Biology 9 to 12 - Dominican
advertisement

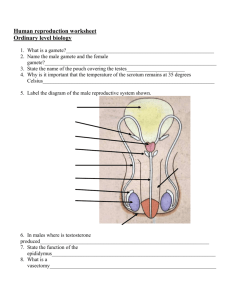
Biology: 9. The Senses and the Nervous System Syllabus OB28 Recall five sense organs in the human (eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue) and understand how these enable humans to gather information from their surroundings OB29 Describe the role of the central nervous system and the sensory and motor functions of nerves OB30 Locate the main parts of the eye on a model or diagram and describe the function of the cornea, iris, lens, pupil, retina, optic nerve and ciliary muscle Student Notes Humans have five sense organs; eyes, ears, nose, skin and tongue The central nervous system The central nervous system is composed of the brain plus the spinal cord. Its function is to rapidly transmit messages to and from the brain to all other parts of body and to coordinate the body’s response. The spinal cord carries signals to and from the brain in the form of electrical impulses. Sensory organ Eyes Ears Nose Skin Tongue Sense Vision Hearing Smell Touch Taste Sensory and motor nerves Sensory nerves carry signals towards the central nervous system. Motor nerves carry signals away from the central nervous system. Communication between sense organ and brain 1. The sensory organ (e.g. the eye) receives a stimulus (e.g. sunlight). 2. A message is sent from sense organ to brain or spinal cord via a sensory nerve. 3. The brain or spinal cord decides what to do (e.g. reduce size of iris) then sends a message along the motor nerves to the muscles and glands which cause them to respond. The Eye Part Function Cornea Allows light to pass into the eye Iris Controls the amount of light that enters the eye (it acts like a shutter) Focuses light on the retina Lens Pupil Retina Opening through which light enters the back of the eye Absorbs light and produces nerve impulses Optic nerve Carries messages from the eye to the brain Ciliary muscle Changes the shape of the lens when we look at near or far objects 1 Exam Questions 1. [2007] Nerves carry electrical messages around our bodies. Nerves have motor functions and sensory functions. Explain the underlined terms. 2. [2007 OL] Choose the correct part of the human body from the list on the right to complete the following sentence. The _________________ detects light. Eye Joint Kidney Muscle 3. [2007] The diagram is of the human eye. Name the part labelled A. 4. [2007] What function has the ciliary muscle? 5. [2008 OL] The diagram shows the human eye. Examine the diagram and answer the questions that follow. (i) In the table write the letter A beside the name of the part labelled A. (ii) In the table write the letter B beside the name of the part labelled B. (iii) In the table write the letter C beside the function of the part labelled A. (iv) In the table write the letter D beside the function of the pupil. 6. [2008] Give the function of the iris 7. [2008] Give the function of the pupil. 8. [2008] The pupil is transparent. Why does the pupil appear to be black in most situations? 9. [2009 OL] In the table write the letter L beside the name of an organ which detects light. Write the letter S beside the name of an organ which detects sound. 2 Brain Eye Heart Ear Other Test Questions 1. Name the five sense organs and state what stimulus each sense organ responds to (e.g. “the eye responds to sight”). 2. The central nervous system consists of the __________________ and the ________________. 3. What is the function of the central nervous system? 4. There are two types of neuron: sensory and motor. What is the difference between them? 5. Draw a diagram of the eye and include each of the following: the cornea, iris, lens, pupil, retina, optic nerve and ciliary muscle. 6. Give the function of each of the parts named above using the table below: Eye part The cornea The iris The lens The pupil The retina The optic nerve The ciliary muscle Function 3 Biology: 10. Human Reproduction Syllabus OB31 Use wall charts or other illustrative diagrams to identify and locate the main parts of the male and female reproductive systems OB32 Recall that the menstrual cycle lasts about 28 days and that menstruation occurs at the start of the cycle OB33 Understand the following in relation to human reproduction: • fertile period in the menstrual cycle • sexual intercourse • fertilisation is the fusion between male and female gametes (sperm and egg) resulting in a zygote; a zygote undergoes cell division and develops within the womb into a foetus • pregnancy and birth • growth and puberty OB34 Understand that there are many forms of contraception, and that some of these prevent fertilisation Student Notes The male sex cell is called sperm; the female gamete is called the egg. Fertilisation is the fusion between a sperm and an egg Fertilisation occurs in the fallopian tube The male reproductive systems Part Testes Function To produce sperm Scrotum To hold the testes outside body, which favours sperm production (temp = 2oC lower) To carry sperm from the testes to the penis Sperm duct Prostate gland Penis To produce fluids which nourish the sperm (fluid + sperm = semen) To deliver sperm into the woman’s body The female reproductive systems Part Ovary Fallopian tube Womb (uterus) Function