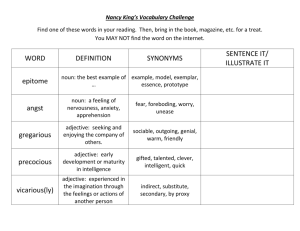
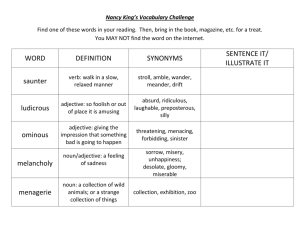
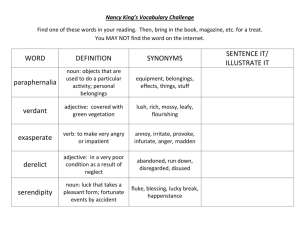
Adjective endings
advertisement

Adjective Suffixes (From: http://www.grammar-quizzes.com/passive3a.html) Forming adjectives from other word forms Noun → Adjective word form NOUN WORD FORM Some adjectives are formed from nouns and others are formed from verbs. The word forms are from Latin, Greek and other languages. There is no simple rule for adding suffixes, but there are common patterns. DET + NOUN (N) The sky was a spectacle. (a very beautiful thing to see) The sky was filled with colors. The sunset was red. We felt awe. (a feeling of inspiration and respect) ADJECTIVE WORD FORM Adding a suffix to a noun form is one way of forming an adjective. A suffix is a part added to the end of a word to mark the word form. An adjective is often used after It is or It seems (stative verbs). BE + ADJ DET + MODIFIER + N It was spectacular.¹ It was a spectacular sky. It was colorful. It was a colorful sky. It looked reddish. It was a reddish sky. It was awesome. It was an awesome sight. ¹It + be + adjective (predicate adjective or predicate complement) See describing "be" (ascriptive "be"). NP –noun phrase; N – noun; Det – determiner; AdjP– adjective phrase; Adj – adjective Also see Noun Suffixes – changing adjectives to noun forms. Common Suffixes — noun to adjective SUFFIX -AL accident – accidental brute – brutal NOUN – ADJECTIVE region – regional region – regional custom – customary person – personal universe –universal moment – momentary caution – cautionary honor – honorary diet – dietary wonder – wonderful awe – awful success – successful base – basic delight – delightful history – historic NOUN – ADJECTIVE NOUN – ADJECTIVE relating to -ARY relating to quality or place compliment – complimentary beauty – beautiful -FUL full of -IC having the nature of; caused by skill – skillful athlete – athletic photograph – photographic science – scientific rhythm– rhythmic -ICAL having the nature of history – historical magic – magical logic – logical practice – practical statistic – statistical fool – foolish child – childish alphabet – alphabetical self – selfish sheep – sheepish power – powerless pink – pinkish friend – friendless girl – girlish worth – worthless use – useless like – lifelike home – homeless lady – ladylike penny – penniless war – warlike child – childlike friend – friendly bird – birdlike cost – costly spring – springlike month – monthly day – daily poison – poisonous order – orderly danger – dangerous coward – cowardly nerve – nervous courtesy – courteous rain – rainy mystery – mysterious fun – funny victory – victorious dirt – dirty mess – messy dirt – dirty spot – spotty -ISH origin, nature -LESS without -LIKE like -LY like -OUS quality, nature -Y like Changing verbs to adjectives Verb word form → Adjective word form VERB WORD FORM Some adjectives are formed by adding a suffix to the verb form. A suffix is a part added to the end of a word to mark the word form. VERB They create ideas. She is expecting a baby. They don't permit smoking here. They urge us to come immediately. Today's news interests me. ADJECTIVE WORD FORM Adjectives commonly occur after be verbs as predicate adjectives or predicate complements. Adjectives also occur as modifiers to nouns (pre-position and post-position) BE + ADJECTIVE MODIFIER TO A NOUN They are creative. They have creative minds. She is an expectant mother. We congratulated the expectant mother. Smoking is permissible. allowed Smoking is a permissible activity. The matter is urgent. This urgent matter needs your attention. The news is interesting. We have interesting news. I am interested. I am an interested reader. Modifiers ending in -ed / -ing Participial Modifiers -ed vs. -ing PAST PARTICIPIAL MODIFIER -ED The past participle modifies the noun that is the receiver of the feeling or emotion. an amused child The child receives the feeling of amusement. Interested people can sign up for the class. (The people feel interest in the subject.) Bored speakers should find something exciting to say. (The speaker feels boredom while