Name____________________________ 2nd Quarter Unit 1
advertisement

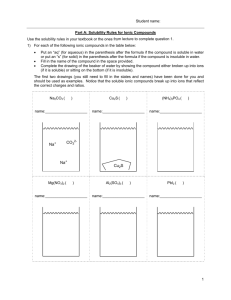
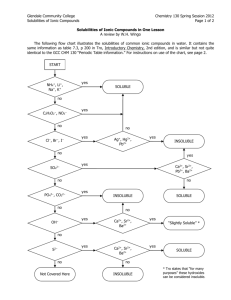
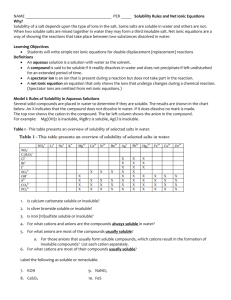
Name____________________________ nd 2 Quarter Unit 1 Homework Packet Ionic Basics 1. Which elements on the periodic table do not react with anything, they are inert? 2. What about an atom determines if it is chemically stable or not? 3. What are the “magic” or “perfect” number of electrons that make an atom stable? 4. If an atom does not have one of the numbers of electrons from question #3 above, what will it do to try to get to one of those numbers? 5. What is an ion? 6. What is an ionic bond? 7. An atom gains an electron, what charge is it’s ion? 8. An atom loses an electron, what charge is it’s ion? 1 Name____________________________ Octet Rule and Charges 1. How many valence electrons does each of the following atoms have? A. Potassium, K B. Sulfur, S C. Phosphorous, P D. Neon, Ne E. Aluminum, Al F. Boron, B G. Fluorine, F H. Carbon, C I. Magnesium, Mg J. Sodium Na 2. What charge do each of these atoms go to when they become stable ions? A. Potassium, K B. Sulfur, S C. Phosphorous, P D. Neon, Ne E. Aluminum, Al F. Boron, B G. Fluorine, F H. Carbon, C I. Magnesium, Mg J. Sodium Na Charge s +1 0 +2 +3 +/-4 -3 -2 -1 2 Name____________________________ 3. What are the stable numbers of electrons? 4. What is the octet rule? 5. What charges do metals tend to go to, positive or negative? 6. What charges do non-metals tend to go to, positive or negative? 3 Name____________________________ Forming Ionic Compounds 1. What is a cation? 2. What is an anion? 3. Do metals tend to become cations or anions? 4. Do non-metals tend to become cations or anions? 5. What charge to all compounds have to be, positive, negative, or neutral? 6. Write the formula for the following ionic compounds: A. Magnesium bromide B. Aluminum fluoride C. Potassium oxide D. Lithium nitride E. Sodium sulfide F. Beryllium nitride G. Aluminum sulfide H. Calcium iodide I. Cesium oxide 7. Write the name for the following ionic compounds: A. NaBr B. K2S C. Ca3N2 D. BaO E. BeCl2 4 Name____________________________ Polyatomic Ions and Transition Metals 1. Write the formula for the following ions: A. Acetate B. Bicarbonate C. Thiocyanate D. Peroxide E. Ammonium 2. Write the name of the following ions: A. CN-1 B. Cl-1 C. ClO3-1 D. SO4-2 E. PO3-3 3. Why are Roman numerals necessary for most transition metals? 4. Write the formula for the following ionic compounds: A. Calcium iodide B. Sodium oxide C. Potassium oxalate D. Ammonium hypochlorite E. Aluminum hydroxide F. Iron (III) phosphate G. Copper (II) nitrite H. Silver chloride I. Zinc cyanate 5 Name____________________________ 5. Write the name for each of the following ionic compounds: A. KCN B. (NH4)2O C. AlPO4 D. CaSO3 E. Na2CrO4 F. LiH2PO4 G. Mg(OH)2 H. Cu2CO3 I. Fe2(S2O3)3 J. ZnCl2 6. Each of these formulas has something wrong with it. Fix it: A. MgCl3 B. Na3SO4 C. CaOH2 D. Fe(III)Br3 E. Na+1I-1 F. OCa 6 Name____________________________ Crystal Lattices 1. Why do ionic compounds form crystal lattices when they are made? 2. What term is used to describe the strength of a crystal lattice? 3. How are lattice energy and ionic charge related? 4. How are lattice energy and ionic size related? 5. How is melting point related to lattice energy? 