Economics Practice Test: Market Systems & Economic Questions
advertisement

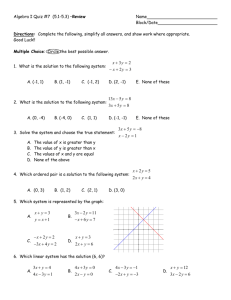
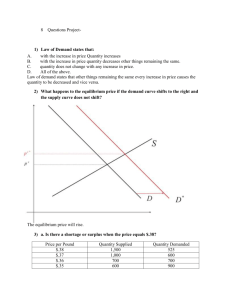
Practice test #1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. Which of the following is NOT characteristic of a centrally planned economy? a. The central government owns all land and capital. b. The central government makes all economic decisions. c. Each collective or factory sets its own goals. d. Each person is assigned a job. 2. What is the struggle among various producers for the consumer’s business called? a. socialism c. incentive b. competition d. self-regulation 3. Why does even a free market economy need some government intervention? a. to provide for things that the marketplace does not address b. to ensure that the government has the freedom to tax as necessary c. to make sure that the government can fulfill its needs for military personnel d. so that the government has some control over factor resources 4. Which of the following is NOT a key economic question? a. What goods and services should be produced? b. How should these goods and services be produced? c. Who consumes these goods and services? d. How should it be ensured that goods and services are paid for? 5. What does the process of specialization do for an economy? a. It eliminates unemployment. c. It fosters competition. b. It makes it more efficient. d. It makes it easier to control. 6. How could the Chinese economy be characterized? a. free market b. centrally planned c. mixed, but on the side of centrally planned d. mixed, but on the side of free market 7. What is one of the most important advantages of a free market? a. It can change rapidly. c. It is easy to regulate. b. It protects the less fortunate. d. It encourages growth. 8. What incentive motivates a manufacturer to sell a product? a. making profits on sales c. pleasing the consumer b. putting others out of business d. popularity of the product 9. Which of the following was a free market philosopher? a. Karl Marx c. Vladimir Lenin b. Adam Smith d. Friedrich Engels 10. Which of the following is characteristic of a traditional economy? a. Communities tend to be fast-growing. b. They are usually based on light industrial production. c. They have a high standard of living. d. Children tend to have the same jobs as their parents did. 11. What is the product market? a. the market in which payments are received for selling products to consumers b. the market in which income is received for supplying land, labor, or capital ____ 12. ____ 13. ____ 14. ____ 15. ____ 16. ____ 17. ____ 18. ____ 19. ____ 20. ____ 21. ____ 22. c. the market in which firms purchase the factors of production from households d. the market in which households purchase the goods and services that firms produce What incentive do manufacturers have to sell their products? a. making profits on sales c. putting others out of business b. pleasing the consumer d. popularity of the product In what kind of an economy does the government make all the decisions? a. socialist c. centrally planned b. laissez faire d. free enterprise What is the purpose of competition? a. to act as a regulating force in the marketplace b. to cause producers to attempt to put each other out of business c. to cause buyers to have to be careful about spending their money d. to act as a motivating force behind the free market What is the function of an economic system? a. to make sure all people have equal access to goods b. to produce and distribute goods and services c. to give all producers the same access to consumers d. to make sure people are paid for their labor Which of the following is a condition that most people would NOT expect the safety net of the government to provide for? a. injuries c. natural disasters b. joblessness d. low income How would the economy of Canada be likely to be characterized? a. free market b. centrally planned c. mixed, but on the side of centrally planned d. mixed, but on the side of free market What is an important advantage of a free market? a. It does not change unless the government directs it. b. It offers a wide variety of goods and services. c. It is easy to regulate. d. It protects the less fortunate. Who was the leader that introduced communism and central planning to the former Soviet Union? a. Karl Marx c. Vladimir Lenin b. Joseph Stalin d. Friedrich Engels What is the motivating force behind the free market? a. competition c. self-interest b. the invisible hand d. specialization What might be a hardship for citizens of a centrally planned economy making a transition to a market-based system? a. Farmers would have to grow the crops that the government instructed them to. b. Only poor quality goods would be available to consumers, because manufacturers focused on quantity, not quality. c. Workers