Chapter 25-26 Class Notes - Germantown School District
advertisement

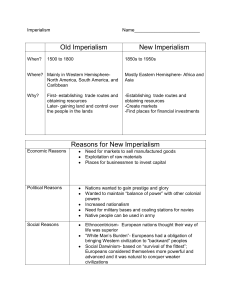
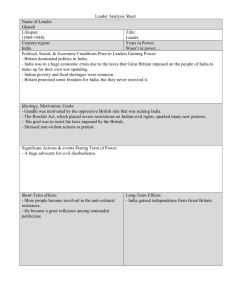
A Western-Dominated World (Chapter - 25 / Section - 1) The New Imperialism Imperialism is the domination by one country of the political, economic, or cultural life of another country or region. The Causes: 1. Industrial Revolution 2. Social Darwinism 3. Missionary Zeal 4. Ethnocentrism- The belief that one's own race or ethnic group is the most important and/or those some or all aspects of its culture are superior to those of other groups. 5. Nationalism 6. Naval Refueling Bases 1. By the mid-1800s, Europe had gained considerable power. 2. Encouraged by their new industrial, economic and military strength, Europeans embarked on a path of aggressive expansion that today’s historians call the “new imperialism.” Pressures for Expansion 1. Economic Interests: Oversea expansion was the result of the desire for New Markets and Natural Resources Factories in Europe and the US searched for new raw materials and new markets for their products (rubber, copper, gold, cotton, and tin) Seeking New Opportunities : To sell their factory goods 2. Political & Military Interests: (Is closely linked to the economic motives for expansion) The need to maintain their navy’s depended upon refueling stations. Countries seized ports/harbors that could accommodate the navy’s needs. Nationalism created each countries drive to inhibit others from having an advantage over them. Nations claimed that colonies were needed for national security & having global empires a nation would boost their prestige around the world 3. Humanitarian Goals: “Civilizing” Mission: missionaries believed to become “civilized”, the people of Africa and Asia must convert to Christianity. Europeans had the duty to spread the greatness that existed within their civilization (medicine, law and religion) 4. Social Darwinism: Europeans believed Western civilization was superior to all others. They encouraged others to use European languages and Western lifestyles Europeans believed they were superior to all others ______________________________________________________ Evolution Influences Imperialism This is a great example of how science can influence social, political and economic values and actions! Darwin’s theory (define) was published in 1852. Some Europeans adapted Darwin’s ideas about the evolution of animals to explain differences among human beings: “survival of the fittest” Social Darwinists believed white Europeans were the fittest people and conquests & destruction of weaker races was nature’s way of improving the human race Forms of Imperial Control Many of the older civilizations had declined & gotten weaker (Ottoman / Middle Eastern / Far Eastern) African slave trade had weakened the ability of states to develop & they were too weak to stand up to the stronger Western nations. The invention of medicine, weapons and warships often were persuasive tools to persuade nations to give in to an outside powers rule RESISTANCE Europeans had the advantage of: Strong economies Well-organized governments Powerful armies and navies Some societies attempted to strengthen their societies by reforming their own traditions Also western educated natives helped create a sense of nationalism in their countries to expel the outside nations CRITICS AT HOME A group of anti-Imperialists emerges in individual nations home. They argue that colonialism is: Tool of the rich It is immoral what a country does to another country How does a democracy create an undemocratic existence in another country? Are we not forcing our will upon others that have currently the inability to fight back? Forms of Imperial Rule Colonies: French Colonial Rule: The French practiced “Direct Rule”. They would send officials & soldiers from France to administer the colonies. The goal of the French colonization was to impose French culture on their colonies and to turn them into French provinces. British Colonial Rule: They relied upon the “Indirect Rule” by using sultans, chiefs or any other local rulers to maintain order. The advantage of using this was to slowly convert the rulers over to western ways. The rulers would then groom future generations to “westernized” lifestyle. The French & British would any force necessary to maintain control of their colonies PROTECTORATE Is where a local ruler is left in place to rule, however they must follow the advice of the European advisor on issues of “trade” or “missionary activity”. The advantage if use a Protectorate was less costly than having a standing army in a country. Spheres of Influence Is an area in which an outside power claims exclusive investment or trading privileges. Britain would control China while the US would dominate Latin American The Partition of Africa (Chapter - 