207_syllabus_F2015
advertisement
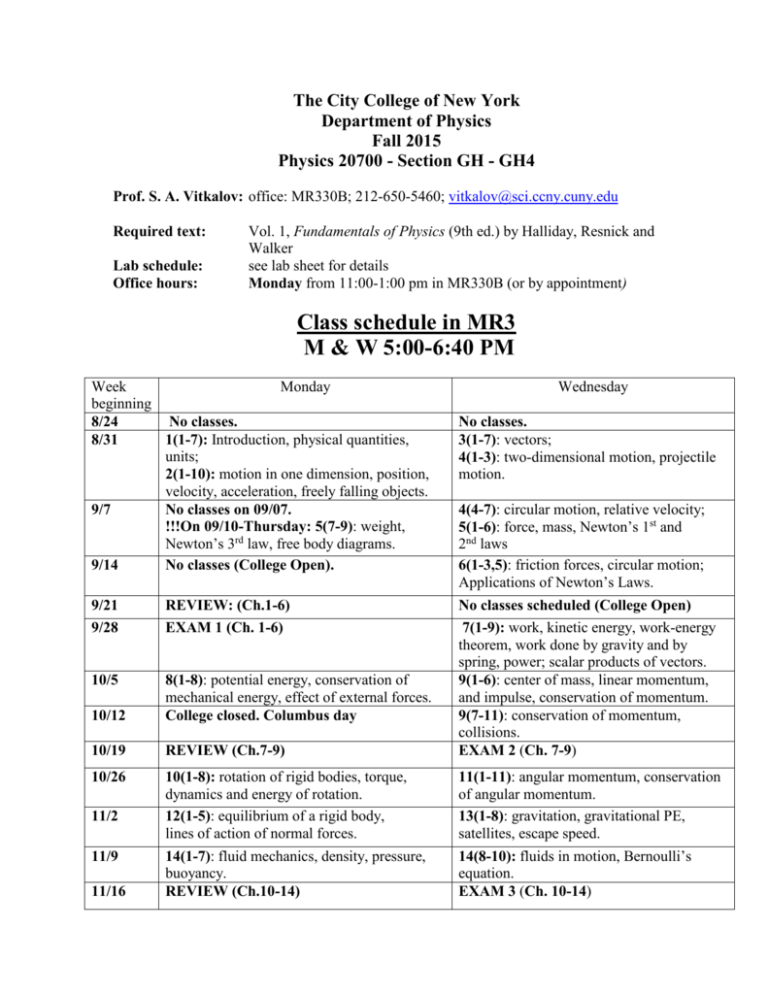
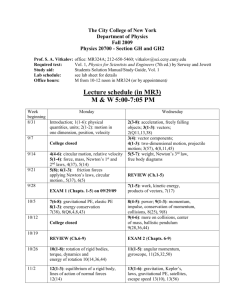
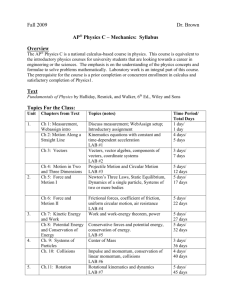
The City College of New York Department of Physics Fall 2015 Physics 20700 - Section GH - GH4 Prof. S. A. Vitkalov: office: MR330B; 212-650-5460; vitkalov@sci.ccny.cuny.edu Required text: Lab schedule: Office hours: Vol. 1, Fundamentals of Physics (9th ed.) by Halliday, Resnick and Walker see lab sheet for details Monday from 11:00-1:00 pm in MR330B (or by appointment) Class schedule in MR3 M & W 5:00-6:40 PM Week Monday beginning 8/24 No classes. 8/31 1(1-7): Introduction, physical quantities, units; 2(1-10): motion in one dimension, position, velocity, acceleration, freely falling objects. 9/7 No classes on 09/07. !!!On 09/10-Thursday: 5(7-9): weight, Newton’s 3rd law, free body diagrams. 9/14 No classes (College Open). Wednesday No classes. 3(1-7): vectors; 4(1-3): two-dimensional motion, projectile motion. 4(4-7): circular motion, relative velocity; 5(1-6): force, mass, Newton’s 1st and 2nd laws 6(1-3,5): friction forces, circular motion; Applications of Newton’s Laws. 9/21 9/28 REVIEW: (Ch.1-6) EXAM 1 (Ch. 1-6) 10/5 10/12 8(1-8): potential energy, conservation of mechanical energy, effect of external forces. College closed. Columbus day 10/19 REVIEW (Ch.7-9) No classes scheduled (College Open) 7(1-9): work, kinetic energy, work-energy theorem, work done by gravity and by spring, power; scalar products of vectors. 9(1-6): center of mass, linear momentum, and impulse, conservation of momentum. 9(7-11): conservation of momentum, collisions. EXAM 2 (Ch. 7-9) 10/26 10(1-8): rotation of rigid bodies, torque, dynamics and energy of rotation. 12(1-5): equilibrium of a rigid body, lines of action of normal forces. 11(1-11): angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum. 13(1-8): gravitation, gravitational PE, satellites, escape speed. 14(1-7): fluid mechanics, density, pressure, buoyancy. REVIEW (Ch.10-14) 14(8-10): fluids in motion, Bernoulli’s equation. EXAM 3 (Ch. 10-14) 11/2 11/9 11/16 11/23 15(1-5): oscillatory motion, simple harmonic motion, energy in SHM. 11/30 12/7 18(6-9):, thermal expansion, heat, specific heat; work and heat, internal energy. 19(4,5,8,11): kinetic theory of gases II. 12/14 REVIEW of P207 15(5-7): reference circle, pendulum; 18(1-5): Introduction to thermodynamics, temperature, thermometry. 18(10,11): first law of thermodynamics; 19(1-3): kinetic theory of gases, ideal gases 20(1-5): heat engines, second law of thermodynamics. Final exams: 12/15-12/23 HOMEWORK _____________________________________________________________________________ Week Topics covered Homework Assignment beginning _____________________________________________________________________________ 8/31 physical quantities, units, motion 1(1,3,9,12,21,23) in one dimension, position, velocity, 2(2,3,17,19,25,30,45,46,49,77) acceleration, freely falling objects ,vectors, 3(1,2,3,6,9,11,16,46) two-dimensional motion, 4(1,6,7,8,15,19,22,26,33) projectile motion ______________________________________________________________________________ 9/7 circular motion, relative velocity, 4(56,62,70) force, mass. Newton’s 1st and 2nd laws 5(3,4,7,17,31,49,55,57,65) weight, Newton’s 3rd law, ____________________________________________________________________________ 9/14 free body diagrams friction forces, circular motion 6(1,7,10,16,23,27,29) __________________________________________________________________________ 9/28 EXAM 1 (Chapts. 