would lose job security and guaranteed incomes. d. Entrepreneurs would have fewer opportunities to start new businesses. A person who believed in the doctrine of laissez faire would disapprove of a. the invisible hand of the marketplace. b. consumer sovereignty. c. self-interest as the motivating force in the free market. ____ 23. ____ 24. ____ 25. ____ 26. ____ 27. ____ 28. ____ 29. ____ 30. ____ 31. ____ 32. ____ 33. d. government funding of education. Which of the following does a government provide as part of a safety net for the people? a. general elections every four years c. a strong military defense b. unemployment compensation d. regulation of commerce Suppose there is a family in which all the boys are expected to become farmers when they are adults, just as their fathers and grandfathers did. In which kind of economy do they participate? a. false economy c. traditional economy b. command economy d. centrally planned economy You are an entrepreneur with an innovative idea for a new business. In which kind of economy would you have the most opportunity to try to achieve success? a. market economy c. traditional economy b. command economy d. economy of scale Why do markets exist? a. Markets ensure that government does not intervene in the production of goods and services. b. Markets provide self-sufficient people with public places for the exchange of ideas. c. Markets ensure economic equity for all people. d. Markets allow people to buy what they need to consume and sell the specialized goods and services they produce. Households pay firms for goods and services. Firms supply households with goods and services. The purchase and supply of goods and services takes place in the a. product market. c. after market. b. factor market. d. traditional market. Which of the following goals is difficult to achieve in a pure free market system? a. economic efficiency c. economic freedom b. economic equity d. economic growth A government prints and distributes posters to inspire workers to increase their productivity. In which kind of economy does this most likely take place? a. weak economy c. market economy b. traditional economy d. centrally planned economy A person believes that real equality can only exist when political equality is coupled with economic equality. This person believes that democratic means should be used to distribute wealth evenly throughout society. This person is a a. socialist. c. capitalist. b. communist. d. authoritarian. Collectives in the Soviet Union were inefficient producers of agricultural products. Why? a. The farms were too small to produce substantial crops. b. Most farmers were poor and had to pay for their own equipment, seeds, and fertilizer out of their own pockets. c. Farm workers had guaranteed incomes, so they had few incentives to produce more or better crops. d. Soviet central planners ignored the farms in favor of factories producing consumer goods. Which of the following is NOT a weakness of centrally planned economies? a. Most workers lack job security. b. Consumers’ needs are generally not met. c. Workers lack incentives to be innovative. d. Individual freedoms are sacrificed for societal goals. The economy of China is in transition. What does this mean? a. Investments are determined by state control instead of by private decision. ____ 34. ____ 35. ____ 36. ____ 37. ____ 38. ____ 39. ____ 40. ____ 41. ____ 42. ____ 43. b. The economy is moving from central planning toward a market-based system. c. Individual firms are in the process of being sold to the state. d. The government rarely interferes in the free market and is highly receptive to foreign investment. In which of the following lists of mixed economies does the market system dominate? a. France, Canada, South Africa, United Kingdom b. United States, United Kingdom, Singapore, Hong Kong c. Cuba, Greece, China, United States d. Russia, Peru, France, Canada When a consumer is able and willing to buy a good or service, he or she creates which of the following? a. consumption c. elasticity b. demand d. allocation What determines the price and the quantity produced of most goods? a. the consumer’s perception of necessity b. the interaction of supply and demand c. the availability of substitutes for the goods d. the quality of the goods that are produced What are inferior goods? a. goods that are not well produced b. goods that no one wants to buy c. goods for which the demand rises when income falls d. goods for which the demand falls when income rises How is future price related to current demand? a. If the price is expected to rise, current demand will drop. b. If the price is expected to fall, current demand will rise. c. If the price is expected to rise, current demand will rise. d. Future price is not related to current demand. What determines how a change in prices will