25 / Section - 2) Africa is a huge continent that is four times the size of Europe. Much of Africa consisted of hundreds of languages and a variety of governments which existed in small villages or in large states. North Africa Throughout history Sahara barrier has culturally separated the North from the rest of Africa. The seafaring civilizations of the Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans and others facilitated communication and migration across the Mediterranean, the cultures of North Africa became much more closely tied to Southwestern Asia and Europe. Long Before the 1800 the area was under the control of the Muslims. In the early part of the 1800’s North Africa was still controlled by a declining Ottoman Empire. West Africa A reform movement emerges under the Islamic religion. It is an attempt to purify Islam and in doing so over threw many of the leaders in the area. The Asante kingdom was dominating in the forest regions and was ready and willing to accept the Europeans in trade. Other regional tribes began to rise up & attempt to defeat the Asante tribes. East Africa The region was controlled by Islamic rule. Islamic control helped promote trade that consisted of Ivory, copper and slaves that were sent to the Middle East. In exchange they would receive clothing or firearms from Europeans that were used to defeat local advisories. _________________________________________ Southern Africa In the early 1800’s southern Africa was in turmoil. The tribal factor of family support system was a key factor to the various groups, like Native Americans in the U.S. The conquests of Zulu leader “Shaka” set off great migrations, wars and chaos across the region. By the 1830’s Zulu’s were fighting with the Boers. Slave Trade In the early 1800’s Europeans began to outlaw the transatlantic slave trade. Britain & the US helped resettle freed slaves. In 1787 Britain organized Sierra Leone in Western Africa & the US established in Liberia colonies for former slaves to live. European Contacts Increased From the 1500s through the 1700s, difficult geography and disease prevented European traders from reaching the interior of Africa. Medical advances and river steamships changed all that in the 1800s. EXPLORERS MISSIONARIES Explorers were fascinated by African geography but had little understanding of the people they met. Catholic and Protestant missionaries sought to win people to Christianity. Most took a paternalistic view of Africans. They urged Africans to reject their own traditions in favor of western civilization. The Partition of Africa Dr. David Livingston: first white man to do humanitarian and religious work in Africa. Newspaper reports created European interest in Africa. By 1914, European nations controlled 90% of the continent. ___________________________________________ The Berlin Conference Took place in Berlin & was attended by Great Britain, AustriaHungary, France, Germany, Russia, US, Denmark, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Netherlands, Sweden, Turkey and Belgium. European powers recognized King Leopold’s of Belgium private claims to the Congo Free State, but called for free trade on the Congo & Niger rivers. Also a European power could not claim any part of Africa unless it had set up a government office. This led to European’s to send officials that would exert power over the local rulers & people. Horrors in the Congo King Leopold would exploit the riches in the Congo by taking as much copper, rubber and ivory as possible. However, his treatment of the workers shocked the world in the beatings, poor wages and the loss of so many lives. International outrage eventually forces Leopold to turn his control over. In 1908 it becomes the Belgian Congo and the abuses come to an end. The Belgians still exploited the people and gave them little say in the government French Expansion France moved to takes it share of Africa. It won battles against Algeria, Tunisia and took colonies along the West and Central parts of Africa. At the height of its empire France had territory as big as the United States Britain takes its Share Great Britain may not have had as much territory then France, but it held more of the heavier populated areas within Africa. The British clashed with the Boers in South Africa. The Boer War 1899-1902 came with the discovery of gold & diamonds. In 1910 Great Britain unites the Cape Colony’s and establishes a new constitution. The new constitution is run by whites and creates the foundation for a racial segregation that would last until 1993. South Africa’s Long Struggle with Apartheid In 1910, South Africa won self-rule from Britain. Over the next decades, the white minority government imposed apartheid, a system of racial laws which separated the races and kept the black majority in a subordinate position. From the beginning, black