To produce eggs To carry the egg towards the womb. Fertilisation occurs here. To hold the baby during pregnancy Cervix The entrance to the womb Vagina To hold the penis during sexual intercourse. To allow childbirth The menstrual cycle 4 Menstruation is the shedding of the lining of the uterus (commonly referred to as ‘having a period’) The menstrual cycle lasts about 28 days and menstruation occurs at the start of the cycle Ovulation is the release of an egg from the ovary and occurs around day 14 A woman is most likely to be fertile (be able to conceive) for a few days either side of day 14 Sexual intercourse occurs when the erect penis of the male is placed in the vagina of the female Fertilisation is the fusion between male and female gametes (sperm and egg) resulting in a zygote A zygote undergoes cell division and develops within the womb into a foetus 1. 2. 3. 4. Pregnancy: the foetus inside the womb Implantation occurs when the dividing zygote (ball of cells) attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. Human pregnancy usually lasts about 40 weeks After 8 weeks the embryo is recognisable as a human and is the called a foetus. Placenta acts as a link between the mother’s bloodstream and that of the developing embryo (it brings in nutrients and takes away waste). The birth itself Contractions begin (muscles in the uterus contract). ‘breaking of the waters’ (liquid, or amniotic fluid or fluid escapes). Cervix dilates(widens). The baby is pushed through the cervix (into the vagina) Growth and puberty Puberty is the stage in life during which a person becomes sexually mature In girls: 1. Puberty brings about an increase in size of ovaries and womb 2. Marks the start of the menstrual cycle. 3. Other characteristics include pubic hair, wider hips, growth spurt, breasts grow, ‘spots’. In boys: 1. Puberty brings about an increase in the size of the penis and testes. 2. Marks the start of semen production. 3. Other characteristics include pubic, facial and body hair; growth spurt; deeper voice, increased muscle, ‘spots’. Contraception Contraception involves the prevention of a woman getting pregnant. There are many forms of contraception: 1. Using a condom. 2. Taking ‘the pill’ which prevents an egg forming or being released in the ovary. 3. Surgery to close off the sperm ducts or fallopian tubes. 5 Exam Questions 1. [2008] Explain the term fertilisation. 2. [2008 OL] The diagram shows the male reproductive system. (i) In the table on the right write the letter A beside the name of the part labelled A. (ii) Write the letter B beside the name of a substance produced by B. 3. [2006 OL] Name the parts of the female reproductive system labelled A and B in the diagram on the right. 4. [2008] (i) Mark clearly on the diagram, using an arrow and the label S, where the semen (liquid containing sperm) was released into the female. (ii) Mark clearly on the diagram, using an arrow and the label F, where fertilization took place. 5. [2009 OL] The diagram shows the female reproductive system. (i) In the table write the letter A beside the name of the part labelled A. (ii) Write the letter B beside the name of the gamete produced by B. 6. [2009] The diagram shows a sperm. The tail enables the sperm to swim. (i) Why does the sperm need to be able to swim? (ii) Where does fertilisation occur? 7. [2006] What happens in the ovary during the fertile period of the menstrual cycle? 8. [2006] What happens to the lining of the uterus during the fertile period of the menstrual cycle? 9. [2008] State two events that occur in the hours before birth and one event that takes place shortly after the baby is born. 6 Other Test Questions 1. What is the male sex cell called? 2. What is the female sex cell called? 3. On what days of a girl’s menstrual is she most fertile? 4. Why is she most fertile on these days? 5. What is the function of the placenta? 7 Biology: 11. Genetics Syllabus OB35 Understand that humans have inheritable and non-inheritable characteristics, and that inheritable characteristics are controlled by genes OB36 Recall that genes are located on chromosomes and that in a human there are 23 pairs of chromosomes, which are located in the nucleus OB37 Recall that chromosomes are made of DNA and protein. Student Notes Genetics is the study of heredity Inherited characteristics such as eye and hair colour are controlled by genes Non-inherited characteristics, such as playing a guitar or riding a bike, must be learned Genes are found on chromosomes In a human there are 23 pairs of chromosomes (i.e. 46 chromosomes) Chromosomes are located in the nucleus of a cell Chromosomes are made of DNA and protein 8 Exam Questions 1. [2007] (i) Where is DNA located in cells? (ii) Name a second substance associated with DNA. 2. [2008] At certain stages in the life of a cell thread-like structures that contain genes can be seen in the nucleus. (i) What are these thread-like structures called? (ii) Genes are located on these thread-like structures. Give a role that genes play in life processes. 3. [2006] Eye colour, hair texture and many other human characteristics are controlled by genes. (i) Name the structures in the nuclei of our cells where genes are located. (ii) Name the substance that genes are made of. Ability to drive Freckled skin 4. [2009 OL] Tongue rolling Inheritable characteristics are controlled by genes. Ability to knit Write the letter I beside two inheritable characteristics in the table. 