affect total revenue for a company? a. elasticity of demand c. values of elasticity b. the company’s pricing policy d. the consumers’ incomes What kind of system is the United States economy based on? a. cause and effect c. market b. centralized d. production Ceteris paribus, or “all other things held constant,” is an assumption that has which of the following effects on a demand schedule? a. It takes only prices into account. b. It considers the effects of all possible changes on demand. c. It is accurate no matter what changes occur. d. It is accurate only at one price level. What shows the quantities of products demanded at each price by all consumers in a market? a. an elasticity and consumption list c. a market pricing list b. a schedule of consumer prices d. a market demand schedule How did the existence of the baby boom generation change demand in the United States? a. Demand was raised for different goods with each age the baby boomers reached. b. After they reached the teenage years, the baby boomers were integrated into the society and no longer affected demand. c. People were poorer because they had so many children, so demand was lowered. d. The baby boomers did not raise demand until they became adults, when they had their own money to spend. ____ 44. What does it mean when the demand for a product is inelastic? a. People will not buy any of the product when the price goes up. b. A price increase does not have a significant impact on buying habits. c. Customers are sensitive to the price of the product. d. There are very few satisfactory substitutes for the product. ____ 45. What kind of table lists the quantity of a good that a person will buy at different prices? a. demand schedule c. market demand schedule b. demand curve d. market demand curve ____ 46. What is a basic principle of the law of demand? a. The higher the price, the more people will want the good. b. Everyone has a limited income that they will spend. c. When a good’s price is lower, people will buy more of it. d. Services are of interest in the same way that goods are. ____ 47. How is the current demand for a good related to its future price? a. If the price is expected to drop, current demand will fall. b. If the price is expected to drop, current demand will rise. c. If the price is expected to rise, current demand will fall. d. Current demand is not related to future price. ____ 48. Which of the following is a good that might not be bought when prices rise? a. complement c. inferior good b. substitute d. luxury ____ 49. What kind of changes would be expected in the demand of a country that has a growing population? a. a rise in the demand for recreation b. a shift in the demand for high-quality food c. a rise in the demand for shelter d. a lowering in the demand for automobiles ____ 50. A shift in the demand curve means which of the following? a. a change in demand at every price b. a rise in prices c. a decrease in both price and quantity demanded d. a change in consumer income ____ 51. What does unitary elastic demand mean? a. The elasticity of demand is mathematically determined. b. The elasticity of demand is different at each unit on the price range. c. The demand is inelastic at a low price but becomes elastic as the price rises. d. The percentage change in quantity demanded is exactly equal to the percentage change in price. ____ 52. What is a company’s total revenue? a. the price of a company’s goods b. the amount a company receives for selling its goods c. the amount of goods a company can expect to sell d. the amount of profit a company can expect to make ____ 53. When prices rise, which of the following happens to income? a. It goes down. c. It rises to meet prices. b. It buys less. d. It is used to buy different things. ____ 54. Which of the following goods would be likely to be bought in the same quantity even if it doubled in price? a. shoes c. pencils b. telephones d. computers ____ 55. Which of the following events could cause the demand curve for sports magazines to shift to the right? ____ 56. ____ 57. ____ 58. ____ 59. ____ 60. ____ 61. ____ 62. ____ 63. a. The publisher cuts the price of an issue from $3.95 to $2.50. b. The price of an issue of a popular computer game magazine rises from $2.95 to $3.95. c. A star basketball player interests thousands of people in professional sports for the first time. d. A local library buys a subscription to the sports magazine for its reading room. The price of movie tickets in a town has risen from $7 to $9. What is the most likely effect of the change in price? a. The demand curve for movie tickets will move right. b. The quantity demanded of movie tickets will increase. c. The demand curve for movie tickets will move left. d. The quantity demanded of movie tickets will decrease. Alex receives a raise at work and continues to work