South Africans protested apartheid. In 1912, the African National Congress (ANC) was set up to oppose white domination. Nelson Mandela mobilized young South Africans to take part in acts of civil disobedience against apartheid laws. As protests continued, government violence increased. In the late 1980s, President F. W. de Klerk abandoned apartheid, lifted the ban on the ANC, and freed Mandela. In 1994, Mandela was elected president in South Africa’s first multiracial elections. Mandela welcomed longtime political foes into his government. The Algerians battle the French. The British battle the Zulu’s in southern Africa and Asante in West Africa. Germans had battles in East Africa against the Yao & Herero. In Zimbabwe, Nehanda was a clever tactician & leader. He was captured & later killed. Ethiopia Survives King Menelik II held off the colonial advancements by adopting a series of modernization. Upgrades his roads Bridges Creates a Western School system Imports the latest weapons European’s train his troops Ethiopia’s success in beating the Italians at the Battle of Adowa allowed them to preserve their independence. Liberia was the only other nation to maintain its independence from European rule Why Were They Successful? In just a few decades, imperialist nations gained control over much of the world. 1. While European nations had grown stronger in the 1800s, several older civilizations were in decline. 2. Europeans had the advantages of strong economies, Well-organized governments, and powerful armies and navies. 3. Europeans had superior technology and medical knowledge. Effects of Imperialism on Africa Imperialists profited from African colonies by obtaining natural resources 1. Imperialists profited from African colonies by obtaining natural resources 2. Africans paid low wages imposed taxes that had to be paid in cash and were subjected to brutal discipline 3. Schools set up taught Africans that European ways were best 4. Imperialism contrary to western ideals of liberty and equality 5. Nationalist groups had won their political independence from European rule by the 1960s and 1970s! Free at Last! European Challenges to the Muslim World (Chapter - 25 / Section - 3) Napoleon’s conquest of Egypt exposed the weakness of the Ottoman Empire and opened the door for future European contact. At the height of the Muslim Empires (3) giants ruled, the Mughals in India, the Ottomans in the Middle East and the Safavids in Iran. Empires in Decline The major causes for the decline were due to: Central governments have lost control over Nobles, landowners, military and guilds. Corruption within the ruling class Undermining the rulers by scholars that endorsed changes. The Wahhabi Movement In the late 1700’s & early 1800’s a reform movement began to sweep across the Muslim world. _____________________________________________ The Wahhabi: Stressed religious piety (devotion to religious duties) & strict rules of behavior Wahhabi made the point that the reform movement principle was that absolutely every idea added to Islam after the third century of the Muslim era was false and should be eliminated. Muslims, in order to be true Muslims, must adhere solely and strictly to the original beliefs set forth by Muhammad They wanted recapture the purity and simplicity of Muhammad's original teachings. Revolt in Sudan • Wahhabis revolts against the imperialistic countries failed yet the movement survived. ____________________________________________ • Muhammad Ahmad announces he is the “Savior of the faith” and leads the Mahdi against the British expansion in the Sudan. Western Imperialism European Empires used a variety of tactics to establish control within a region. Imperialist nations would us force or diplomacy to ensure what they wanted. They also secured favorable treaties that helped them in trading rights. Nationalist Revolts The ideas of nationalism spread from Western Europe to the Ottoman Empire creating the effect of subject peoples attempting to break away. The Ottomans ended the revolts yet lost Egypt. European Pressure France wants more territory Russia moves to gain territory in the Bosporus & Dardanelles so they have a greater access to the Mediterranean Sea Britain attempts to stop the Russians for fear of losing its power in the region which is key to India’s exports. Germany attempts to build a railway from Berlin to Baghdad Efforts to Westernize The Ottoman’s were constantly looking to the West for ideas and means to improve their empire. The following would cause unrest and create a growing population increasing pressure within the lands: Bureaucracy and taxation Building of railroads Modernized military Science & technology Democratic ideas Improved medical care & farm improvements Young Turks Were a group of young liberals insisting that reform was the only way to save the Ottoman