Solutions - School of Electrical
advertisement

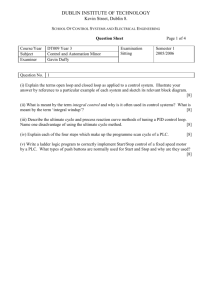
DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8. SCHOOL OF CONTROL SYSTEMS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Solution Sheet Course/Year Subject Examiner DT009 Year 3 Control and Automation Minor Gavin Duffy Question No. 1 Examination Sitting Page 1 of 8 Semester 1 Winter 2007/2008 (a) Types of pushbuttons: Start is normally open or press to close switch – done this way so that if wire breaks motor can’t start. Stop is normally closed or press to open switch – done this way so that if wire breaks the motor stops (it’s the same as pressing stop button). [4] Ladder logic – two ways of doing this. Option 1 is as follows: Option 2: DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8. SCHOOL OF CONTROL SYSTEMS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Solution Sheet Course/Year Subject Examiner DT009 Year 3 Control and Automation Minor Gavin Duffy Examination Sitting Page 2 of 8 Semester 1 Winter 2007/2008 Option 1 or 2 [4] (b) A proportional plus integral plus derivative controller is usually referred to as a three term controller. Equation is: Output Ke K de edt KTd Ti dt [2] The proportional term acts in proportion to the error. It acts on the present state of the error. [2] The integral term eliminates the proportional offset or steady state error. It acts on the past history of the error. [2] The derivative mode reduces the tendency towards oscillations and provides a control action which anticipates changes in the error signal. The derivative mode is useful if the process has sudden load changes. It anticipates the future direction of the error. [2] (c) Open loop - simple, inexpensive. Result of output not measured. Good knowledge of system required [2] Suitable example [2] Closed loop - more complicated but better. Output is measured and compared against setpoint to give an error. [2] Suitable example [2] DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8. SCHOOL OF CONTROL SYSTEMS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Solution Sheet Course/Year Subject Examiner DT009 Year 3 Control and Automation Minor Gavin Duffy Examination Sitting Page 3 of 8 Semester 1 Winter 2007/2008 (d) Ultimate cycle - set controller to P control only; increase gain until oscillations develop; stop increasing gain when system becomes unstable [3] Process reaction curve - place controller in manual mode; set output to a constant value and allow system to reach a steady state; make a step change in the output and record the process variable response with time [3] Disadvantage of ultimate cycle is that it operates on the borderline of instability - this could cause damage to plant and/or personnel [2] (e) Step 1 is Self Test – check for errors in hardware/software Step 2 is Input Scan – Reads input values from input cards to the memory Step 3 is Execute Logic – each ladder in program is executed and outputs are updated Step 4 is Output Scan – Writes output values from memory to output cards [8] DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8. SCHOOL OF CONTROL SYSTEMS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Solution Sheet Course/Year Subject Examiner DT009 Year 3 Control and Automation Minor Gavin Duffy Question No. (a) 2 Examination Sitting Page 4 of 8 Semester 1 Winter 2007/2008 Channel configuration [4] Averages for channels [4] Read averages for channels [4] Comments [4] (Note – above code has a length of read/write of 3 on the second and third lines. This can also be done using individual lines of code.) DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8. SCHOOL OF CONTROL SYSTEMS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Solution Sheet Course/Year Subject Examiner DT009 Year 3 Control and Automation Minor Gavin Duffy Examination Sitting V+ I+ VIFG Channel 1 Input Terminals V+ I+ VIFG Channel 2 Input Terminals V+ I+ VIFG Channel 3 Input Terminals V+ I+ VIFG Channel 4 Input Terminals Page 5 of 8 Semester 1 Winter 2007/2008 [6] (b) Shield is a metal foil covering wire to prevent electrostatic coupling or electric field effects and is grounded at one point only [4] Twisting is to prevent inductive coupling due to magnetic field effects. Voltages are still induced but in opposite directions. [4] DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8. SCHOOL OF CONTROL SYSTEMS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Solution Sheet Course/Year Subject Examiner DT009 Year 3 Control and Automation Minor Gavin Duffy Question No. 3 Page 6 of 8 Examination Sitting Semester 1 Winter 2007/2008 (i) Convert the system into a single block to give the equation below: KpK KpK KpK 1 K pK o s s 1 K p K s 1 K p K i s 1 s 1 1 K pK s 1 the overall output over input = transfer function the static gain is above the line the time constant is the constant in the s term (ii) new [4] [4] [4] 1 10 1 K pK 10 1 K p K K pK 9 Kp 9 3 3 i.e. proportional gain = 3 [5] At steady state we have: KpK o s 9 0.9 i s 1 K p K 1 9 o s 0.9 i s E ( s) steadystate i s o s i s 0.9 i s 0.1 i s Therefore, the error is 10% of the input. [5] (iii) Proportional offset is the steady state error observed when using proportional control. [2] It can be removed by adding integral action. The integral term acts on the integral of the error and removes any steady state error. [2] (iv) Yes. A high gain may result in overshoot and undershoot oscillations which may not die off. This causes instability. [4] DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8. SCHOOL OF CONTROL SYSTEMS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Solution Sheet Course/Year Subject Examiner DT009 Year 3 Control and Automation Minor Gavin Duffy Question No. 4 (i) P&ID TIC-01 Examination Sitting Page 7 of 8 Semester 1 Winter 2007/2008 [6] HS-01 TET-01 TK-01 Hot Water Supply Tank (ii) Error = SP – PV (PV = Temp in this case). [2] When error is positive, heater is On. When error is negative, heater is Off. [2] Without deadband – can get rapid switching of output (chattering) if error is hovering around zero or traveling slowly through zero. PV stays as close to SP as possible. [2] If deadband is added, frequency of switching is reduced but PV fluctuates more. [2] DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8. SCHOOL OF CONTROL SYSTEMS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Solution Sheet Course/Year Subject Examiner DT009 Year 3 Control and Automation Minor Gavin Duffy Examination Sitting Page 8 of 8 Semester 1 Winter 2007/2008 (iii) PLC Error SPPV i SP + o Temp Controller On-Off Process Water Tank - A/D card Transmitter RTD [8] (iv) Temperature Temp off 67ºC 65ºC 63ºC off on on Power Time [6] Error +ve 0 -ve Time [2]