File
advertisement
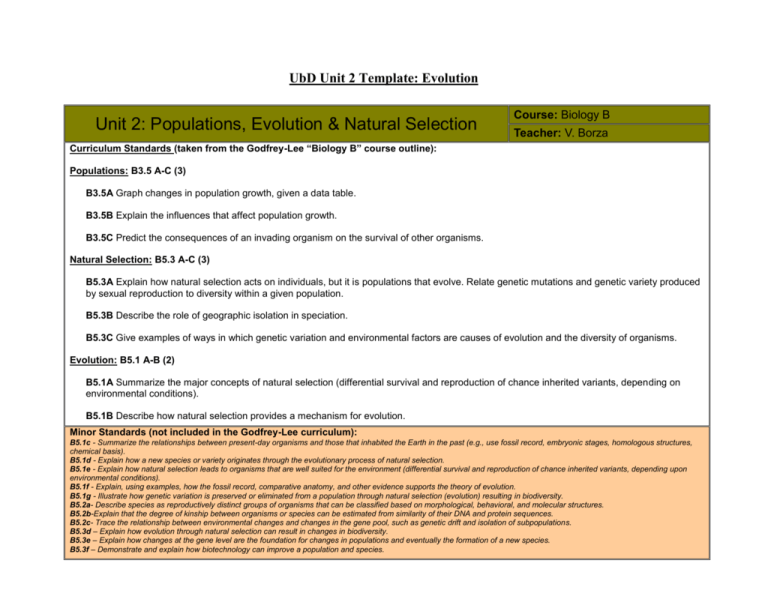
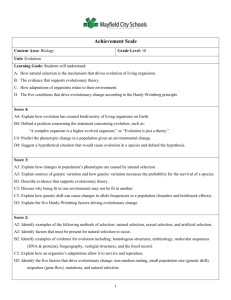
UbD Unit 2 Template: Evolution Unit 2: Populations, Evolution & Natural Selection Course: Biology B Teacher: V. Borza Curriculum Standards (taken from the Godfrey-Lee “Biology B” course outline): Populations: B3.5 A-C (3) B3.5A Graph changes in population growth, given a data table. B3.5B Explain the influences that affect population growth. B3.5C Predict the consequences of an invading organism on the survival of other organisms. Natural Selection: B5.3 A-C (3) B5.3A Explain how natural selection acts on individuals, but it is populations that evolve. Relate genetic mutations and genetic variety produced by sexual reproduction to diversity within a given population. B5.3B Describe the role of geographic isolation in speciation. B5.3C Give examples of ways in which genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and the diversity of organisms. Evolution: B5.1 A-B (2) B5.1A Summarize the major concepts of natural selection (differential survival and reproduction of chance inherited variants, depending on environmental conditions). B5.1B Describe how natural selection provides a mechanism for evolution. Minor Standards (not included in the Godfrey-Lee curriculum): B5.1c - Summarize the relationships between present-day organisms and those that inhabited the Earth in the past (e.g., use fossil record, embryonic stages, homologous structures, chemical basis). B5.1d - Explain how a new species or variety originates through the evolutionary process of natural selection. B5.1e - Explain how natural selection leads to organisms that are well suited for the environment (differential survival and reproduction of chance inherited variants, depending upon environmental conditions). B5.1f - Explain, using examples, how the fossil record, comparative anatomy, and other evidence supports the theory of evolution. B5.1g - Illustrate how genetic variation is preserved or eliminated from a population through natural selection (evolution) resulting in biodiversity. B5.2a- Describe species as reproductively distinct groups of organisms that can be classified based on morphological, behavioral, and molecular structures. B5.2b-Explain that the degree of kinship between organisms or species can be estimated from similarity of their DNA and protein sequences. B5.2c- Trace the relationship between environmental changes and changes in the gene pool, such as genetic drift and isolation of subpopulations. B5.3d – Explain how evolution through natural selection can result in changes in biodiversity. B5.3e – Explain how changes at the gene level are the foundation for changes in populations and eventually the formation of a new species. B5.3f – Demonstrate and explain how biotechnology can improve a population and species. Students will be able to independently use their learning to…. Meaning Enduring Understandings Students will understand that… Essential Questions Students will keep considering… Acquisition of Knowledge and Skills Students will know… Students will be skilled at… Vocabulary Terms: Populations biodiversity, changing environment, population growth, differentiation, environment, differential survival, Thomas Malthus Natural Selection: natural selection, sexual selection, genetic variation, sexual reproduction, selective pressures, adaptation, speciation Populations: I can construct a graph to display how a population grows over time. (B3.5A) I can explain the influences of population growth. (B3.5B) I can postulate what effect an organism might have on another organism living in the same environment. (B3.5C) Natural Selection: Evolution: biological evolution, chance inherited variants, gene pool, genetic