the same number of hours each week. His demand for $3 t-shirts, which he considers an inferior good, will a. increase. c. stay the same. b. decrease. d. have no relation to his income. Demand for movie rentals is highly elastic. A video store that raises the price of a rental will a. lose revenue. c. possibly gain or lose revenue. b. gain revenue. d. see no change in revenue. When movie rentals were $2.95, Sara rented ten movies a month. The price of a rental increased by fifty cents and Sara decided to rent two fewer movies a month. When the price increased by one more dollar, Sarah decided to cut the number of movies she rented in half. What is her quantity demanded by month at the current price? a. five c. four b. one d. two Will, a sprinter on the track team, has inelastic demand for sports drinks. The local store has raised the price of a sports drink from $1.00 to $1.50. Which of the following could describe Will’s response to the price change? a. He bought 15 bottles a month at $1.00 and 20 bottles a month at $1.50. b. He bought 10 bottles a month at $1.00 and 8 bottles a month at $1.50. c. He bought 15 bottles a month at $1.00 and 5 bottles a month at $1.50. d. He bought 10 bottles a month at $1.00 and 5 bottles a month at $1.50. Which of these events could permanently shift a individual’s demand curve for umbrellas to the right? a. He buys a car so he no longer needs to walk to and wait at a bus stop every morning to get to work. b. He moves from a desert community to a rainy city by the ocean. c. The price of umbrellas decreases significantly as inexpensive umbrellas are imported from China. d. Weather forecasters predict that a major hurricane will hit his city the following week. Jasmine is willing to buy 40 pencils at 25 cents apiece. When the price is ten cents apiece, she is willing to buy 100 pencils. Which of the following statements could be true about Jasmine’s demand for pencils? a. She will buy 80 pencils at 15 cents apiece. b. She will buy 20 pencils at 20 cents apiece. c. She will buy 100 pencils at 5 cents apiece. d. None of these statements is likely to be true. What term describes demand with an elasticity of less than 1? a. unitary elastic c. low b. inelastic d. elastic ____ 64. According to Figure 4.4, how many slices of pizza will Ashley buy if the price is $1.00 per slice? a. one c. three b. two d. four ____ 65. According to Figure 4.4, at what price will Ashley’s quantity demanded of pizza be three slices? a. $ .50 c. $1.50 b. $1.00 d. $3.00 ____ 66. The price of a slice of pizza has just increased by $1 from an earlier, low price. Based on Ashley’s demand curve in Figure 4.4, which of the following statements is true? a. Ashley will buy two fewer slices of pizza. b. Ashley will buy four slices of pizza. c. Ashley’s quantity demanded is unchanged. d. Ashley will not buy any pizza. ____ 67. According to Figure 4.4, what is Ashley’s elasticity of demand as the price of a slice of pizza decreases from $2.00 to $1.00? a. 5.0 c. 2.0 b. 1.0 d. 4.0 ____ 68. A new restaurant has opened. Ashley’s demand for pizza has decreased and her demand curve has shifted. Based on Figure 4.4, which combination of price and quantity demanded would you expect to find on her new demand curve? a. $1.50, three slices c. $2.00, one slice b. $2.00, three slices d. $1.00, five slices ____ 69. A slice of pizza costs $4.00. Based on Ashley’s demand curve in Figure 4.4, what is her quantity demanded of pizza at this price? a. one b. zero c. five d. There is not enough information to answer the question. ____ 70. Which of the following is an example of lower production costs brought about by the use of technology? a. the delivery costs of gasoline to the consumer by diesel trucks b. the use of e-mail to replace slower surface mail c. the making of breads and pastries in local shops rather than large bakeries ____ 71. ____ 72. ____ 73. ____ 74. ____ 75. ____ 76. ____ 77. ____ 78. ____ 79. ____ 80. ____ 81. d. the importing of fresh vegetables from South America rather than using canned vegetables What is the effect of import restrictions on prices? a. They cause prices to drop. b. They cause prices to rise. c. They often cause prices to rise steeply and then drop. d. They usually do not have any lasting effect on price. What do sellers do if they expect the price of goods they have for sale to increase dramatically in the near future? a. sell the goods now and try to invest the money instead of resupplying b. sell the goods now but try to get the higher price for them c. store the goods until the price rises d. store the goods indefinitely regardless of when the price rises Which of the following is the best example of the law of supply? a. A sandwich shop increases the number of sandwiches they supply every day when the price is increased. b. A food producer increases the