perimeter and area
advertisement

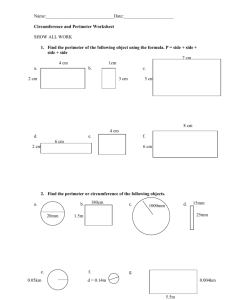
Numeracy Application of Number ______________ L2 Workbook 12 Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 MSS1/L2.8 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 Definitions The Perimeter of a rectangle is the distance round the edge. The Circumference of a circle is the distance around the edge. The Diameter of a circle is the distance across the centre. The Radius of a circle is the distance from the edge to the centre. Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 2 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 Circumference of a circle The distance around the edge of a circle has a special name. It is called the circumference. The circumference is just like the perimeter but is only used when talking about circles. If you know the radius or the diameter of a circle you can calculate its circumference. The circumference is given by: C=2 π πr is a special number and is always 3.14 Example 1 5 cm C=2 πr C = 2 × 3.14 × 5 Circumference = 31.4 cm Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 3 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 Example 2 6 cm Firstly we need to find the radius The radius is half the length of the diameter 6 r= 2 r = 3 cm So C=2 πr C = 2 × 3.14 × 3 = 18.84 cm Exercise 1 Find the circumference of each of the following circles 1. 2. 2 cm 3. 5 cm 8 cm 4. 5. 12 cm 6. 2.4 cm 16.4 cm Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 4 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 The area of parallelogram NB. In a parallelogram the opposite sides are parallel. Height (h) Parallelogram area = b × h A=b×h Base (b) Example 6 cm 8 cm Area = b × h =8×6 = 48 Area = 48 cm2 Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 5 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 Area of a triangle Height (h) Triangle Area = Base × Height = b × h 2 2 Base (b) A=b×h 2 Area of a trapezium (a) Trapezium Area = (a + b) × Height (h) 2 Height (h) Base (b) Workbook 12 A = (a + b) × h 2 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 6 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 Area of a circle The area of a circle is given by Area = π × (radius) 2 A π r2 = Example 5 cm Area = = π r2 π × 52 = 3.14 × 25 = 78.5 cm2 Remember that area always has square units. In this case since the radius is in cm, the area is in square centimetres (cm2) Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 7 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 Exercise 2 Find the area of the following circles 1. 2. 2 cm 4 cm 3. 4. 1.4 cm 8 cm 5. 6. 3.4 cm 18 cm Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 8 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 Exercise 3 For each of the following shapes find: a) the perimeter or circumference b) the area 1. 2.6 cm 4.3 cm 2. 12 cm 5 cm 13 cm 3. 6 cm 4 cm 5 cm 5 cm 10 cm 4. 8.2 cm Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 9 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.7 Exercise 4 1. A circular pond has a diameter of 3.2 m. a) What is the area of the pond? b) What is the circumference? 2. A baseball stadium has a circular patch with a radius of 100 metres. a) The groundsman is going to use a fertilizer and needs to know the area of the pitch. What is the area? b) He also needs to know what the distance is all the way round. What is this dimension called and what is its value? 3. The diameter of the Earth at the equator is rather difficult to measure – we would need to dig a very long tunnel!! It is much easier to measure the circumference. The circumference of the Earth is 40,000 km. Can you calculate its diameter? You could use a calculator and trial and improvement but make a note of each trial and the result. Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 10 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.8 Composite shapes The area of a composite shape is calculated by splitting the shape into separate shapes. The area of each one is then calculated and the areas are added together to find the total area. In examples below the shapes have been divided into two shapes. 6 cm Example 1 4 cm A 7 cm 4 cm B A = 6 × 4 = 24 cm2 Area of shape B = 3 × 2 = 6 cm2 Total Area = 24 + 6 = 30 cm2 Example 2 5 cm C 3 cm D 4 cm Area of shape C = D= Total Area 1 2 (5 × 4) = 10 cm2 4×3 = 12 cm2 = 10 + 12 = 22 cm2 Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 11 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.8 Exercise 5 1. You need to order turf to make a new lawn as illustrated below 12·4 m 4·6 m 7·8 m 8·6 m Find the total area in order that you can buy the correct amount of square metres of turf. 2. A triangular shape has to be painted on some scenery in an outdoor theatre. The triangle has a base of 6 m and a height of 7 m. To calculate the amount of paint required find the total area. Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 12 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.8 Borders 12 m 2 m border 9m To calculate the area of the border (area of large rectangle) - (area of small rectangle) (12 x 9) - (8 x 5) 108 - 40 = 68m2 Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 13 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.8 Exercise 6 1. A photographer has for sale three sizes of photographs with a border round Z 10.5 cm 1 cm border 13.5 cm X 16.5 cm 2 cm border 13.5 cm Y 19.85 cm 2 cm border 24.4 cm For each size, find the area of: a) the photograph without its border b) the photograph and border together c) the border. Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 14 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004 basic & keySKILLBUILDER Measures, Shape and Space Perimeter and Area MSS1/L2.8 2. A rectangular garden is 18.5 m long and 12.4 m wide. It has a central lawn 10.8 m long and 6.5 m wide. Find the area of a) the garden b) the lawn c) the border round the lawn 3. A postcard 14.2 cm by 9.5 cm has a stamp stuck in one corner. The stamp is 24 mm by 2 cm. Find the area of a) the postcard b) the stamp c) the postcard not covered by the stamp. NB. You must make all units the same before calculating c) i.e. convert mm to cm. 4. A garden has a lawn 8.2 m long and 6·5 m wide. The border round the lawn is 1.5 m wide on each side as shown. Find l a) the area of the lawn b) the length l of the garden c) the width w of the garden d) the total area of the garden e) the area of the border w Workbook 12 Level 2 Numeracy/Application of Number 15 © West Nottinghamshire College 2004