1-6) __________________________________________________________________________ 9/30 work, kinetic energy, potential energy 7(2,8,9,12,16,19,20,26,30,34,36,45) 10/5 energy conservation, power 8(1,2,3,5,10,11,13,49,54) center of mass, momentum, impulse, conservation of momentum 9(2,9,12,13,18) _____________________________________________________________________ 10/12 collisions, ballistic pendulum 9(25,39,49,52,58) _______________________________________________________________________________ 10/19 EXAM 2 (Ch. 7-9) _____________________________________________________________________________ 10/26 rotation of rigid bodies, torque 10(4,9,10,15,33,35,44,45,52,58) dynamics and energy of rotation, angular momentum 11(2,14,7,19,26,28,29,31,37,38,45,51) __________________________________________________________________________ 11/2 equilibrium of a rigid body, 12(3,5,12,17,21,40) lines of action of normal forces gravitation, satellites, 13(3,4,8,19) gravitational PE, escape speed ____________________________________________________________________________ 11/9 fluid mechanics, density, pressure, 14(3,4,14,18) buoyancy, fluid flow, Bernoulli’s equation 14(31,32,51,52,57,67) _________________________________________________________________ 11/16 EXAM 3 (Ch. 10-14) _____________________________________________________________________________ 11/23 oscillatory motion, simple harmonic motion, 15(1,7,11,15,27,29,30,31) energy in SHM, reference circle, pendulum, 15(39,41,42) introduction to thermodynamics, temperature _____________________________________________________________________________ 11/30 thermal expansion, ideal gas law, heat, 18(8,9,21,23,24,30) internal energy, work and heat, first law of thermodynamics 18(43,46,48) kinetic theory of gases, 19(3,4,11,15,19,2642,48,58) _____________________________________________________________________________ 12/7 second law of thermodynamics heat engines, 20(1,2,5,11) Important Information for Physics 20700 students: Course Objectives: Students are expected to understand the basic physics involved in mechanics (the study of motion and its causes) and in thermodynamics (the study of heat and work) which is needed for science and engineering. The emphasis will be on analytical reasoning and problem-solving skills. A list of course objectives is given below. Reading Assignment: The text material that will be covered in class each day is listed on the Class schedule. You should read the indicated sections in the textbook before coming to class. Solutions of some illustrative examples will be presented in lecture. Homework: The homework problems are taken from the textbook. In addition, students will be able to use WebAssign to practice solving homework problems online. WebAssign will evaluate your homework. You will need the access card that comes with your textbook. If you have purchased a used text, you will be able to purchase access to WebAssign online. To see detail of the access to WebAssign, please go to http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~vitkalov/teaching/teaching.html