Module 4 - Mercer University
advertisement

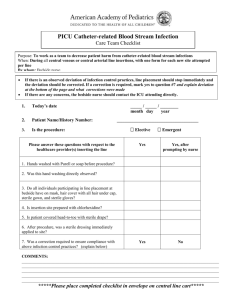
NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 1 of 13 Georgia Baptist College of Nursing Of Mercer University NUR 216 Skills Lab MODULE FOUR – IMMOBILITY/ASSISTIVE DEVICES/RANGE-OF-MOTION (Part 1 of 3) Focus: Assistive Devices Outcomes: Upon completion of this laboratory activity, the learner will: 1. Demonstrate correct use of cane, crutches, and walker. 2. Perform the following movements made with crutches: a. Stand from sitting position b. Four-point gait c. Three-point gait d. Two-point gait e. Swing-to gait f. Swing-through gait g. Sitting in chair 3. Perform passive range-of-motion exercises correctly. Required Readings: Elkin, M., Perry, A., & Potter, P. (2007). Nursing Interventions & Clinical Skills. (4th Ed.). (pp. 115-131). St. Louis: Mosby. Learning Activities: 1. Perform walking with assistive devices and performance of rang-of-motion exercises. 2. Participate in activities and discussion. 3. Define related module vocabulary Validation: 1. 2. 3. 4. Demonstrate proficiency in related lab activities. Use correct body mechanics for nurse and client. State scientific rationale/principles for each action. Complete module checklist. Clinical Application: 1. Provide safe, thorough, and effective care for the pre and postoperative client with mobility needs. 2. Initiate interventions designed to prevent complications related to the surgical experience or immobility. Rev. 9/07 MH NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 2 of 13 Georgia Baptist College of Nursing Of Mercer University NUR 216 Skills Lab (Part 2 of 3) MODULE FOUR: BANDAGES AND BINDERS WOUND DRESSINGS STAPLE REMOVAL OPENING STERILE PACKAGES AND POURING STERILE SOLUTIONS APPLICATION OF STERILE GLOVES (Part 2 of 3) Focus: Application of binders/ Wound dressing identification/ Surgical Asepsis/SterileTechnique Outcomes: Upon completions of the laboratory activity, the learner will: 1. Correctly identify assorted types of bandages. 2. Demonstrate application of ace bandage utilizing assorted turns. 3. Discuss removal of staples/sutures. 4. Identify situations in which sterile technique is needed. 5. Assemble a sterile field and pour sterile solution. 6. Demonstrate donning sterile gloves. Required readings: Elkin, M., Perry, A., & Potter, P. (2007). Nursing Interventions & Clinical Skills. (4th Ed.). (pp. 83-89, 500-504, 521-523, 531-535). St. Louis: Mosby. Learning Activities: 1. Identify indications for various wound dressings. 2. Demonstrate ability to apply ace bandaging utilizing different turns. 3. Construct use of staple and suture removal kits. 4. Perform opening of sterile package and pouring of sterile solution maintaining sterility. Validation: 1. Demonstration of competence in required learning activities. 2. Completion of module check-off list. Clinical Application: 1. Identify situations in which sterile technique is needed. 2. Implement principles of sterile technique when appropriate. 3. Recognize different types of dressings seen in clinical setting. Rev. 9/07 MH NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 3 of 13 Georgia Baptist College of Nursing Of Mercer University NUR 216 Skills Lab MODULE FOUR – HEALTH ASSESSMENT: MUSCULOSKELETAL AND INTEGUMENTARY ASSESSMENT (Part 3 of 3) Focus: Assessment of musculoskeletal and integumentary systems Outcomes: Upon completion of the laboratory activity the learner will: 1. Demonstrate accurate assessment of an individual’s skin, nails, and hair, utilizing inspection and palpation. 2. Document findings from skin, nails, and hair assessment. 3. Demonstrate accurate assessment of an individual’s musculoskeletal system. 4. Document findings from assessment of the musculoskeletal system. Required Readings: Jarvis, C. (2004). Physical examination & health assessment. (4th ed). (pp. 230-247, 614-645). St. Louis: Saunders. Learning Activities: 1. Practice required assessment skills, using assessment sheets, with partner in lab. 2. Complete module vocabulary lists and knowledge assessments. Validation: 1. Successful performance of end of semester assessment checks off. Clinical Application: 1. Weekly performance of assigned assessments on clinical patients. Rev. 9/07 MH NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 4 of 13 Georgia Baptist College of Nursing Of Mercer University NUR 216 Skills Lab MODULE FOUR – VOCABULARY Directions: Define each word in the space provided. 1. Articulation 2. Synovial 3. Ligament 4. Fasciculi 5. Supination 6. Abduction 7. Circumduction 8. Eversion NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 5 of 13 9. Partial Weight Bearing 10. Surgical Aseptic Technique 11. Package integrity 12. Montgomery straps 13. Vaseline gauze 14. Pallor 15. Profile sign 16. Turgor 17. Primary lesion 18. Secondary lesion Georgia Baptist College of Nursing NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 6 of 13 Of Mercer University NUR 216 Skills Lab MODULE FOUR – KNOWLEDGE ASSESSMENT Directions: Select the BEST answer for the following questions: 1. When a patient is standing, the crutch pads should be three inches below the axilla. A. True B. False 2. The type of gait a client uses in crutch walking depends on the A. B. C. D. type of crutch being used. height and weight of the patient. client’s ability to be independent with movement. amount of weight client is able to support with legs. 3. An audible and palpable crunching that accompanies movement is known as A. B. C. D. crackles. articulation. crepitus. bursa. 4. On assessment a patient with scoliosis will have A. B. C. D. limited ROM. a difference in shoulder elevation. tenderness. unequal leg lengths. 