drift, genetic diversity, genetic mutation, genetic variation, homologous structures, morphological structures, Charles Darwin Groups of individuals are called populations. (B3.5A) The size of populations change, and this change can be represented using a graph. (B3.5A) Population growth is affected by several factors. (B3.5B) An organism introduced into a population will have an impact on surrounding organisms. (B3.5C) Different traits provide certain benefits to individuals and can be reproduced and inherited by offspring (B5.1A) The basis of evolution depends on the process of natural selection. (B5.1B) Natural selection is a process that acts on individuals but has an effect on entire populations (B5.3A) A species can become separated by geography and over time become two species. (B5.3B) There is diversity between organisms in a population, and this variation along with environmental factors is what accounts for evolutionary change. (B5.3C) I can identify that selective pressures act on individuals directly within a population. (B5.3A, B3.5B) I can describe how individual changes affect entire populations (B5.3A, B3.5C) I can demonstrate how genetic mutations/ variety produced be sexual reproduction can have an effect on the diversity within a population. (B5.3A) I can evaluate the effects that a genetic mutation/ variation will have on the diversity of a population (B5.3A,C) I can demonstrate how geographically isolating individuals within a population can produce separate species (speciation). (B5.3B) I can define the concept of speciation. (B5.3B) I can describe how environmental factors affect individual diversity and in turn, cause evolutionary change. (B3.5C) Evolution: I can list the conditions under which natural selection occurs (B5.1A, B5.3) I can explain how genetic diversity offers different opportunities for survival to different organisms. (B5.1A, B5.3C) I can describe how natural selection steers the process of evolution over time. (B5.1B) Content Outline & Assessment Plan: Unit 2: Evolution Vlad Borza/ EDG 680 04 - Fall 2011 Sec 1. Populations: 1. I can explain the influences of population growth. (B3.5B) 2. I can construct a graph to display how a population grows over time. (B3.5A) 3. I can postulate what effect an organism might have on another organism living in the same environment. (B3.5C) ASSESSMENT #1 (Formal Formative on Targets #1-3 - Study a ‘populations case study’, plot a graph, evaluate the causes of change) Sec 2. Natural Selection & Evolution: 4. I can identify that selective pressures act on individuals directly within a population. (B5.3A, B3.5B) 5. I can describe how individual changes affect entire populations (B5.3A, B3.5C) 6. I can list the conditions under which natural selection occurs (B5.1A, B5.3) ASSESSMENT #2 (Formative- Targets #4-6) 7. I can evaluate the effects that a genetic mutation/ variation will have on the diversity of a population (B5.3A,C) 8. I can demonstrate how genetic mutations/ variety produced by sexual reproduction can have an effect on the diversity within a population. (B5.3A) ASSESSMENT #3 (Formative #7-8 or Summative #4-8) 9. I can define the concept of speciation. (B5.3B) 10. I can demonstrate how geographically isolating individuals within a population can produce separate species (speciation). (B5.3B) 11. I can explain how genetic diversity offers different opportunities for survival to different organisms. (B5.1A, B5.3C) 12. I can describe how environmental factors affect individual diversity, and in turn, cause evolutionary change. (B3.5C) 13. I can describe how natural selection steers the process of evolution over time. (B5.1B) ASSESSMENT #4 (Formative Targets #9-13) And FINAL ASSESSMENT (Summative- Targets #4-13)