number of acres of wheat he grows to supply a milling company. c. A catering company buys a new dishwasher to make their work easier. d. A milling company builds a new factory to process flour to export. Which of the following is an example of a good with an inelastic supply? a. beanbags c. apples b. toothbrushes d. hats Which of the following receives government subsidies that are in place to protect the population rather than for economic reasons? a. a national car company in Indonesia c. tobacco growers in the United States b. small farmers in France d. national airlines in Western Europe When the selling price of a good goes up, what is the relationship to the quantity supplied? a. The cost of production goes down. b. The profit made on each item goes down. c. It becomes practical to produce more goods. d. There is no relationship between the two. What factor has the greatest influence on elasticity and inelasticity of supply? a. profit c. labor b. time d. financing Which of the following is a fixed cost for a store? a. short-term workers c. advertising b. rent d. inventory Which of these events would indicate a movement along a supply curve for batteries? a. Workers at a major battery factory go on strike and stop production. b. A new law requires battery manufacturers to spend more money on environmentallysound trash disposal. c. Battery manufacturers raise the price of eight AA batteries from $3.50 to $3.95 a set. d. A new trade agreement enables stores to import foreign batteries. Which of these is an example of a good with elastic supply? a. large hand-made rugs c. sandwiches b. plums d. passenger airplanes If the supply of a good is inelastic, a. producers will not change their quantity supplied by much if the market price doubles. b. a small increase in price will lead producers to sharply increase their quantity supplied. ____ 82. ____ 83. ____ 84. ____ 85. ____ 86. ____ 87. c. producers have diminishing marginal returns of labor. d. producers will increase their quantity supplied in response to sharp drops in the market price. An entrepreneur knits sweaters for sale. The entrepreneur has fixed costs of $100. When he makes 10 sweaters in one month, he must spend $15 on wool. To make eleven sweaters in one month, he must spend $17 on wool. If he has no other costs, what is the marginal cost of the eleventh sweater? a. $1 c. $17 b. $2 d. $117 A baker calculates that by spending $16 on labor and materials, she can bake 10 cakes a day. $24 will allow her to bake 12 cakes, while $36 spent on labor and materials produces 14 cakes. In terms of capital and labor, the baker has a. increasing marginal returns. c. decreasing marginal returns. b. constant marginal returns. d. negative marginal returns. A shoe factory has an elasticity of supply of .5 as the price of shoes rises from $50 to $75. If the factory produced 100,000 shoes at a market price of $50, how many will be produced at the new price? a. 75,000 c. 200,000 b. 125,000 d. 400,000 What is an example of a variable cost in a major league baseball franchise? a. stadium rent c. stadium maintenance b. manager’s salary d. ticket-takers’ salaries Complete the following sentence: At the most profitable level of production, a firm’s marginal cost will be _____ the market price. a. equal to c. less than b. set by d. greater than Which of the following is an example of government influence on supply? a. law of supply c. marginal costs b. subsidies d. market supply curve ____ 88. If the market price for pizza is $2.00 a slice, how many slices will be supplied by all producers in the market, according to Figure 5.4? a. 200 c. 250 b. 2,000 d. 2,500 ____ 89. According to Figure 5.4, how many slices of pizza will one pizzeria be willing to supply at a market price of $1.50 a slice? a. 100 c. 300 ____ 90. ____ 91. ____ 92. ____ 93. ____ 94. ____ 95. ____ 96. ____ 97. ____ 98. ____ 99. ____ 100. b. 200 d. 1,000 According to Figure 5.4, what term describes elasticity of supply in this market as the price increases from $1.00 to $2.00 a slice? a. Elastic c. Unitary elastic b. Inelastic d. Extremely elastic A shortage of tomato sauce and mozzarella cheese causes the market supply curve for pizza slices to shift. Based on Figure 5.4 Supply Curves, which of the following combinations of quantity supplied and price would you expect to find on the new curve? a. 2,500 slices at $2.50 each c. 3,500 slices at $2.50 each b. 1,500 slices at $1.00 each d. 3,000 slices at $1.50 each The market price of a slice of pizza has risen from $1.50 to $2.00. Based on Figure 5.4, the average pizzeria will respond by a. making 50 fewer slices a day. c. making 500 fewer slices a day. b. making 50 more slices a day. d. making 500 more slices a day. According to Figure 5.4, what is the elasticity of supply as the price decreases from $3.00 to $1.50 a slice? a. 