Empire. In 1908 the Young Turks over throw the sultan, yet before the Young Turks could implement their new reforms the empire was thrown into a world war. Massacre of Armenians Religious toleration had existed throughout the history of the Ottoman Empire. Nationalism was now causing tensions between Turks and minority groups seeking their own state. The tensions triggered a brutal Genocide (is the deliberate attempt to destroy an entire religious or ethnic group) of the Armenians-a Christian people. The attack was based upon mistrust in their helping the Russians over throw the Ottoman’s. Muhammad Ali • Called the “Father of Modern Egypt” • During his rule he introduced a number of economic & political reforms. • The expansion of cotton production & industry development had the effect of increasing Egypt’s growth in international trade Muhammad Ali helped Egypt become a future power by: Improving tax collection Reorganized the landholding system Improved irrigation systems to help farm production Built a well-trained & modern army Suez Canal Future rulers lacked the skills of Muhammad Ali. This created greater foreign control on the Egyptian Empire. In 1859 a Frenchman organized a company to construct the Suez Canal. The canal greatly shortened the route from Europe to the Far East. To Great Britain this became a life line to India. In 1875 when the Egyptian ruler was unable to repay the loans for the construction of the canal it caused the ruler to sell his shares in the canal to the British. British Prime Minister Disraeli effectively gained controlling interest in the canal. In 1882 Egyptian nationalists revolt the growing control of foreign nations. Britain moves in and makes Egypt a protectorate. Iran -v- European Powers Two nations maneuvered for power with Iran in the early 1900’s. Russia attempting to protect their southern frontier Great Britain was concerned in protecting its interests in India. The discovery of oil complicated matters. The effect was that Russia & Britain persuaded the Iranian government to give concessions Both countries send in troops to protect their interests. Iranian nationalists are separated into two different groups: The middle class wanted a swift move to western ways Muslim religious leaders condemn the government & any western influences. The British Take Over India (Chapter - 25 / Section - 4) First ships arrive in India in 1608 and the British East India Company secures trading rights with the Mughals. By the mid-1800’s the company controlled three fifths of India British East India Company1608 - 1858 Control trade and government from late 1770s until 1858 ______________________________________________ Controlled India’s foreign trade using sepoys (Indians trained by the British soldiers) ______________________________________________ Native princes and Mughal court are puppet leaders ______________________________________________ Both Hindus and Muslims resented British harsh treatment and low pay! The British were able to conquer the country by exploiting the diversity of the people. Different traditions and many languages prevented the Indians from uniting. _______________________________________________ Britain encouraged competition among rival princes _______________________________________________ When all else failed the British used their superior weapons Cash Crop: a crop grown that is primarily for sale in the world rather than for the use by the country that produced it. East India Company The East India Company’s main goal was to make money. The British also: *Improved Roads *Introduced Western Education & Legal procedures *Worked toward ending slavery & the cast system *Improve the position of women within the family Ram Mohun Roy In 1803 he composed a tract denouncing India's religious divisions and superstitions and advocating a monotheistic Hinduism that would worship one supreme God. He revived pride in the Hindu culture by setting up educational societies and advocated freedom of speech and of religion, and denounced the caste system and suttee. He was hailed as the founder of Indian Nationalism Cause of Discontent The East India Company made several mistakes: *Required sepoys (Indian soldiers) to serve anywhere in India or overseas. *To the Hindus to serve overseas was an offense against their religion *The British pass a law that allowed Hindu widows to remarry. *Viewed as a Christian law to undermine Muslim beliefs. *According to Hinduism, three Lords rule the world. Brahma: the creator; Vishnu: the preserver and Shiva: the destroyer. *Lord Vishnu did his job of preserving the world by incarnating himself in different forms at times of crisis. *They outlawed the practice of Sati – the practice of throwing the surviving widow into the funeral fire. *The British issue new rifles to the sepoys. Part of the new method in firing the rifle is to bite off the tip of the cartridge before loading them. Cartridges are greased with animal fat from cows (which are sacred) or pigs (which are forbidden to Muslims) No firing of gun sent home without pay. The Rebellion & Aftermath The sepoys marched onto Delhi (old Mughal capital and hail the last Mughal ruler as their leader. The sepoys brutally massacre British men, women & children British Respond: The British crush the revolt and revenge earlier attacks by torching villages and slaughtering thousands of unarmed Indians Sepoy Rebellion Results: There were atrocities on both sides but Britain wins the “prize” and was best described as savage! 