Name

Name __________________________________ Date _______________ Period __________
Partner’s Name _____________________________________
Title: Introductory Histology Lab
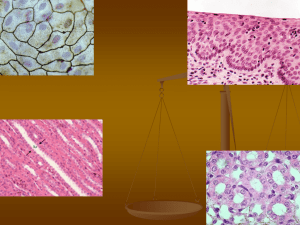
Purpose: To become familiar with the structure and function of the four major types of animal tissues.
Background: Tissues are groups of specialized cells that work together for a particular function. In humans, combinations of different types of tissues make up organs, and groups of organs work together to form organ systems. For example, the digestive system includes the stomach, small intestine, large intestine as well as other organs. Each of these organs is made up of different tissues.
There are four main types of tissue—epithelial, muscle, nervous, and connective. Each type has a particular function and can be found to some degree in most organs. Epithelial tissue covers the outside of the body and lines the organs and cavities within the body. This tissue type serves both as a barrier and a point of contact between the body and the outside environment. Muscle tissue is made up of cells capable of contracting when stimulated by the nervous system. Muscle allows for body movement as well as control of organ size and shape. Nervous tissue senses stimuli and transmits impulses, and it processes information to formulate a response. Connective tissue is a diverse group of tissues that link and support other tissues. Generally, cells in a connective tissue secrete nonliving material, called a matrix, which actually performs the functions of support and connection.
Materials:
Compound microscope
Prepared histology slides
Experimental Procedures:
1. Obtain a prepared slide from your teacher.
2. Focus the slide first under scanning power. Turn the nosepiece and focus using the low power objective.
3. Turn the nosepiece to the high power objective. Remember to ONLY use FINE adjustment knob when using high power.
4. Use the laminated reference sheets to ensure you are focusing on the correct part of the slide.
5. In the spaces provided, draw a picture of a few (2-3) cells that represent each of the four main tissue types.
6. Complete the data table entitled Observations of Selected Animal Cells as Seen through the
Compound Microscope.
7. Repeat steps 1-6 with the remaining slides.
Organelles that may be visible in cells
Cell membrane Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Results:
Observations of Selected Animal Cells as Seen through the Compound Microscope
Cell Type
Amphibian Simple Columnar
Epithelial Cell
Cell Shape Organelles Visible
Human Simple Cuboidal
Epithelium
Mammal Adipose Tissue
Human Red Blood Cell
Human White Blood Cell
Compact Bone
Mammal Skeletal Muscle
Mammal Cardiac Muscle
Not applicable
Not applicable
Not applicable
Mammal Neuron, Motor
Nerve Cells
Mammal Elastic Cartilage
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Mammalian Adipose Tissue
Human Simple Cuboidal
Human Red Blood Cell
Human White Blood Cell
Mammalian Skeletal Muscle
Mammal Neuron, Motor Nerve Cells
Compact Bone
Mammalian Cardiac Muscle
Mammal Elastic Cartilage
Conclusions:
1. Animals possess four main tissue types. Name the four types (4 points).
2. Where in an animal’s body is epithelial tissue located? (1 point)
3. State two functions of epithelial tissue (2 points).
4. Where in an animals’ body would simple columnar epithelium be located? (1 point)
5. In general, what is the function of connective tissue? (1 point)
6. Animals possess many different kinds of connective tissue. List three different types (3 points).
7. Name two functions of adipose tissue (2 points)
8. Name the three types AND locations of muscular tissue (6 points).
9. What is one function of nervous tissue? (1 point)
10. Name one location of nervous tissue in an animal’s body (1 point)