0 c. .86 b. .43 d. 1.71 What happens when wages are set above the equilibrium level by law? a. Firms tend to try to break the law and hire people at the equilibrium level. b. Firms employ more workers than they would at the equilibrium wage. c. Firms employ fewer workers than they would at the equilibrium wage. d. Firms hire more workers but for fewer hours than they would at the equilibrium wage. On which kinds of goods do governments generally place price ceilings? a. those that are cheap but could become more expensive without the ceiling b. those that are not necessary but have become customary c. those that are essential and cheap d. those that are essential but too expensive for some consumers When buyers will purchase exactly as much as sellers are willing to sell, what is the condition that has been reached? a. supply and demand c. equilibrium b. excess demand d. price floor Which of the following is an example of a good whose price goes down because of improvements in technology? a. computer printers c. hard-bound books b. running shoes d. typewriters What happens when the supply of a nonperishable good is greater than the consumer wants to buy? a. the good is discarded b. the good becomes a luxury and the price rises c. either the good remains unsold or the price drops d. either the good is saved for later sale or the price is raised Why did Communist governments use a command economic system for many years? a. as a way to avoid the expense and difficulties of a free market b. in an attempt to create a society in which everyone was equal c. to limit the costs of production of many goods d. as a method of keeping the consumer from getting what he or she wanted Why did the U.S. government use rationing for some foods and consumer goods during World War II? a. to guarantee each civilian a minimum standard of living in wartime b. to keep sellers from raising prices on necessary goods c. because the English government had also decided on rationing ____ 101. ____ 102. ____ 103. ____ 104. ____ 105. ____ 106. ____ 107. ____ 108. ____ 109. ____ 110. ____ 111. d. to earn more money to support the military Which of the following is a situation that makes the market behave inefficiently? a. when consumers do not have enough information to make good choices b. when producers have the power to find out exactly what to produce c. when both consumers and producers are fully informed about a product d. when the market is in perfect competition and prices are high What happens to a market in equilibrium when there is an increase in supply? a. Excess supply means that producers will make less of the good. b. Quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied, so the price will drop. c. Quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded, so the price will drop. d. Undersupply means that the good will become very expensive. What is it called when the government uses some tool other than money to allocate goods? a. supply management c. disequilibrium b. rationing d. resource allocation What is the name of the smallest amount that can legally be paid to most workers for an hour of work? a. equilibrium price c. price floor b. supply cost d. minimum wage The price ceiling that was used to control the price of housing in New York City and other cities was called which of the following? a. rent control c. housing control b. rent abatement d. equilibrium price In response to rising car traffic, demand for bicycles has increased. The new equilibrium point will show a. more bicycles sold, but at a higher price. b. fewer bicycles sold, but at a higher price. c. more bicycles sold, but at a lower price. d. fewer bicycles sold, but at a higher price. Which of these is most likely to lead directly to a black market? a. a supply shock c. rationing b. a price floor d. equilibrium Rent control is a type of a. price ceiling. c. rationing. b. price floor. d. surplus. Elena is looking for an apartment. Which of the following is an example of her search costs? a. Elena must pay the first and last months’ rent before she can move into a new apartment. b. Elena pays movers $400 to help her transfer her belongings to the new apartment. c. Elena misses two days of work at the supermarket to visit several different apartments available for rent. d. Elena pays $300 to stay at a hotel for four nights before the apartment is ready. A shortage will develop when a. the quantity supplied of a good is greater than the quantity demanded of that good. b. the equilibrium quantity supplied is lower than the actual quantity supplied. c. the government provides subsidies to producers. d. the market price is below the equilibrium price. In a free market, prices lead to an efficient allocation of resources. In other words, a. consumers can buy unlimited amounts of any good they like at a price of their