data warehouse have access to the OLTP sources, data is loaded
from the source to the target not daily or weekly, but may be every 10 minutes through
replication or logshipping or something like that. SAP BW is providing real time DW, with the
help of extended starschma, source data is shared.
19. What is data mining
Data mining is a process of extracting hidden trends within a datawarehouse. For example an
insurance dataware house can be used to mine data for the most high risk people to insure in
a certain geographial area.
In its simple definition you can say data mining is a way to discover new meaning in data.
20. What is Normalization, First Normal Form, Second Normal Form , Third Normal Form
3
General WH questions
Normalization : The process of decomposing tables to eliminate data redundancy is called
Normalization.
1N.F:- The table should caontain scalar or atomic values.
2 N.F:- Table should be in 1N.F + No partial functional dependencies
3 N.F :-Table should be in 2 N.F + No transitive dependencies
2NF - table should be in 1NF + non-key should not dependent on subset of the key ({part,
supplier}, sup address)
3NF - table should be in 2NF + non key should not dependent on another non-key ({part},
warehouse name, warehouse addr)
{primary key}
more...
4,5 NF - for multi-valued dependencies (essentially to describe many-to-many relations)
21. What is ODS
An Operational Data Store presents a consistent picture of the current data stored and
managed by transaction processing system. As data is modified in the source system, a copy
of the changed data is moved into the ODS. Existing data in the ODS is updated
A collection of operation or bases data that is extracted from operation databases and
standardized, cleansed, consolidated, transformed, and loaded into an enterprise data
architecture. An ODS is used to support data mining of operational data, or as the store for
base data that is summarized for a data warehouse. The ODS may also be used to audit the
data warehouse to assure summarized and derived data is calculated properly. The ODS may
further become the enterprise shared operational database, allowing operational systems that
are being reengineered to use the ODS as there operation databases.
22What type of Indexing mechanism do we need to use for a typical datawarehouse
On the fact table it is best to use bitmap indexes. Dimension tables can use bitmap and/or
the other types of clustered/non-clustered, unique/non-unique indexes.
To my knowledge, SQLServer does not support bitmap indexes. Only Oracle supports
bitmaps.
23.Which columns go to the fact table and which columns go the dimension table
The Aggreation or calculated value colums will go to Fac Tablw and details information will go
to diamensional table.
To add on, Foreign key elements along with Business Measures, such as Sales in $ amt, Date
may be a business measure in some case, units (qty sold) may be a business measure, are
stored in the fact table. It also depends on the granularity at which the data is stored.
24. What is a level of Granularity of a fact table
Level of granularity means level of detail that you put into the fact table in a data warehouse.
For example: Based on design you can decide to put the sales data in each transaction. Now,
level of granularity would mean what detail are you willing to put for each transactional fact.
Product sales with respect to each minute or you want to aggregate it upto minute and put
that data.
It also means that we can have (for example) data agregated for a year for a given product
as well as the data can be drilled down to Monthly, weekl and daily basis...teh lowest level is
known as the grain. going down to detail s is Granularity
25. What does level of Granularity of a fact table signify
In simple terms, level of granularity defines the extent of detail. As an example, let us look at
geographical level of granularity. We may analyze data at the levels of COUNTRY, REGION,
TERRITORY, CITY and STREET. In this case, we say the highest level
26.How are the Dimension tables designed
Find where data for this dimension are located. Figure out how to extract this
data. Determine how to maintain changes to this dimension (see more on this in the next
section). Change fact table and DW population routine
Most dimension tables are designed using Normalization principles upto 2NF. In some
instances they are further normalized to 3NF.
4
General WH questions
27. What are slowly changing dimensions
Dimensions that change over time are called Slowly Changing Dimensions. For instance, a
product price changes over time; People change their names for some reason; Country and
State names may change over time. These are a few examples of Slowly Changing Dimensions
since some changes are happening to them over a period of time
28. What are non-additive facts
fact table typically has two types of columns: those that contain numeric facts (often called
measurements), and those that are foreign keys to dimension tables. A fact table contains
either detail-level facts or facts that have been aggregated.
29. What are conformed dimensions
Conformed dimentions are dimensions which are common to the cubes.(cubes are the
schemas contains facts and dimension tables) Consider Cube-1 contains F1,D1,D2,D3 and
Cube-2 contains F2,D1,D2,D4 are the Facts and Dimensions here D1,D2
Conformed dimensions mean the exact same thing with every possible fact table to which they
are joined
Ex:Date Dimensions is connected all facts like Sales facts,Inventory facts..etc
30.What is VLDB
VLDB stands for Very Large DataBase.
It is an environment or storage space managed by a relational database management system
(RDBMS) consisting of vast quantities of information.
The perception of what constitutes a VLDB continues to grow. A one terabyte database would
normally be considered to be a VLDB.
31. What is SCD1 , SCD2 , SCD3
SCD Stands for Slowly changing dimensions.
SCD1: only maintained updated values.
Ex: a customer address modified we update existing record with new address.
SCD2: maintaining historical information and current information by using
A) Effective Date
B) Versions
C) Flags or combination of these
SCD3: by adding new columns to target table we maintain historical information and current
information.
32.What are Semi-additive and factless facts and in which scenario will you use such kinds of
fact tables
Semi-Additive: Semi-additive facts are facts that can be summed up for some of the
dimensions in the fact table, but not the others. For example:
Current_Balance and Profit_Margin are the facts. Current_Balance is a semi-additive fact, as it
makes sense to add them up for all accounts (what's the total current balance for all accounts
in the bank?), but it does not make sense to add them up through time (adding up all current
balances for a given account for each day of the month does not give us any useful
information
Snapshot facts are semi-additive, while we maintain aggregated facts we go for semi-additive.
EX: Average daily balance
A fact table without numeric fact columns is called factless fact table.
Ex: Promotion Facts
While maintain the promotion values of the transaction (ex: product samples) because this
table doesn’t contain any measures.
33. What are conformed dimensions
A conformed dimension is a single, coherent view of the same piece of data throughout the
organization. The same dimension is used in all subsequent star schemas defined. This
enables reporting across the complete data warehouse in a simple format
34.Differences between star and snowflake schemas
5
General WH questions
Star schema - all dimensions will be linked directly with a fat table.
Snow schema - dimensions maybe interlinked or may have one-to-many relationship with
other tables.
The star schema is created when all the dimension tables directly link to the fact table. Since
the graphical representation resembles a star it is called a star schema.
It must be noted that the foreign keys in the fact table link to the primary key of the
dimension table. This sample provides the star schema for a sales_ fact for the year 1998. The
dimensions created are Store, Customer, Product_class and time_by_day. The Product table
links to the product_class table through the primary key and indirectly to the fact table. The
fact table contains foreign keys that link to the dimension tables.
The snowflake schema is a schema in which the fact table is indirectly linked to a number of
dimension tables. The dimension tables are normalized to remove redundant data and
partitioned into a number of dimension tables for ease of maintenance. An example of the
snowflake schema is the splitting of the Product dimension into the product_category
dimension and product_manufacturer dimension..
35. How do you load the time dimension
Every Datawarehouse maintains a time dimension. It would be at the most granular level at
which the business runs at (ex: week day, day of the month and so on). Depending on the
data loads, these time dimensions are updated. Weekly process gets updated every week and
monthly process, every month.
36. Why are OLTP database designs not generally a good idea for a Data Warehouse
OLTP cannot store historical information about the organization. It is used for storing the
details of daily transactions while a datawarehouse is a huge storage of historical information
obtained from different datamarts for making intelligent decisions about the organization.
37.Why should you put your data warehouse on a different system than your OLTP system
An DW is typically used most often for intensive querying . Since the primary responsibility of
an OLTP system is to faithfully record on going transactions (inserts/updates/deletes), these
operations will be considerably slowed down by the heavy querying that the DW is subjected
to.
OLTP system stands for on-line transaction processing.
These are used to store only daily transactions as the changes have to be made in as few
places as possible. OLTP do not have historical data of the organization
Datawarehouse will contain the historical information about the organization
OLTP system is basically " data oriented " (ER model) and not " Subject oriented
"(Dimensional Model) .That is why we design a separate system that will have a subject
oriented OLAP system...
Moreover if a complex querry is fired on a OLTP system will cause a heavy overhead on the
OLTP server that will affect the daytoday business directly.
38. Explain the advanatages of RAID 1, 1/0, and 5. What type of RAID setup would you put
your TX logs
Raid 0 - Make several physical hard drives look like one hard drive. No redundancy but very
fast. May use for temporary spaces where loss of the files will not result in loss of committed
data.
Raid 1- Mirroring. Each hard drive in the drive array has a twin. Each twin has an exact copy
of the other twins data so if one hard drive fails, the other is used to pull the data. Raid 1 is
half the speed of Raid 0 and the read and write performance are good.
Raid 1/0 - Striped Raid 0, then mirrored Raid 1. Similar to Raid 1. Sometimes faster than
Raid 1. Depends on vendor implementation.
Raid 5 - Great for readonly systems. Write performance is 1/3rd that of Raid 1 but Read is same as Raid 1.
Raid 5 is great for DW but not good for OLTP.
Hard drives are cheap now so I always recommend Raid 1.
6
General WH questions
39. Is it correct/feasible develop a Data Mart using an ODS?
the ODS is technically designed to be used as the feeder for the DW and other DM's -- yes. It
is to be the source of truth.
40. Difference between Snow flake and Star Schema. What are situations where Snow flake
Schema is better than Star Schema to use and when the opposite is true?
star schema and snowflake both serve the purpose of dimensional modeling when it come to
datawarehouses.
star schema is a dimensional model with a fact table ( large) and a set of dimension tables (
small) . the whole set-up is totally denormalized.
however in cases where the dimension table are split to many table that is where the schema
is slighly inclined towards normalization ( reduce redundancy and dependency) there comes
the snow flake schema.
the nature/purpose of the data that is to be feed to the model is the key to your question as to
which is better.
41. What is the main differnce between schema in RDBMS and schemas in DataWarehouse....?
RDBMS Schema
*
*
*
*
*
*
Used for OLTP systems
Traditional and old schema
Normalized
Difficult to understand and navigate
Cannot solve extract and complex problems
Poorly modelled
DWH Schema
*
*
*
*
*
*
Used for OLAP systems
New generation schema
De Normalized
Easy to understand and navigate
Extract and complex problems can be easily solved
Very good model
42. What is degenerate dimension table?
the values of dimension which is stored in fact table is called degenerate dimensions. these
dimensions doesn,t have its own dimensions.
43. What are the possible data marts in Retail sales.?
1. Online Analytical Processing
Online Analytical Processing A tool to evaluate and analyze the data in the data warehouse
using analytical queries. A tool which helps organize data in the data warehouse using
multidimensional models of data aggregation and summarization. Supports the
2. What is the difference between Data Warehouse and Online Analytical Processing
Ralph Kimball the co-founder of the data warehousing concept has defined the data warehouse
as a “"a copy of transaction data specifically structured for query and analysis”. Both
definitions highlight specific features of the data warehouse. The former
3. Compare Data Warehouse database and OLTP database
The data warehouse and the OLTP data base are both relational databases. However, the
objectives of both these databases are different. The OLTP database records transactions in
real time and aims to automate clerical data entry processes of a business
4. How to enable security in cognos connection in cognos report net
You can imlement security via your Windows NT system accounts, LDAP accounts for Cognos
connection. To do this configure the desired Security section in the Cognos Configuration.
7