Atomic Worksheet
advertisement

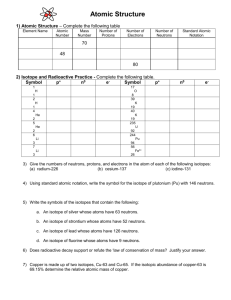
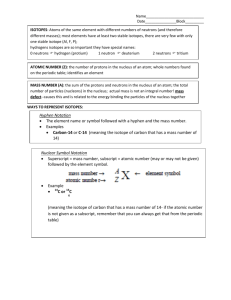
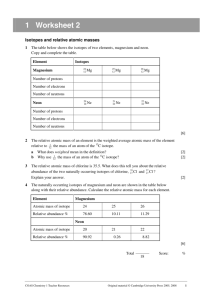
Atomic Worksheet Name _______________________ 1. Write the symbol or name for each of the following elements, as appropriate. ___________a. gold ___________e. Mn ___________i. lead ___________b. Hg ___________f. Zn ___________j. Co ___________c. uranium ___________g. fluorine ___________k. nitrogen ___________d. sodium ___________h. Fe 2. List the atomic number, the average mass number, and the mass number of the most common isotope for each of the following elements. Atomic Most common isotope Element Average Mass Number mass number Li ____________ ____________ ____________ N ____________ ____________ ____________ Al ____________ ____________ ____________ Ti ____________ ____________ ____________ Os ____________ ____________ ____________ 3. Determine the number of protons, neutrons & electrons in each of the following isotopes: Be – 10, As – 73, Kr – 85, and the most common isotopes of Mg, Al, La. Isotope Be – 10 As – 73 Kr – 85 Mg Al La Protons Neutrons Electrons 4. Complete the table by filling in the empty boxes. Element Calcium (Ca) Nickel (Ni) Gold (Au) Atomic Number 79 6 Number of Protons 20 28 Number of Neutrons 20 Mass Number 59 118 14 Isotope Symbol 5. Assume that an element found in nature has two isotopes: 40% is an isotope with mass number 35, and 60% is an isotope with mass number 37. What would be the average mass of the element? 6. Draw energy level diagrams for neutral atoms of C-14 and Ca-41.(see example of Si-30 below) 14 P 16 N 2 e- 4 e- 8e Si-30 7. Indicate which element in each set is not in the same group or period as the others. (Hint: “One of these things is not like the others, one of these things just doesn’t belong…”) a. hydrogen, calcium, sodium, cesium b. calcium, barium, magnesium, vanadium c. sulfur, phosphorus, nitrogen, arsenic d. uranium, neon, xenon, helium e. Cl, Al, Tl, Na, Ar 8. Use the periodic table to decide which element in each of the following pairs is more active. a. potassium or sodium b. oxygen or sulfur c. chlorine or iodine d. magnesium or calcium 9. Dmitri Mendeleev (1834 – 1907) was a Russian chemist that is credited with the modern periodic table. He arranged the elements in order of increasing Average Atomic Mass, not by Atomic Number. Mendeleev’s table as he derived it did not work for three pairs of elements. He assumed their atomic masses were incorrect. Which pairs are reversed in Mendeleev’s original table (don’t go past element 56)?