Solutions - Amazon Web Services
advertisement

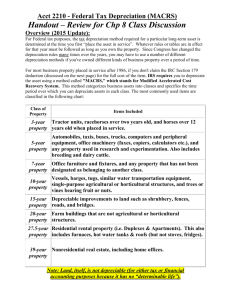
Accounting Solutions Name: Series 2 / Item: 10 Date: Answers 1 (c) Reducing balance method of depreciation ignores residual value. If the straight-line method of 10 years i.e. 10% pa and the reducing balance method is twice that rate, it must be 20% pa. Year 1 – $ 50,000 x 20% = $ 10,000 depreciation; Year 2 – ($ 50,000 – $10,000) x 20% = $ 8,000 depreciation; Year 3 – ($ 50,000 – $18,000) x 20% = $ 6,400. 2 (c) The depreciation method is chosen from evaluating the cost of the asset (cost), the residual value at the end of its useful life (scrap value) and the rate in which the assets will loose its value (depreciation rate). 3 (c) There are three causes of depreciation: 1 - The wear and tear of an asset through use in excess of that which maintenance can restore. 2 – Technical obsolescence, that is, the asset goes out of date because of the introduction of new technology. 3 – Commercial obsolescence, that is, the asset becomes redundant (useless) because of a fall in the demand for the goods or services that the asset was used to produce. 4 (b) Amortisation is similar to depreciation. Depreciation is the allocation of the cost a noncurrent asset over a period of time. Amortisation is applied to those non-current assets that do not have a physical presence but still have value to the business over time. Examples of non-current assets that would be amortised include: leasing rights to a mine or pit, copyright, patent rights, goodwill and trade marks. 5 (b) Diminishing balance method of depreciation is also known as the reducing balance method. It is calculated by: Cost less Accumulated Depreciation = Written Down Value x annual depreciation rate = annual depreciation. 6 (a) Expenses are those costs incurred during the financial period that will help the business generate income for the same period of time. 7 (b) The reducing balance method is the one out of place. The alternative name for this method is the diminishing balance method. Fixed instalment method, on cost method and straight-line method are all the same methods. 8 (b) Amortisation is applied to those assets that do not have a physical presence, such as lease agreements and patent rights. 9 (c) The alternative name for the straight line method of depreciation is the Fixed Instalment Method. This method is also known as ‘on cost’ and ‘prime cost method’. ________________________________________________________________________________________ Academic Teacher Resources ________________________________________________________________________________________ Accounting Solutions Series 2 / Item: 10 True / False 1 True The straight-line method (or on cost method) of depreciation results in the same amount of depreciation expense being charged against income each year. 2 False The terms ‘Written Down Value’ and ‘Book Value’ mean exactly the same thing, regardless of the method of depreciation. The ‘Written Down Value’ and ‘Book Value’ is equal to: Cost less Accumulated Depreciation. 3 False The accumulated depreciation under the reducing balance method will be ever increasing in a decreasing rate as the simple graph below reflects. $ Time 4 True Since the asset Computer is likely to generate more income in its earlier years of operations than its latter years, it would be appropriate to use the diminishing balance method of depreciation. 5 False Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the accumulated depreciation amount will be increasing steadily and at a constant rate as the graph below reflects. $ Time ________________________________________________________________________________________ Academic Teacher Resources ________________________________________________________________________________________ Accounting Solutions Series 2 / Item: 10 6 True The Proceeds on the Disposal of a non-current asset can take the form of: Cash Received, Trade-in Allowance or a Debtor. It is possible for a non-current asset to be traded in on a new asset, or receive a cash consideration. It is also possible for the asset to be sold to an individual or business on credit and hence the creation of a debtor. 7 True The reducing balance method of depreciation applies a fixed percent rate of depreciation to the cost of the asset less the accumulated depreciation. This method of depreciation results in a higher depreciation charge in the earlier years of an asset’s life than in its latter years of its life. 8 True The carrying amount is equal to the cost $33,700 less the accumulated depreciation $1,000 = $32,700. The cost of the asset is equal to: the invoice amount $30,000. Air-conditioning $2,000, window tinting $1,000 plus the burglar alarm $700 = $33,700. The depreciation of $1,000 was given. The insurance cost $800, registration cost $500 and the tyres cost of $770 are not taken into account in determining the carrying amount of the asset. 9 False An asset using the reducing balance method will never have its written down value reach zero. Since the formula is continuously applied to the book value, the remainder will never actually reach zero. 10 False The written down value is Cost less Accumulated Depreciation. 30 June 2017: Written Down Value = $98,400 - $ 44,400 = $ 54,000 30 June 2018: Depreciation = $ 54,000 x 20% x 12 months = $ 10,800 30 June 2018: Written Down Value = $98,400 - $ 55,200 = $ 43,200 30 June 2019: Depreciation = $ 43,200 x 20% x 12 months = $ 8,640 30 June 2019: Written Down Value = $98,400 - $ 63,840= $ 34,560 31 August 2019: Depreciation = $ 34,560 x 20% x 2 months = $ 1,152 31 August 2019: Written Down Value = $98,400 - $ 64,992 = $ 33,408 Gain = Gross Proceeds – Carrying Cost or Gross Proceeds = Carrying Cost + Gain = $ 4,500 + $ 33,408 = $ 37,902 Consideration. ________________________________________________________________________________________ Academic Teacher Resources ________________________________________________________________________________________ Accounting Solutions Series 2 / Item: 10 Match the Word to the Statement 1 G - Written Down Value of the Asset Sold Difference between the cost of the asset and the total depreciation of the asset over its effective working life shown in the balance sheet. 2 E - Carrying Amount of Asset Sold Difference between the cost of the asset and the total depreciation of the asset over its effective working life shown in the one account on the date of disposal. 3 A - Proceeds on the Asset Sold Consideration on the sale of the asset – cash, credit or trade-in. 4 C - Gain on Asset Sold Asset over depreciated over its effective working life. 5 H - Commercial Obsolescence Asset becomes redundant because of a fall in the demand for the goods or services that the asset was used to produce. 6 B - Wear and Tear Asset loss in value due to excess use which is greater than the value added through maintenance and service. 7 F - Technical Obsolescence Asset is out of date because of the introduction of newer methods and routines. 8 D - Depletion Asset loses value over time due to the fact that the asset cannot be replaced or renewed. ________________________________________________________________________________________ Academic Teacher Resources ________________________________________________________________________________________