5. When assessing for which assistive device to use, it is important for the nurse to know the client’s A. B. C. D. level of compliance. weight-bearing status. favorite assistive device. expected outcome. 6. List 3 things to check for to confirm the sterility of a package. NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 7 of 13 A. B. C. 7. Put the following steps in order for opening a sterile package correctly. _____Right hand opens right side _____Open the top layer away from you _____Left hand opens left side _____Place package in center of work area _____Open bottom layer towards you 8. When working in sterile attire, you keep your hands above your waist and keep sterile equipment on top of the tables because A. B. C. D. everything below the waist or table is nonsterile. sterility is a matter of certainty, not conjecture. contamination often occurs accidentally. your back is considered potentially contaminated. 9. Application of sterile technique includes all of the following EXCEPT A. considering the border or edge of a sterile drape to be contaminated. B. avoiding talking over a sterile field. C. keeping the sterile field within the range of vision. D. considering the objects sterile if the outer wrap is wet, but not the inner wrap. 10. Edema is most evident in A. the face. B. dependent parts of the body. C. central areas of the body. D. the feet. 11. When assessing pigmented lesions, the E in ABCDE, stands for A. Easy to see. B. Eccyhmotic. C. Enlargement. D. Erythemic. Georgia Baptist College of Nursing Of Mercer University NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 8 of 13 NUR 216 Skills Lab Directions: Participate in the following activities. Check or initial when complete. Have faculty sign or initial in the space provided when you have completed all activities. _____1. Identify various assistive devices _____2. Demonstrate ability to walk with crutches using all 5 gaits _____3. Perform ROM exercises with partner (one side) _____4. Practice musculoskeletal assessment on partner _____5. Perform 5 types of bandage turns using ace bandages or kerlix gauze _____6. Is familiar with various types of gauze/dressing material _____7. Demonstrates ability to open a sterile package _____8. Demonstrates ability to pour sterile solution _____9. Demonstrates ability to don sterile gloves ____10. Practice assessment of skin, hair, and nails on partner ____11. I feel I have mastered the content of this module and am able to apply in the clinical setting. ____12. I need more practice/instruction. ___________________________ (Faculty/Date) _______________________ (Student) NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 9 of 13 NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 10 of 13 Nursing Process, Skills, and Concepts (NUR216) Assessment Guidelines: SKIN, HAIR, and NAILS Procedure Y N NUR216 Skills Lab Wash Fallhands 2007 Pagesupplies 11 of 13needed for the exam and bring them to the bedside. Gather Greet patient using the patient’s proper name COMMENTS NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 12 of 13 Identify patient by checking the armband. Create and maintain an appropriate environment Provide privacy throughout the exam Introduce self and purpose of exam Wear appropriate attire (Use PPE if indicated) Indicate confidentiality Utilize effective communication skills Use and respond to nonverbal behavior Use appropriate terminology/language Position patient appropriately Don gloves (when indicated) Inspect skin for: Color Lesions Vascularity or bruising Palpate skin for: Temperature Moisture Thickness Turgor Inspect hair for: Color Lesions (including infestations) Texture Distribution Palpate hair noting texture Inspect and palpate nails for: Shape and contour Color Capillary refill Clean work space, make bed. Return supplies to the appropriate location. Document findings ___________________________________ Student signature date 07/06 KS/JR _______________________________________ Instructor signature date NUR216 Skills Lab Fall 2007 Page 13 of 13 Nursing Process, Skills, and Concepts (NUR216) Assessment Guidelines: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Procedure Y N COMMENTS Wash hands Gather supplies needed for the exam and bring them to the bedside. Greet pt using patient’s proper name; Identify patient by checking armband. Create and maintain an appropriate environment Provide privacy throughout the exam Introduce self and purpose of exam Wear appropriate attire (Use PPE if indicated) Indicate confidentiality Utilize effective communication skills Use and respond to nonverbal behavior Use appropriate terminology/language Position patient appropriately Don gloves (when indicated) Observe for symmetry of the upper and lower extremities. Inspect for size, contour, and range of motion (active movement of at least two of each joint’s normal range of motion movements): temporomandibular joint wrists ankles neck fingers toes shoulders hips Spine elbows knees Palpate, noting temperature, bony articulations, abnormalities during range of motion: temporomandibular joint wrists ankles neck fingers toes shoulders hips Spine elbows knees Palpate bilaterally: Pterygoid(jaw) deltoids Suppraspinatus (shoulders) biceps quadriceps (thigh) gastrocnemius(ca lf) Assess for muscle strength bilaterally: temporomandibular joint wrists ankles neck fingers toes shoulders hips Spine elbows knees Clean work space, make bed. Return supplies to the appropriate location; Document findings Student signature: date: Instructor signature: 07/06 KS date: