Suggested Lecture Outline - Morgan Community College
advertisement

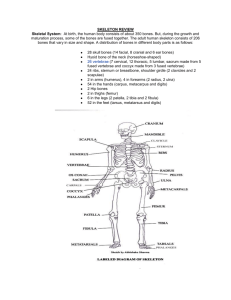
A&P I Chapter 7 Worksheet p 1/5 Name:______________________________________ Chapter 7 1) The bones, muscles, and joints together form the ___________________________ system. 2) The ________________________consists of bones arranged along the longitudinal axis of the body. It is composed of 80 bones, are the skull, hyoid bone, vertebral column, sternum, and ribs. 3) 4) 5) The _________________________comprises one of the two major divisions of the skeletal system.It consists of 126 bones in the upper and lower extremities (limbs or appendages) and the pectoral (shoulder) and pelvic (hip) girdles, which attach them to the rest of the skeleton. Almost all of the bones of the body can be classified on the basis of_________________: long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid. Bones show characteristic _________________________which are structural features adapted for specific functions. There are two major types of surface markings. A. appendicular skeleton B. Attachment C. axial skeleton D. Cranial E. Depressions F. Facial G. Mandible H. Musculoskeletal I. Ossicles J. Processes K. Protect L. shape 6) ___________________________________and openings participate in joints or allow the passage of soft tissue. 7) ________________are projections or outgrowths that either help form joints or serve as attachment points for connective tissue. N. Skull 8) The skull, composed of 22 bones, consists of the ____________ bones (cranium) and the _________________ bones (face) P. surface markings 9) The ________________forms the large cranial cavity and smaller cavities, including the nasal cavity and orbits (eye sockets). 10) Certain skull bones contain mucous membrane lined cavities called paranasal______________________. 11) The only moveable bone of the skull, other than the ear ___________________ within the temporal bones, is the ___________________________. 12) Immovable joints called ________________________hold the skull bones together. 13) The functions of the cranial bones include: M. Sinuses O. Stabilize Q. Sutures a. They _______________________the brain. b. Their inner surfaces attach to membranes that _________________________the positions of the brain, blood vessels, and nerves. c. The outer surfaces of cranial bones provide large areas of ___________________ for muscles that move the various parts of the head. A&P I Chapter 7 Worksheet p 2/5 Name:______________________________________ d. Facial bones form the __________________________ of the face and protect and provide support for the nerves and blood vessels in that area. 14) The Cranial Bones include: a. The _____________________form the forehead, the roofs of the orbits, and most of the anterior part of the cranial floor 15) A. Cleft palate B. ethmoid bone C. framework D. frontal bones E. lacrimal bones F. Maxillae b. The _________________________________form the greater portion of the sides and roof of the cranial cavity. G. Nasal bones c. The ________________________________form the inferior lateral aspects of the cranium and part of the cranial floor. I. occipital bone d. The _____________________________forms the posterior part and most of the base of the cranium. K. Parietal bones e. The _____________________________ is called the keystone of the cranial floor because it articulates with all the other cranial bones, holding them together. M. Temporal bones f. The ______________________________forms part of the anterior portion of the cranial floor, the medial wall of the orbits, the superior portion of the nasal septum, and most of the superior side walls of the nasal cavity. It is a major superior supporting structure of the nasal cavity O. zygomatic bones H. nasal conchae J. Palatine bones L. sphenoid bone N. vomer The Facial Bones include a. The _______________________________form part of the bridge of the nose b. The _______________________________unite to form the upper jawbone and articulate directly with every bone of the face except for the mandible a. __________________________and cleft lip result from a lack of fusion of portions of the palatine and maxillary bones during fetal development. c. The _____________________________(cheekbones) form the prominences of the cheeks and part of the lateral wall and floor of each orbit. d. The __________________________form a part of the medial wall of each orbit and are the smallest bones of the face. e. The ___________________________form the posterior portion of the hard palate, part of the floor and lateral wall of the nasal cavity, and a small portion of the floors of the orbits. f. The inferior ____________________________(turbinates) form a part of the inferior lateral wall of the nasal cavity (Figures 7.3, 7.9a). g. The_______________________________, found on the floor of the nasal cavity, is one of the components of the nasal septum. A&P I Chapter 7 Worksheet p 3/5 Name:______________________________________ h. The ________________________(jawbone) is the largest, strongest facial bone and the only moveable skull bone (other than the ear ossicles). A. anterior 1. The mandible articulates with the temporal bone to form the ______________________________________joint C. coronal 2. Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) ___________________ is dysfunction to varying degrees of the temporomandibular joint. Causes appear to be numerous and the treatment is similarly variable. 16) The nasal _____________________________is a vertical partition that divides the nasal cavity into right and left sides. 1. A _______________________nasal septum is a lateral deflection of the septum from the midline, usually resulting from improper fusion of septal bones and cartilage. 