Protein Synthesis - TangHua2012-2013
advertisement

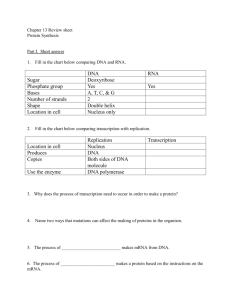
1/6 Transcription and Translation Inquiry into Life – pg. 493-501 Today’s Objectives: Demonstrate an understanding of the process of protein synthesis, including: Identify the roles of DNA, messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomes in the process of transcription and translation, including initiation, elongation, and termination Determine the sequence of amino acids coded for by a specific DNA sequence (genetic code), given a table of mRNA codons Identify the complementary nature of the mRNA codon and the tRNA anti-codon DNA VS RNA Both are nucleic acids made up of nucleotides. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) 1. 2. 3. 4. ______________________________ Double stranded ______________________________ Bases: A – Adenine C– Cytosine G – Guanine T – Thymine Sugar is ribose (5 carbon) _____________________________ Found in nucleus and cytoplasm. Bases: __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Introduction *DNA ____________________ produces an __________________________________________________ *Protein synthesis _______________________________ to produce __________________. Do not confuse these 2 processes!!!!!! 2/6 DNA is the _____________________________ (or template) containing ____________ for the ________________________________________________. (structural and functional) Proteins are __________________________________, but DNA never leaves the _________. A copy of the DNA must be made. This copy is called _________________________ (mRNA). Only genes for required proteins are copied into mRNA. The process of making mRNA is called ____________________________. mRNA travels into the cytoplasm where it is _______________________into proteins. _________________________________________________________________ The nitrogenous bases in DNA contain the instructions for making proteins. _______________________ ______________________________________________. Many amino acids make up a protein. Each 3 base set is called a _____________________. _________________________________________________________________ There are _____________possible combinations: However, we only have about ____ amino acids, therefore most amino acids have more than 1 codon. Often the codons only differ in the last base. Example: CAA CAG _______________________________________________. Duplicate codons may be a way of __________________________________________________. The duplication of codons is called _______________________________. The genetic code is basically “______________________.” The _____________________________________ _______________________________________. This suggests that all living things ______________________ ____________________________________________. AUG (Methionine) is a ______________________, whereas UAA, UGA and UAG are ____________________. At the end of each mRNA strand there are long chains of ____________________ bases (Adenine Tail, poly-A tail). ______________________________________________________________________________________. When enough protein is created the adenine tail ________________. This tells the body that this particular mRNA is _____________________________ to produce its protein. The cell will then digest the no longer functional m-RNA (lysosomes will be involved in this process). 3/6 Types of RNA mRNA – Messenger RNA tRNA – Transfer RNA rRNA – Ribosomal RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Transcription • The first step of protein synthesis is called transcription. • Transcription is the _________________________________________________________________. • Only RNA can _______________________. A. The gene in DNA is ________________________________________________ by enzymes. The gene codes for the ___________________that will be eventually produced. B. The gene is then _____________by enzymes. (H bonds broken between bases) C. Free – floating _____________________ join complementary to the selected gene. This DNA strand is called the _______________________________. **Uracil joins to adenine always in RNA. There is no ________________in RNA** D. The Ribose –phosphates join together to complete the backbone. The _______________________ that is temporarily formed breaks by enzymes and is pulled __________________________________________________________. We now have an mRNA strand. Steps A, B, C and D= Transcription 4/6 E. mRNA is released (Enzymes break the Hydrogen bonds). DNA ________________ back together. mRNA is first processed (_________________________________________________________) so it can leave the nucleus then passes through the _________________________ through the nuclear pores into the cytoplasm. F. DNA recoils back up into its ___________________________ with the help of enzymes. Translation • The second step in protein synthesis is called translation. • Translation is the process of ________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ (protein). It occurs in 3 steps. • Translation occurs at ________________________. (cytoplasm or RER) G. Step 1 – Initation. mRNA becomes associated with a ribosome which are made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. When the mRNA comes near the two subunits, the large one ___________________ the mRNA in the smaller one. H. The ribosome reads the first codon (______________________________________). tRNA contains a set of bases which are complementary to the bases on the mRNA. tRNA bases are called _______________. The ribosome bonds the _____________________________. I. Step 2 – Elongation. The ribosome moves to the next __________. A complementary tRNA arrives with an amino acid and joins to the mRNA codon. The A.A. from the first tRNA is joined to the A.A. on the new tRNA. The first tRNA is released and goes off to find another identical amino acid. J. Step 3 – Termination. The ribosome continues to read the mRNA and the ______________________________ chain grows until a _________________________ is reached. The finished polypeptide is released. The mRNA will disintegrate or be read by more ribosomes. (mass production of identical proteins) Many ribosomes may be found together, ______________________________________. This group of ribosomes is called a ____________________________________. The maximum number of tRNA on a ribosome at one time is ____________. 5/6 Summary of Protein Synthesis IF the DNA strand is TACTTATGCTCCTAAATT 1. What are the codons on the mRNA strand? 2. What is the sequence of amino acids produced? 6/6 Sketch and label the process of transcription and translation – Try to work from your memory!