System of Checks and Balances
advertisement

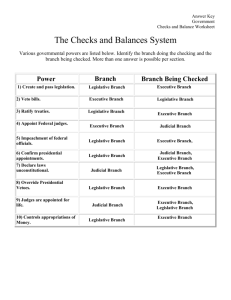
System of Checks and Balances In the system of checks and balances the powers of an individual branch also serve as a check (a way to guarantee a balance of power) on another of the three branches. Executive Branch President carries out the laws Legislative Branch (consisting of the House of Representatives and the Senate) makes the laws Judicial Branch (made up of the Supreme Court, Lower Courts, Special Courts) interprets the laws Checks on the legislative Can propose laws Can veto laws Can call special sessions of Congress Makes federal appointments Negotiates foreign treaties Checks on the Executive Can override Presidents veto Confirms appointments made by President Ratifies treaties Appropriate money(for Federal projects) Can impeach or remove President Checks on the Executive Can declare the President’s actions unconstitutional Checks on the Judicial Appoints federal judges Can grant pardons to Federal offenders Checks on the Judicial Creates lower federal Courts Can impeach or remove judges Can propose amendments to overrule judicial decisions Approves appointments of federal judges Checks on the Legislative Can declare acts of Congress unconstitutional The Checks and Balances System: A Worksheet Various governmental powers are listed below. Identify the branch doing the checking and the branch being checked. More than one answer is possible per section. Power Which Branch Has The Power? Which Branch's Power is Being Checked? (Could be more than one) 1) Create and pass legislation. 2) Veto bills. 3) Ratify treaties. 4) Appoint Federal judges. 5) Impeachment of federal officials. 6) Confirm the appointment of presidential appointments. 7) Declare laws unconstitutional. 8) Override Presidential Vetoes. 9) Judges are appointed for life. 10) Controls appropriations of money.