17) The _______________________(eye sockets) contain the eyeballs and associated structures and are formed by seven bones of the skull 18) ____________________________are immovable joints found only between skull bones and hold skull bones together. 19) Sutures include the _________________________, _________________________, ____________________,and _________________________ sutures, among others. 20) Paranasal ________________________are cavities in bones of the skull that communicate with the nasal cavity. 21) They are lined by _______________________membranes and also serve to lighten the skull and serve as ________________ chambers for speech. B. anterolaterals D. Deviated E. ethmoid F. Fontanels G. frontal H. lamboidal I. Mandible J. maxillae K. mucous L. Orbits M. posterior N. posterolaterals O. resonating P. sagittal Q. Septum R. sinuses S. Sinusitis T. sphenoid U. squamous V. Sutures W. Syndrome X. Temporomandibular 22) Cranial bones containing the sinuses are the ______________, _______________________, ______________________, and ___________________. 23) _________________________occurs when membranes of the paranasal sinuses become inflamed due to infection or allergy. 24) ____________________________are dense connective tissue membrane-filled spaces between the cranial bones of fetuses and infants. They remain unossified at birth but close early in a child’s life. 25) The major fontanels are the ____________________, ______________________, _______________________________, and _______________________________. A&P I 26) Chapter 7 Worksheet p 4/5 Name:______________________________________ Two major functions of Fontanels are: 1) They enable the fetal skull to modify its size and shape as it passes through the______________________________________. 2) They permit ___________________________ of the brain during infancy. 27) 28) 29) 30) 31) The hyoid bone is a unique component of the axial skeleton because it does not _______________with any other bones. A. 12 B. 5 C. 7 D. articulate E. atlas F. axis The vertebral column, along with the sternum and ribs, makes up the _____________________of the skeleton. G. birth canal The 26 bones of the vertebral column are arranged into five regions: _______________________, __________________, _________________________, ____________________ and _________________________. I. coccygeal The four normal vertebral curves are the cervical and lumbar (anteriorly _______________________curves) and thoracic and sacral (anteriorly ____________________curves). L. fetus In the__________________________, there is only a single anteriorly concave curve. H. cervical J. concave K. convex M. intervertebral discs N. lumbar O. lumbar Between adjacent vertebrae, from the first cervical (atlas) to the sacrum, are _____________________________that form strong joints, permit various movements of the vertebral column, and absorb vertical shock. P. rapid growth 33) There are ______________________cervical vertebrae. S. thoracic 34) The first cervical vertebra is the _____________________and supports the skull. T. trunk 32) Q. ribs R. sacral U. vertebra prominens 35) The second cervical vertebra is the__________________________, which permits side-to-side rotation of the head. 36) The seventh called the ______________________________is somewhat different 37) There are _____________________________ thoracic vertebrae. 38) The thoracic vertebrae articulate with the_____________________. 39) There are _______________________lumbar vertebrae. 40) The _______________________ vertebrae are the largest and strongest vertebrae in the column. A&P I 41) 42) Chapter 7 Worksheet p 5/5 Name:______________________________________ The ______________________is formed by the union of 5 vertebrae and serves as a strong foundation for the pelvic girdle. The _____________________(tail bone) is formed by the fusion of 4 vertebrae. A. 12 pairs B. 7 pairs C. body Caudal anesthesia (____________________), frequently used during labor (in childbirth), causes numbness in the regions innervated by the sacral and coccygeal nerves (approximately from the waist to the knees). D. Coccyx 44) The term ______________________refers to the entire chest. G. false ribs 45) The skeletal part of the thorax (a bony cage) consists of the ______________________, _______________________, _______________________, and the bodies of the thoracic _________________________. H. floating ribs 43) 46) 47) The thoracic cage encloses and ___________________the organs in the thoracic and superior abdominal cavities. It also provides ________________________for the bones of the shoulder girdle and upper limbs. The _______________________is located on the anterior midline of the thoracic wall. E. costal cartilages F. epidural block I. kyphosis J. lordosis K. manubrium L. protects M. ribs N. Sacrum O. scoliosis It consists of three parts:______________________, __________________, and________________________. P. slipped 49) The __________________________of ribs give structural support to the sides of the thoracic cavity. R. sternum 50) The first ______________________of ribs are called true ribs; 51) The remaining five pairs are called ____________________ (with the last two false ribs called______________________). 52) Protrusion of the nucleus pulposus of the IVD into an adjacent vertebral body is called a herniated (___________________) disc. This movement exerts pressure on spinal nerves, causing considerable pain. 48) Q. Spina bifida S. sternum T. support U. thorax V. vertebrae W. xiphoid process 53) Abnormal curvatures of the vertebral column include________________, a lateral bending of the vertebral column;_________________, an exaggerated cuve of the thoracic curve; and _____________________, an exaggeration of the lumbar curve. 54) ________________________is a congenital defect caused by failure of the vertebral laminae to unite at the midline. This may involve only one or several vertebrae; nervous tissue may or may not protrude through the skin.