speaking!) Amused viewers enjoy the short films. (The viewers feel the amusement.) Overwhelmed students end up dropping a course or two . (The students feel overwhelmed.) PRESENT PARTICIPIAL MODIFIER -ING The present participle modifies the noun that is the source of the feeling or emotion. an amusing ride The ride causes amusement. Interesting people will speak during the class. (People cause others to feel interest.) Boring speakers put their attendees to sleep. (The speaker causes others to be bored.) Amusing short films are shown at the animated film festival. (The films cause the amusement.) Overwhelming amounts of work are given to high school students. (The amount of work causes the overwhelming.) Common suffixes — verb to adjective SUFFIX VERB – ADJECTIVE VERB – ADJECTIVE VERB – ADJECTIVE agree – agreeable expand – expandable laugh – laughable -ABLE able, can do pass – passable access – accessible remark – remarkable force – forcible pay – payable sense – sensible flex – flexible please – pleasant permit – permissible rely – reliant force – forcible ignore – ignorant resist – resistant vacate – vacant comply – compliant -IBLE able, can do -ANT performing agent excel – excellent depend – dependent confide – confident urge – urgent attract – attractive differ – different create – creative equal – equivalent select – selective posses – possessive amuse – amusing prevent – preventive excite – exciting destruct – destructive confuse – confusing relax –relaxing amuse – amused surprise –surprising excite – excited amaze – amusing confuse – confused relax – relaxed freeze – frozen surprise – surprised lighten – lightened overwhelm – overwhelmed darken – darkened braze – brazen shorten – shortened widen – widened -ENT performing agent -IVE causing effect -ING causing effect -ED receiving effect -EN receiving effect Adjectives: Similar but Different VERB SIMILAR BUT DIFFERENT PAIRS It was an awesome movie. having a great quality, inspiring AWE It was an awful movie. having a terrible quality We have two dependent children. needing someone for care DEPEND We have two dependable children. having a nature of completing promises The laughing child was playing. having a good nature LAUGH The laughable car was powered with tequila. impossible to be serious about She has light hair. a natural quality LIGHT She has lightened hair. an unnatural/changed quality He is a loving son. having a quality of giving love LOVE He is a lovable son. having a nature of attracting love He is selective a bout what he eats. having a quality of being choosy SELECT They are selling selected items. particular, carefully chosen Select people can live there. a small number, exclusive, wealthy He is a sensible person. reasonable [sensible] SENSE He is a sensitive person. easily irritated or hurt [L. sensitivus] NOUN SIMILAR BUT DIFFERENT PAIRS It was childish behavior (behavior). having immature behavior, negative CHILD It was childlike behavior. qualities like a child, positive We are confident about winning. sure [L.confidere] CONFIDE The message is confidential. private [L. confident] It is a crisp day, today. cool and dry CRISP It is a crispy cracker. thin and crunchy (makes a pleasant sound) We had a fun time at the movies. amusing FUN We saw a funny movie. causing laughter The general made a tactical advance. military move [L. tacticus] TACT He is a tactful politician. having skills handling situations [L. tactus] tact (n.) – skill in dealing with difficult or delicate situations Your food is tasty. having a good taste TASTE You are a tasteful dresser. having good judgment for fashion He is a worthy competitor. having good value, character WORTH He is a worthless competitor. having no value or importance Suffixes -ic versus –ical: Adjectives -ic and -ical -IC There is no particular way to know whether a word will use the -ic or the -ical ending. The suffix -ic comes from French -ique, or Greek -ikos. and means having the nature of , or causing something. academic, algebraic, arithmetic, artistic, athletic, catholic, domestic, dramatic, egoistic, emphatic, energetic, fantastic, geometric, strategic, linguistic, majestic, neurotic, pathetic, pedagogic, phonetic, public, semantic, syntactic, systematic, tragic