Area Approximation Quiz
advertisement
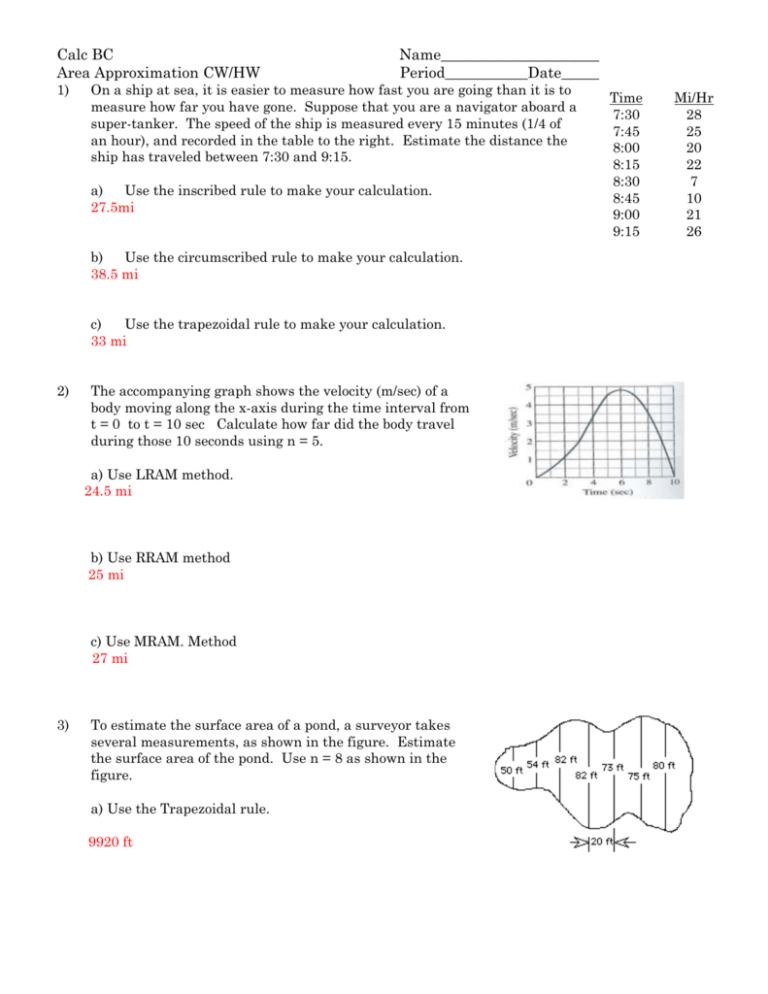
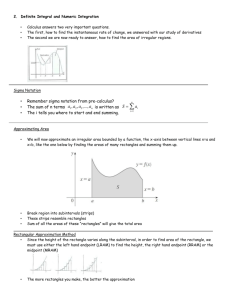
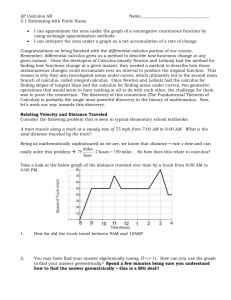
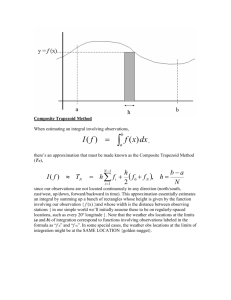
Calc BC Area Approximation CW/HW 1) Name_____________________ Period___________Date_____ On a ship at sea, it is easier to measure how fast you are going than it is to measure how far you have gone. Suppose that you are a navigator aboard a super-tanker. The speed of the ship is measured every 15 minutes (1/4 of an hour), and recorded in the table to the right. Estimate the distance the ship has traveled between 7:30 and 9:15. a) Use the inscribed rule to make your calculation. 27.5mi b) Use the circumscribed rule to make your calculation. 38.5 mi c) Use the trapezoidal rule to make your calculation. 33 mi 2) The accompanying graph shows the velocity (m/sec) of a body moving along the x-axis during the time interval from t = 0 to t = 10 sec Calculate how far did the body travel during those 10 seconds using n = 5. a) Use LRAM method. 24.5 mi b) Use RRAM method 25 mi c) Use MRAM. Method 27 mi 3) To estimate the surface area of a pond, a surveyor takes several measurements, as shown in the figure. Estimate the surface area of the pond. Use n = 8 as shown in the figure. a) Use the Trapezoidal rule. 9920 ft Time 7:30 7:45 8:00 8:15 8:30 8:45 9:00 9:15 Mi/Hr 28 25 20 22 7 10 21 26 4) Compute the following integral a) Find t when n = 6. 2 1 2x 2 + 5 dx . 1/2 5) b) Use inscribed rectangles with n = 6. 18.75 c) Use circumscribed rectangles with n = 6. 23.75 d) Use LRAM rule with n = 6. 19.75 e) Use RRAM rule with n = 6. f) Use MRAM rule with n = 6. 20.875 g) Find the exact integral. 21 22.75 When calculating area under a curve, is the upper sum (circumscribed) approximation always equivalent to the RRAM approximation? Provide justification for your answer. – verbally and graphically. No, the only way they are equal is if your function is monotonic.