choice. b. resources are used in the most valuable and productive way according to the needs of consumers and producers. c. the government decides who controls natural resources. d. people who own resources are unable to bargain with people who wish to buy resources. ____ 112. Why do fads often lead to shortages, at least in the short term? a. Buyers and sellers are unable to agree on a price for the good. b. Laws prevent stores from responding to excess demand in time to prevent a shortage. c. Manufacturers charge extremely high prices for the goods that stores are unwilling to pay. d. Demand increases so quickly and unexpectedly that time is needed for the quantity supplied and price to increase to reach a new equilibrium point. ____ 113. Technological process has reduced the cost of manufacturing MP3 players. If demand is unchanged, a. more MP3 players will be sold at a higher price. b. fewer MP3 players will be sold at a higher price. c. more MP3 players will be sold at a lower price. d. fewer MP3 players will be sold at a higher price. ____ 114. According to Figure 6.2, in this market, a price of $1.00 would be a. the equilibrium price. c. a price ceiling. b. a price floor. d. a subsidy. ____ 115. According to Figure 6.2, in this market, a price of $1.50 would be a. the equilibrium price. c. a price ceiling. b. a price floor. d. a subsidy. ____ 116. According to Figure 6.2, at the equilibrium price, how many slices of pizza will be sold? a. 150 c. 250 b. 200 d. 300 ____ 117. If the government set a price of $2.00 a slice, how many slices of pizza will be sold each day, according to Figure 6.2? a. none c. 200 b. 150 d. 250 ____ 118. The price of a slice of pizza is $2.50. At the end of the day, how many unsold slices of pizza will be left, according to Figure 6.2? a. none c. 100 b. 50 d. 200 ____ 119. A new office building has opened and the demand for pizza has increased. The new demand curve states that consumers will buy 200 slices at $2.50 each and 300 slices at $1.50 each. Based on Figure 6.2, if the slope of the curve has not changed, what is the new equilibrium price and quantity supplied? a. $1.00, 300 slices c. $2.00, 250 slices b. $1.50, 200 slices d. $2.00, 150 slices ____ 120. Based on Figure 6.2, what is a possible equilibrium point in this market after it has been affected by a supply shock? a. $1.00, 100 slices b. $1.50, 100 slices c. $1.50, 200 slices d. $2.00, 150 slices Matching Identifying Key Terms Match each term with the correct statement below. a. standard of living f. b. privatize g. c. economic system h. d. self-interest i. e. safety net j. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 121. 122. 123. 124. 125. 126. 127. 128. the method used by society to produce and distribute goods and services one’s own personal gain the income people receive for supplying such things as land, labor, or capital a situation in which households purchase the goods and services that firms produce to sell a state-run firm to individuals a large Soviet farm leased from the state to groups of peasant farmers the doctrine that government generally should not intervene in the marketplace level of economic prosperity Identifying Key Terms Match each term with the correct statement below. a. free enterprise f. b. continuum g. c. incentive h. d. safety net i. e. collective j. ____ ____ ____ ____ 129. 130. 131. 132. ____ 133. ____ 134. ____ 135. ____ 136. communism laissez faire collective product market factor payments socialism transition traditional economy authoritarian standard of living government programs that protect people experiencing unfavorable economic conditions an economic system that permits the conduct of business with minimal government intervention an expectation that encourages people to behave in a certain way an economic system that relies on habit, custom, or ritual to decide questions of consumption and production of goods and services a philosophy based on the belief that democratic means should be used to distribute wealth evenly throughout a society requiring strict obedience to someone such as a dictator a range with no clear divisions a period of change in an economy Identifying Key Terms Match each term with the correct statement below. a. elasticity of demand f. b. substitution effect g. c. law of demand h. d. complement i. e. substitute j. ____ 137. a graphic representation of a demand schedule total revenue normal good inferior good demand curve ceteris paribus ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. a good that replaces another demanded good a good that consumers will demand more of when their incomes increase a good that is always used with another good the amount of money a company receives by selling goods or services what happens when consumers react to an increase in a good’s price by consuming less of that good and more of other goods ____ 143. a measure of how people change their buying patterns when prices change ____ 144. the way that a change in price determines whether or not consumers buy goods Identifying Key Terms Match each term with the correct statement below. a. total revenue f. b. income effect g. c. elastic h. d. inferior good i. e. normal good j. