Echinodermata
advertisement

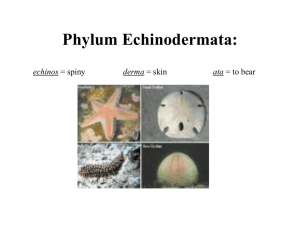
Phylum Echinodermata Classes Cut out and paste on 3 X 5 Notecard Draw and Color Organisms on Backside of Card Class Asteroidea Class Asteroidea 1. Have 5 arms usually 2. Mouth located in center of oral surface pointing downward 3. Has a Water Vascular System with tube feet 4. Has Mouth and Stomach 5. Has short intestine – extends from stomach to anus. 6. Endoskelton made up of calcareous plates that penetrate the dermis as spines 7. Between the spines and plates are projections called papulae, which function in gas exchange and excretion 8. Other projections on the body wall include tiny jaw-like appendages called pedicellaria 9. Has Photoreceptors 10. Examples: Starfish, Brittle stars 1. Have 5 arms usually 2. Mouth located in center of oral surface pointing downward 3. Has a Water Vascular System with tube feet 4. Has Mouth and Stomach 5. Has short intestine – extends from stomach to anus. 6. Endoskelton made up of calcareous plates that penetrate the dermis as spines 7. Between the spines and plates are projections called papulae, which function in gas exchange and excretion 8. Other projections on the body wall include tiny jaw-like appendages called Pedicellaria 9. Has Photoreceptors 10. Examples: Starfish, Brittle stars Class Ophiuroidea Class Ophiuroidea 1. Characteristics similar to class Asteroidea 2. Main difference between starfish and brittle stars is brittle stars have much thinner arms. 3. Examples: Brittle stars Class Echinoidea 1. No arms 2. Body is enclosed in a shell or test 3. Body surface is usually covered with moveable spines 4. Spherical body 5. Ambulacral plates bearing tube feet that radiate out toward the aboral surface 6. Use podia and spines during locomotion 7. The spines are moveable and articulate with the with the calcareous ossicles 8. Examples: Sea Urchins, Sand Dollars 9. Feeding – Scrap algae off of rocks then using a chewing apparatus called Aristotle's Lantern 1. Characteristics similar to class Asteroidea 2. Main difference between starfish and brittle stars is brittle stars have much thinner arms. 3. Examples: Brittle stars Class Echinoidea 1. No arms 2. Body is enclosed in a shell or test 3. Body surface is usually covered with moveable spines 4. Spherical body 5. Ambulacral plates bearing tube feet that radiate out toward the aboral surface 6. Use podia and spines during locomotion 7. The spines are moveable and articulate with the with the calcareous ossicles 8. Examples: Sea Urchins, Sand Dollars 9. Feeding – Scrap algae off of rocks then using a chewing apparatus called Aristotle's Lantern Class Holothuroidea 1. No arms 2. Endoskeleton is reduced to a few Ossicles on the surface 3. Fairly soft-bodied 4. Locomotion – using false feet and by muscular contractions 5. Examples: Sea Cucumber 6. Oral end of the body has a group of tentacles surrounding the mouth; used in feeding 7. Have a muscular cloaca that is partly used in gas exchange 8. Gas exchange structures are branching structures called respiratory trees Class Holothuroidea 1. No arms 2. Endoskeleton is reduced to a few Ossicles on the surface 3. Fairly soft-bodied 4. Locomotion – using false feet and by muscular contractions 5. Examples: Sea Cucumber 6. Oral end of the body has a group of tentacles surrounding the mouth; used in feeding 7. Have a muscular cloaca that is partly used in gas exchange 8. Gas exchange structures are branching structures called respiratory trees Class Crinoidea 1. Most primitive of echinoderms 2. Oral surface is upward 3. Has a stalk 4. Body portion attached to the stalk is the crown; 5. Has branches called pinnules 6. Ciliated around the mouth Class Crinoidea 1. Most primitive of echinoderms 2. Oral surface is upward 3. Has a stalk 4. Body portion attached to the stalk is the crown; 5. Has branches called pinnules 6. Ciliated around the mouth