Experiment 2- The Parallel Plates Capacitor
advertisement

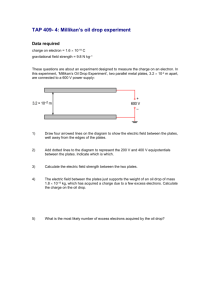
PHYCS 102 Lab. Date: Student Name:_____________________ ID No. :_______________ Student Partners:___________________ ,_____________________ Sec. : (______) ,______________________ Experiment 2- The Parallel Plates Capacitor 1- Experiment Objectives ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2- Apparatus: ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 3- Brief Theoretical Introduction: ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2-1 4- Data and Data Analysis: 4.1 (Part I): Variation of the electric field (E) with the plates’ separation (d) E at constant potential difference (ΔV), (E =ΔV/d) Electrometer Follow the manual instructions and measure the electric field E Light is ON between the plates as you vary (d) while keeping the potential + difference between the plates constant. d (Note: use the middle range on the electrometer) Record the distance between the plates (d) and readings of the V voltmeter that is connected to the electrometer in the following table: Measured potential difference between the plates ΔV= 170 ………(V) Electric field conversion factor: 1V for each 1000V/m d ………( ) VElectrometer (V) E( ) 1/d ( ) 0.050 0.060 0.070 0.080 0.090 0.100 Plot E vs. d on a graph paper and describe the variation. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Plot E vs. 1/d on a graph paper. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Find the slope of the graph E vs. 1/d. (show your calculations). ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Use the slope of the graph to find the potential difference between the plates (ΔV), and calculate the percentage difference in your result. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2-2 4.2 (Part II): Variation of the electric field (E) with the potential difference (ΔV) when the plates’ separation (d) is kept constant, (ΔV = Ed). Follow the manual instructions and measure the electric field E between the plates as you vary the electric potential (ΔV) while keeping the distance between the plates constant. (Note: again use the middle range on the electrometer ) Record the voltage across the plates and readings of the voltmeter that is connected to the electrometer in the following table: Distance between the plates d= 0.060 ……..(m) Electric field conversion factor: 1V for each 1000V/m ΔV ….…(V) VElectrometer (V) E( ) 170 140 110 80 50 Plot E vs. ΔV on a graph paper and describe the variation. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Find the slope of the graph (show you calculations). ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Use the slope of the graph to find the distance between the plates (d), and calculate the percentage difference in your results. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2-3 5- Conclusions ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6- Questions Calculate the absolute error in electric field (E) if electric potential ΔV=(150 ± 1)V, d= (0.050 ± 0.001 )m ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2-4