Example TP-CASTT analysis - KISEnglish102008-2009
advertisement

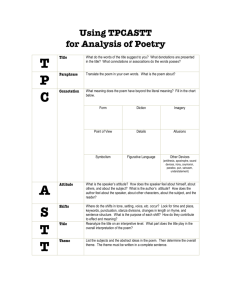
TP-CASTT Analysis Title: Make a prediction about the poem based on the title. Paraphrase: Translate the poem into your own words, focusing on the literal plot (about one sentence per stanza). Connotation: Contemplate the poem for meaning beyond the literal, including all poetic devices. Identify and state how two poetic devices contribute to the meaning of the poem. Attitude: Identify and explain two places in the poem where the speaker's attitude is evident. Shifts: Identify and explain at least one shift in the speaker's attitude or the progress of the poem. Title: Examine the title again, this time on an interpretive level. Explain the deeper meaning of the title. Theme: What is the poet saying about the subject of the poem? Complete the following for a TP-CASTT analysis: Title: Read the title and predict what the poem may be about. Paraphrase: Paraphrase each stanza into your own words – about one sentence per stanza. Connotation: Identify at least two poetic (or literary) devices used in the poem, and state how they contribute to the meaning of the poem. Focus on how the devices contribute to the meaning, the effect, or both of a poem. Here are some to consider: figurative language (simile, metaphor, personification), symbolism, diction, point of view, imagery, irony, allusion, hyperbole, oxymoron, understatement, and sound devices (alliteration, onomatopoeia, rhythm, and rhyme). Attitude (Tone): Examine the speaker’s attitude toward the subject(s) in the poem. Identify and explain two places in the poem where the speaker’s attitude is evident. In other words, what does the speaker think about the subject of the poem. Shift (Progression): Poets do not begin and end poems in the same place – something is always revealed over the course of the poem. Identify the shifts that occur in the poem. The following often indicate a shift: -key words (but, yet, however, although) -punctuation (dashes, periods, colons, ellipsis) -stanza divisions -changes in line or stanza length -effect of structure on meaning -changes in sound that may indicate changes in meaning -changes in diction (slang to formal language) Title (Again): In a sentence, state what the title might mean based on your deeper understanding of the poem. Theme: What is the human experience, motivation, or condition suggested by the poem? The following is a useful method: A formula to determine the theme: Plot: Summarize the plot of the poem. Subjects: List the subject(s) of the poem. Theme: Write a sentence identifying what idea the author is conveying about each subject (each of these sentences is a possible theme).