Cardiovascular III
advertisement

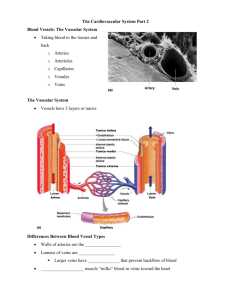
CARDIOVASCULAR III FETAL CIRCULATION Left umbilical vein persists and carries oxygenated blood from placenta to liver Half goes to liver (Less Oxygenated) Half gets shunted through ductus venosus to IVC (More Oxygenated) Blood from IVC Directed by crista dividens (inferior border of septum secundum) Goes through foramen ovale and into left atrium This blood goes to brain and upper extremities Remaining Blood (Less oxygenated from IVC & deoxygenated from upper body) SVC Rt. Atrium Rt. Ventricle Pulm. Artery Ductus Arteriosus Lower Body UPPER BODY RECEIVES MORE OXYGENATED BLOOD THAN LOWER BODY Changes at Birth 1. Breathing Lungs Expand and become functional Ductus Arteriosus Constricts and Closes (via bradykinin) Ductus Arteriosus Ligamentum Arteriosus Anatomical Closure of Duct occurs by 3rd Month Aeration of Lungs: 1. Stretching/Thinning of Walls of Pulmonary Arteries 2. Dramatic Fall in Pulmonary Vascular Resistance 3. Right Ventricular Wall becomes thinner than Left Ventricle 2. More blood Reaches Let Atrium through Pulmonary Veins 3. Ductus Venosus Ligamentum Venosus 4. Closure of Foramen Ovale due to increased pressure of #2 5. Umbilical Cord is Cut: a. Umbilical arteries proximal part Superior Vesical Arteries Distal part Medial Umbilical Ligaments b. Umbilical Veins Ligamentum Teres Hepatis Umbilical Vein remains patent and can be used for blood transfusions.