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 145. 146. 147. 148. 149. 150. 151. 152. the change in consumption resulting from a change in real income a good consumed instead of one whose price has risen a good that is bought and used along with another good the assumption that nothing but the price of a good will change a measure of how consumers react to a change in the price of a good demand that is very sensitive to a change in price a graphic representation of the quantities of a good that will be bought at each price a good for which the demand falls when income rises Identifying Key Terms Match each term with the correct statement below. a. subsidy h. b. supply schedule i. c. supply curve j. d. elasticity of supply k. e. excise tax l. f. law of supply m. g. variable cost ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 153. 154. 155. 156. 157. 158. 159. 160. 161. 162. elasticity of demand demand curve substitute ceteris paribus complement increasing marginal returns diminishing marginal returns marginal revenue marginal product of labor marginal cost market supply schedule the tendency of suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price a payment to the government on the production or sale of a good a measure of the way a quantity supplied reacts to a change in price a chart that lists how much of a good a supplier will offer at various prices a government payment that supports a business or market a level of production in which the marginal production decreases with new investment the cost of producing one more unit of a good a chart that lists how much of a good all suppliers will offer at different prices the additional income from selling one more unit of a good the change in output from hiring one additional unit of labor Identifying Key Terms Match each term with the correct statement below. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 163. 164. 165. 166. 167. 168. 169. 170. 171. 172. increasing marginal returns diminishing marginal returns marginal revenue marginal product of labor marginal cost supply schedule quantity supplied h. i. j. k. l. m. the change in output from hiring one additional unit of labor a chart that lists how much of a good a supplier will offer at different prices the cost of producing one more unit of a good the additional income from selling one more unit of a good a level at which the marginal production goes up with new investment government intervention in a market that affects the production of a good a factor that can change fixed costs plus variable costs the amount a supplier is willing and able to supply at a certain price a graph of the quantity supplied of a good by all suppliers at different prices Identifying Key Terms Match each term with the correct statement below. a. supply shock f. b. shortage g. c. excess supply h. d. spillover costs i. e. search costs j. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 173. 174. 175. 176. 177. 178. 179. 180. 181. 182. 183. 184. 185. 186. disequilibrium minimum wage price floor price ceiling rent control the smallest amount, by law, that can be paid to a worker for an hour of labor a maximum amount that can be legally charged for a good or service a sudden lack of goods when quantity supplied is more than quantity demanded situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied a price ceiling placed on the amount people pay for housing the financial and opportunity costs consumers pay when looking for a good or service when quantity supplied and quantity demanded are not the same in a market Identifying Key Terms Match each term with the correct statement below. a. rationing f. b. price ceiling g. c. excess demand h. d. surplus i. e. equilibrium j. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ market supply curve total cost law of supply variable elasticity of supply regulation disequilibrium search costs supply shock spillover costs price floor a sudden lack of availability of a good costs of production that affect people who have no control over how much of a good is produced when quantity demanded is more than quantity supplied situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded a minimum price for a good or service a system of allocating scarce goods and services using some criteria other than price ____ 187. the point at which quantity supplied and quantity demanded are the same ____ 188. the financial and opportunity costs consumers pay when looking for a good or service