Grades: Grade will be based on the highest score obtained in a) and b): a) exams (3 midterms + final) 80% homework (WebAssign) 10% lab reports (7) 10% b) exams (3 midterms + final) lab reports (7) 90% 10% Exams: There will be three midterm exams (120 min.) and a final exam (140 min.). No exam grades will be dropped and no make-ups will be given except in the case of documented illness. Labs: The Physics Department Lab manual is available on line at http://www.ccny.cuny.edu/physics/upload/207.pdf The Physics Department Lab schedule is available on line at http://www.ccny.cuny.edu/physics/upload/Phys-207-lab-schd-fall-2015.pdf There are seven labs to be completed during the semester; see the schedule on the next page. Lab reports must be submitted at the beginning of the following lab period. Note that the grade of incomplete (INC) will be assigned for Physics 20700 if all seven lab reports have not been submitted by the required dates. Recitations: Please be aware that there has been a recent change in Physics 207. Instead of special sessions for tutoring, as in the past, this semester each week there will be either a lab or a recitation. The lab TA will be responsible EVERY week to teach the lab alternating with the recitation at the time and in the same room that is scheduled for the lab. The recitation sections for Intro Physics 207 are mandatory for students to attend. TAs are responsible for both lab and recitation for the assigned section: TAs will take attendance for recitations just as they do for the labs. Effort required: Don’t underestimate the amount of effort required for you to succeed in this course. Many students, in particular those who have not taken a previous course in physics, will need to spend 5-10 hours per week, every week, studying physics and doing the assigned homework problems, in addition to the time spent in lecture and lab (7 hours per week). Academic Integrity: Academic dishonesty is prohibited in the City University of New York and is punishable by penalties, including failing grades, suspension, and expulsion. Course objectives: After successfully completing this course, students should be able to 1. recognize and use SI units and be able to use vectors and their components. 2. understand the relationships between position, velocity, acceleration and time in the motion of physical objects 3. understand the concepts of force and equilibrium and their relation to Newton’s laws of motion. 4. understand and apply the concepts of work and energy, including kinetic and potential energy; understand and be able to use the principle of conservation of energy. 5. understand and apply the concepts of momentum and impulse; understand and be able to use the principle of conservation of momentum. 6. understand how to describe the rotation of physical objects; understand the concept of torque as applied to the equilibrium of objects. 7. understand gravitational interactions and their relationship to satellite motion. 8. understand the phenomenon of simple harmonic motion. 9. understand and apply the basic principles of fluid mechanics as applied to buoyancy and fluid flow. 10. understand the properties of temperature and heat. 11. understand and apply the first and second laws of thermodynamics involving work, heat and internal energy.