6. For each of the pairs below, circle the ionic compound that should have the stronger lattice energy: A. CaCl2 vs. CaO B. SrS vs. NaF C. Al2O3 vs. AlCl3 D. Na3PO4 vs. K3PO4 E. LiF vs. NaF F. K2O vs. Na2O 7. For each of the pairs below, decide which should have a higher melting point: A. LiI vs. MgS B. CaBr2 vs. BeBr2 C. Al2O3 vs. NaCl D. CaSO4 vs. K2SO4 E. MgF2 vs. MgBr2 8. Arrange the following in order of increasing melting point (smallest to largest): CaO KCl CaF2 BeO 9. Draw an example of a crystal lattice. 7 Name____________________________ Solubility 1. What does it mean that water is polar? 2. What is an aqueous ion? 3. Draw a cation surrounded by water molecules; be sure to point the waters the correct way. 4. Repeat #3 but this time use an anion. 5. When an ionic crystal dissolves in water, what has the water done to the crystal? 6. What is the general rule to decide if an ionic compound is soluble in water or not? 7. Decide whether each of the following compounds will be soluble or insoluble in water: A. NaBr soluble insoluble B. K2SO4 soluble insoluble C. AlPO4 soluble insoluble D. CaCrO4 soluble insoluble E. MgCl2 soluble insoluble F. (NH4)2CO3 soluble insoluble G. PbSO4 soluble insoluble H. Ba(OH)2 soluble insoluble I. LiCl soluble insoluble J. Pb(NO3)2 soluble insoluble 8 Name____________________________ Conductivity 1. Decide whether each of the following compounds will conduct electricity if their crystals are put in de-ionized water and stirred: A. NaBr conduct not conduct B. K2SO4 conduct not conduct C. AlPO4 conduct not conduct D. CaCrO4 conduct not conduct E. MgCl2 conduct not conduct F. (NH4)2CO3 conduct not conduct G. PbSO4 conduct not conduct H. Ba(OH)2 conduct not conduct I. LiCl conduct not conduct J. Pb(NO3)2 conduct not conduct 2. What is the definition of electricity? 3. Why will a solid crystal of an ionic substance not conduct electricity? 4. If a solid dissolves into aqueous solution but does not conduct electricity, what must that mean? 9 Name____________________________ Precipitation 1. What is a precipitate? 2. Do precipitates look cloudy or clear? 3. What is the rule to determine if a ppt will form? 4. For each combination below, determine if a ppt forms. If it does, write its formula: A. Fe(NO3)3 + Na2CO3 B. AlCl3 + NaBr C. Li3PO4 + K2SO4 D. MgBr2 + (NH4)2CrO4 5. For each combination below a ppt forms. Write its formula: A. Na3PO4 + CaCl2 B. K2Cr2O7 + Al(ClO3)3 C. Mg(NO3)2 + Li2CO3 6. What is a spectator ion? 7. For each combination below a ppt forms. Write the ions that are the spectator ions: A. (NH4)2CO3 + BaCl2 B. K3PO4 + Al(NO2)3 C. CaI2 + Li2CrO4 10 Name____________________________ 8. For the chart below, if a ppt forms, write its formula. If no ppt forms, write NR. Also, write the spectator ions for each mixture. A B Ionic Formulas K2CO3 AlBr3 K2CO3 x AlBr3 x x Ca(NO3)2 x x x Mg(ClO2)2 x x x x (NH4)2CrO4 x x x x A B C D E C D E Ca(NO3)2 Mg(ClO2)2 (NH4)2CrO4 x 11 Name____________________________ Spectroscopic Notation 1. What are valence electrons? 2. How many valence electrons do each of the following atoms have: A. Mg B. O C. Si D. K E. I 3. What charge do each of the following atoms go to: A. Mg B. O C. Si D. K E. I 4. Write the full spectroscopic notation for: A. Na B. O C. B D. Cl E. Ti 12 Name____________________________ 5. Write the abbreviated, Noble Gas notation for: A. Na B. O C. B D. Cl E. Ti 6. Write the abbreviated, Noble Gas notation for: A. Ga B. Cd C. Y D. Fe E. Po 7. Why can we ignore many electrons in the Noble Gas configuration? 13