He buys classic cars. traditional, old style His comic verse filled books. artistic comedy His economic theory was proved unsound. of the science of economics An electric motor powered the car. a particular machine That was a/an historic moment. recorded in past history The hysteric / hysterical woman was out of control. unable to control your behavior or emotions The little girl played with a magic wand. of a mysterious source He was a medic in the military. intern or doctor He wrote in a poetic speech. imaginative, having the quality of poetry, like poetry It's not politic to ask such questions wise -ICAL The -ical form is often added to a word that already has a final -ic. Such adjectives often have a different or an additional meaning from the more basic -ic form. alphabetical, alphanumerical, archeological, biblical, biological, chemical, chronological, critical, cynical, ethical, grammatical, fanatical, illogical, logical, mathematical, mechanical, medical, musical, pedagogical, physical, radical, surgical tactical, topical We listen to classical music. from a cultural (sometimes Greek, Roman, European) source, or 18thC. His comical verse entertained audiences. funny He chose an economical car. inexpensive to use Electrical equipment makes our work easier. general, mass This is a/an historical moment. worthy of being recorded in history The movie was hysterical. very funny, causing uncontrollable laughter It was a magical experience. mysterious, wonderful, exciting He did medical research. related to medicine He wrote in a poetical manner. having the form of poetry It was a political question. concerning government and politics Common Mistakes: Errors and Solutions FOCUS His answer was logic, but I didn't agree with him. How can I tell if a word is an adjective or a noun? → My dad likes to listen to classic music on the car radio. Use this to refer to traditional music (not Bach and Beethoven) Do you know where I can buy an economic car? Hal is a tasty dresser. SOLUTION His answer was logical, but I didn't agree with him. Tip: If you want to know if a word is an adjective, place "very" before the word. It's very logical. (OK) / It's *very logic*. (not OK) My dad likes to listen to classical music on the car radio. This book is a classic. enjoyed by generations Use "classical music" to refer to Beethoven, Bach, Haydn, etc. Do you know where I can buy an economical car? (money saving, affordable, gas saving?) Hal is a tasteful dresser. Use tasty for food. Use tasteful for fashion sense (dresses appropriately, has good fashion judgment). It was a chilly, crispy day. It was a chilly, crisp day. (dry, low humidity) Don't shout at my son. He's a very sensible person. He's a very sensitive person. (easily hurt) FORMACION DEL ADJETIVO Puede efectuarse por adición de sufijos, separables o no: a) A PARTIR DE UN SUSTANTIVO hope, esperanza grace, gracia child, niño rain, lluvia gold, oro West, oeste friend, amigo pleasure, placer atom, átomo b) A PARTIR DE UN VERBO hopeless, desesperanzado graceful, gracioso childish, aniñado rainy, lluvioso golden, dorado, de oro Western, occidental friendly, amistoso pleasurable, placentero atomic, atómico to eat, comer to act, actuar to contribute, contribuir to work, trabajar eatable, comestible active, activo contributive, contribuyente working, que trabaja c) A PARTIR DE OTRO ADJETIVO blind, ciego yellow, amarillo practic, práctico blindfold, a ciegas yellowish, amarillento practical, práctico Los sufijos son aquellas partículas que se le agregan a una palabra (después, y no antes como los prefijos), para de esta forma indicar en qué caso gramatical se encuentra, o modificar de alguna manera su significad. Un ejemplo en español: el sufijo –s, o es. al agregarlo a una palabra, le da un significado de plural ej: carro, carros Los sufijos en inglés más usados son los siguientes: - able forma adjetivos a partir de verbos. No se aplica a sustantivos. Significa able, ible : -to reason/reasonable = razonar/razonable -to drink/drinkable = beber/bebible (potable) -ful