1858 British Empire steps in to control situation and set up colonial government. British lived like Southern “plantation masters”. Change in British Policy In 1858 Parliament ended the rule of the East Indian Company and put India under the British crown. The Rebellion had left a bad taste in both sides were filled with hatred, mistrust & fear. British Colonial Rule British policies were designed to fit India into the overall British economy. British officials believed they were helping them modernize by adopting technology and western culture. _________________________________________________ Britain built: • Roads & impressive railway systems • Able develop textile industries • British flood inexpensive machine made textiles ruining India’s once thriving hand weaving industry. • New communication through telegraph Population Growth & Famine Britain introduced new medical improvements and farming methods Led to population growth that put a strain on the food supply. Fields that once produced food were now cash crops. Late 1800’s famines sweep across India. (Is the Westernization good or bad?) Positive Impact on British Rule British creates peace & stability ______________________________________________________ Legal system promotes justice regardless of class or caste ______________________________________________________ Communication and transportation enhance Indian society ______________________________________________________ Bridge of country allow for understanding among different sects creating nationalistic feeling ______________________________________________________ Upper class send sons off to British schools to be educated Negative Impact of British Rule Destroyed ancient traditions _____________________________________________________ Indians at the bottom of the “caste” system- social structure _____________________________________________________ Little chance for social mobility ______________________________________________________ Ruined India’s once- prosperous-hand weaving industry Indian Nationalism The British believed that western educated Indians would form an elite class which would bolster British rule. western______________________________________________________ As it turned out, exposure to European ideas had the opposite effect. By the late 1800s, western educated Indians were spearheading a nationalist movement. ______________________________________________________ In 1885, nationalist leaders organized the Indian National Congress. Its members looked forward to eventual self-rule, but supported western style modernization. By the Indian National Congress was seen as primarily for the Hindu of the noble and middle classes. __________________________________________________ In 1906, Muslims formed the Muslim League to pursue their own goals, including a separate Muslim state. __________________________________________________ By 1912 the Muslims were calling for their own country! Mohandas Gandhi: Father of Resistance of British Rule • Led a middle class movement for independence • United Hindu population for Indian independence • Inspired the civil rights unit in the United States • Principal of “civil disobedience” came from reading American writer David Thoreau Known as the Mahatma, or the Great Soul, Gandhi forced change and an end to British imperialism through a strict policy of non-violence, or passive resistance. His civil disobedience included boycotts such as the Salt March (1930) and hunger strikes. ______________________________________________________ He also forced change at home by attempting to do away with the Hindu caste system. ______________________________________________________ The rigid caste system separated religious and political classes from lower classes of laborers and outcasts with no hope at social mobility. Therefore, the strength and will of the common people both achieved Indian independence and tore India apart. The story of Mahatma Gandhi and Indian nationalism is one of history's greatest ironies Why Was India Patronized ? The Impact of Imperialism (Chapter - 26 / Section - 5) By the 1900’s many of the nations had planted their national flag upon so much of the