9 Biology: 12. Photosynthesis and Plant Responses Syllabus OB48 Describe, using a word equation, how plants make their own food through photosynthesis OB49 Show that starch is produced by a photosynthesising plant OB50 Investigate the growth response of plants to gravity (geotropism) and light (phototropism) Student Notes Photosynthesis is the way in which plants make food Plants take in carbon dioxide from the air and water from the ground. Plant cells then combine this with chlorophyll (which is already in the cells) and sunlight to produce food in the form of glucose. Oxygen is produced as a by-product and is released into the atmosphere. Word equation for photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + Water (+ sunlight and chlorophyll) → glucose + oxygen To show that starch is produced by a photosynthesising plant Starch is a form of glucose To test for starch add a drop of iodine and the material should turn blue-black if starch is present. Procedure 1. Place a plant in the dark for a few days so that all the starch moves out of the leaves. 2. Place aluminium foil over one of the leaves and put the plant in strong sunlight for a day. 3. Put the leaves in boiling water for a minute to kill and soften them. 4. Soak the leaves in alcohol for a few minutes to remove the chlorophyll (this also makes them brittle). 5. Dip the leaves in boiling water again rinse and soften them. 6. Test for starch by putting drops of iodine on the leaves. Result The leaves will go blue-black indicating that starch is present, with the exception of the leaf which was covered with aluminium foil. There is no starch in this leaf because photosynthesis couldn’t occur since there was no sunlight. Geotropism and phototropism A tropism is the response of a plant to a stimulus Geotropism is the response of a plant to gravity To investigate geotropism Procedure 1. Soak some broad bean seeds in water for a day or two to begin germination. 2. Insert the seeds just inside the glass of a beaker of soil, making sure to turn the seeds in lots of different directions. 3. After a few days the plants will start to grow, but in each case the shoots will grow upwards and the roots will grow downwards. Phototropism is the response of a plant to light To investigate phototropism Procedure 1. Place some germinating seeds onto a petri dish of moist cotton wool. 2. Place the petri dish into a covered shoe-box which has a hole at one end and leave it beside a window for a week. 3. Take the cover off of the shoe-box and note that the plant has started to grow towards the hole in the box. 10 Exam Questions 1. [2009] Name two processes that the leaves of green plants carry out. 2. [2007] Pondweed is a green plant that lives in water. In the presence of light pondweed undergoes photosynthesis and a gas is produced as one of the products. Name the gas produced. 3. [2007] Pondweed and all green plants take in and use another gas, from their environment during photosynthesis. Name the gas taken in. 4. [2007] How might the rate of production of bubbles, by the pondweed, be increased? 5. [2007 OL] The diagram shows a plant that was left in sunlight for a few days. A test was carried out in the laboratory on a part of the plant to see if it had made food (starch). Answer the following questions using the table. (i) Write the letter F beside the name of the process by which plants make food. (ii) Write the letter P beside the name of the part of the plant where most of the food (starch) is made. (iii) Write the letter C beside the name of the substance which gives plants their green colour. (iv) Write the letter S beside the name of the chemical that produced a blueblack colour when it is used to test for starch. 6. [2008 OL] Plants make their own food using sunlight. Choose a word from the list on the right that correctly completes each of the statements below. (i) The part of a plant where most food is made is the __________________ . (ii) The chemical used to test if a plant has made food (starch) is _________________ . Root Leaf Iodine Litmus 7. [2006] The plant shown in the diagram was left in total darkness overnight and then exposed to strong sunlight for four hours. The leaf with the foil was removed from the plant and tested for starch. Clearly state the result you would expect from this test. What conclusion can be drawn? 8. [2009 OL] Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants make food (starch). Describe an investigation to show that starch is produced by a photosynthesising plant. Use the following headings: Equipment, Procedure, Result, Labelled diagram 9. [2007 OL] How do plants respond to light? 10. [2007 OL] Describe, with the help of a labelled diagram, how you could set up an investigation to show how plants respond to light. Use the following headings: Equipment: Procedure: Result: Labelled diagram 11. [2009 OL] The diagram shows a plant which was left stand inside a window for a long period. (i) What caused the plant to grow towards the window? (ii) Name this growth response of plants. 11