este sufijo es agregado a sustantivos para formar sustantivos y adjetivos. significan ada, ado, ido, oso : -color/colorful = color/colorido -wonder/wonderful = maravilla/maravilloso -y este sufijo es utilizado en inglés con 3 propósitos: Se añade a sustantivos para convertirlos en adjetivos y expresar semejanza o para indicar abundancia. Y en caso de que un sustantivo finalice en e convierte la e simplemente en y. Significa ado, oso y raramente significa able; Utilizado para obtener el disminutivo, para el efecto si finaliza en consonante esta se repite. significa ito, ita. noise/noisy = ruido/ruidoso water/watery = agua/acuoso anger/angry = enojo/enojado - cal Este sufijo convierte sustantivos. en adjetivos. Sustantivos terminados en c solamente agrega al. Significa ico, ica -medic/medical = médico/médico (a) -alphabet/alphabetical = alfabeto/alfabético(ica) - ous este sufijo equivale al sufijo oso, osa del español, con el trasformamos un sustantivo en adjetivo y de acuerdo al procedimiento siguiente : Sustantivos terminados en r basta agregar ous; los terminados en e cambian e por ous; el terminado en y la cambia por i y agrega ous, al sustantivo terminado en o agrega us, los terminados en on elimina la n y se reemplaza por us. -fury/furious = furia/furioso -danger/dangerous = peligro/peligroso - less Este sufijo altera a los sustantivos para obtener adjetivos. Y es muy útil con los comparativos. Es un sufijo tipo negación y el cual significa sin, in,. -hope/hopeless = esperanza/sin esperanza -worth/worthless = útil/inútil - ish El sufijo ish se le agrega a sustantivos para formar adjetivos y así indicar semejanza o atenuación. Si el sustantivo termina en e cambia la e por i y se le agregas sh. Si el sustantivo finaliza en y la conservara y se le agrega -ish. Si el sustantivo termina en consonante simplemente se le agrega ish para obtener el adjetivo. -boy/boyish = niño/como niño -woman/womanish = mujer/como mujer, mujeril Some more adjective endings: able al an ant ar ary ate ed en ent etic ful ible ic ical id ile ine ish less like ly ory ous sive some tive acceptable, available, capable, comfortable, desirable, … abnormal, central, digital, conventional, personal, rational, … authoritarian, bohemian, republican, urban, veteran, … arrogant, constant, distant, dominant, pleasant, relevant, … familiar, particular, popular, similar, regular, spectacular, … arbitrary, contrary, elementary, involuntary, revolutionary, … accurate, adequate, considerate, delicate, desperate, … complicated, connected, expected, related, sacred, united, … barren, drunken, heartbroken, open, swollen, wooden, … absent, efficient, different, frequent, impatient, insolent, … diabetic, energetic, genetic, magnetic, pathetic, synthetic, … beautiful, careful, colorful, harmful, painful, successful, … audible, compatible, convertible, credible, impossible, … atomic, alcoholic, alergic, analytic, electronic, pacific, … alphabetical, asymetrical, biblical, biological, chemical, … arid, avid, candid, frigid, humid, hybrid, rapid, rigid, … agile, docile, fertile, fragile, hostile, sterile, versatile, … alkaline, bovine, divine, feminine, masculine, genuine, … amateurish, childish, feverish, foolish, lavish, selfish, … aimless, careless, fearless, flawless, friendless, harmless, … alike, childlike, ladylike, lifelike, manlike, warlike, … brotherly. chilly, costly, deadly, ghostly, holy, kindly, … circulatory, compensatory, conciliatory, contradictory, … ambiguous, anonymous, dangerous, famous, nervous, … aggresive, adhesive, compulsive, evasive, impulsive, … awesome, bothersome, tiresome, lonesome, gruesome, … addictive, attractive, constructive, corrective, defective, … EXERCISES: http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-12097.php http://www.englishexercises.org/makeagame/viewgame.asp?id=3677 http://www.autoenglish.org/FCEUse/verbs2adjectives.htm http://www.english-grammar.at/online_exercises/adjective_adverb/kingsley-manor.htm http://www.englisch-hilfen.de/en/word_formation/nouns_adjectives/index.php http://grammar.about.com/od/sentencestructures/a/Practice-In-Using-Adjectives-Formed-FromNouns-And-Verbs.htm