world’s foreign soils. The Great Powers of the world at this time were: Great Britain / Germany / France / Russia “The White Man’s Burden”: Promotes the Glories of Imperialism Rudyard Kipling Poem written in 1899 on US occupation of the Philippines “Take up the White Man's “burden”. Send forth the best ye breed, Go, bind your sons to exile “To serve your captives‘ need; To wait, in heavy harness, -On fluttered folk and wild, Your new-caught sullen peoples, -Half devil and half child.” Born in British India in 1865, Rudyard Kipling was educated in England before returning to India in 1882. Kipling was thoroughly immersed in Indian culture: by 1890 he had published in English about 80 stories and ballads previously unknown outside India. By the time of his death in 1936, he had come to be reviled as the poet of British imperialism, though being regarded as a beloved children's book author. New Economic Patterns During the Age of Imperialism a global economy emerged. Most of the profits from the imperial global exchange went to the industrialized nations The dominating western powers were France, England, Germany and the US. From these countries the finished good from their industries would flow into the regions of Asia, Africa and Latin America. Changes in local Economy The US offered an abundance of cheap labor, natural resources and agricultural goods _____________________________________________________ The demands of the new world economy disrupted traditional local economies of Africa and Asia. _____________________________________________________ Most people of these Continents grew & produced goods by hand for local use. Money Economy The Western capitalists developed plantations & mines but relied upon a steady flow of local labor. The barter system is replaced with money economy. TAXES Colonial powers would recover the cost of their territories by heavily taxing their subject. To meet the growing taxes men would travel across the nations to find jobs that could cover the taxes. Families were severely disrupted where the women would have to fend for all of the family needs. Children were sold off as slave labor ECONOMIC DEPENDENCY The new industrialized world created mass produced products that would severely disrupt the traditional handcraft industries. India was used by Britain to flood the country with cheap factory made clothing. Traditional Indian’s that produced hand-made clothing were driven out of business. MODERNIZATION Benefits of Colonial Rule: Modern banking system New communication systems New transportation systems (railroads) CULTURAL IMPACT Many of the European countries were convinced that they were superior. Their task was to civilize the rest of the world A leading promoter of British imperialism was Cecil Rhodes, “The more we inhabit the earth the better it is for the human race.” _____________________________________________________ WESTERNIZATION The term became to mean the same as modernization during the age of imperialism. Identity crisis Many of the conquered people began to buy into the understanding that they were inferior _____________________________________________________ The success of the westerner’s undermined the confidence in their own leaders _____________________________________________________ To become part of the western success non westerners would learn their rulers languages, customs and wear their clothing _____________________________________________________ However some would reject the colonial countries ways of life SCHOOLS The schools would teach reading and writing. Schools would train men for factory jobs HOSPITALS Medical breakthroughs: Vaccines Modern methods of hygiene Loss useful knowledge of local herbal healers RELIGION Missionaries spread the Christian faith across the globe Areas of great success were in Southern Africa where Christian teachings were adapted to local traditions NEW & OLD WAYS During the age of imperialism, western cultures experienced many changes. Old traditions, such as foot binding in China This can still be found in remote areas of Africa and Central America where the oval shaped-head is considered graceful and beautiful. The effect is achieved at an early age—an infant’s cranium, while it is still soft and malleable, is bound with bandages and wood in order to elongate and lengthen its shape. IMPACT ON WESTERN CULTURE Changes emerged as colonial powers were exposed to the colonies customs and resources. Food and art made their way into both NEW POLITCIAL TENSIONS Imperialism had wide political consequences as it spread across the world. Disrupted traditional political units (tribes) Imposed that rival peoples unite, ending civil wars. New nationalistic movements emerged from western educated colonists However, the competition among western powers for global empires caused increasing political tensions.