Major Models for Instructing ELLs
advertisement

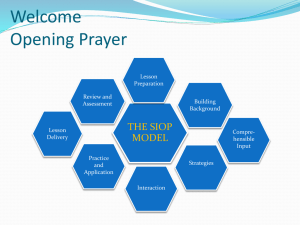
Major Models for Instructing English Language Learners TESOL/504 Version 1 University of Phoenix Material Major Models for Instructing English Language Learners In the first column of the following table, list the major models for instructing English language learners. In the second column, list the components of each model. In the third column, write a brief, real-world example of how that model may be used in a classroom—preferably an example from your own experience. Major models The Integrated ContentBased Method of Instruction, otherwise known as the ICB method Components Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English, otherwise known as SDAIE Classroom example Planning: choose a theme and relevant topics, create both content and language objectives, gather materials, arrange the classroom. Instruction: preteach vocabulary, build background, incorporate collaborative learning opportunities, integrate literacy, ensure cognitive engagement, use visuals, graphic organizers, and learning centers. Assessment: use formative and summative forms of assessment. In an integrated content-based method, academic and language learning are taking place at one time, and lessons are all around one theme. In a primary classroom, a theme could be weather and the water cycle. Although typically a science topic, ELA standards could include compare and contrast and cause and effect, and the math focus could be weather themed word problems involving time. The teacher would preview all vocabulary and display visuals to show the different types of weather and how the water cycle works. Students could participate in hands-on learning experiences, like tracking water evaporation out of cups in the classroom. Goals and Objectives: includes language, content, and social affective goals. Cooperative Learning: students work together in small groups with targeted learning objectives. Modified Instruction: lessons are modified and scaffolded to meet the needs of the students. Multifaceted Assessment: informal and formal assessments are used to evaluate process and product. Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English is a terrific method for students who are already quite proficient in their L2, since this method provides high levels of instruction in content areas and allows CLD students to improve their ability to use their L2 with academics. Lessons taught using this model would be similar to those taught to a classroom of native English speakers, with the addition of comprehensible input, guarded vocabulary, hands-on activities, and the use of visuals or other supplementary materials. Herrera, S. G., & Murry, K. G. (2011). Mastering ESL and bilingual methods: Differentiated instruction for culturally and linguistically diverse (CLD) students (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon. 1 Major Models for Instructing English Language Learners TESOL/504 Version 1 The Sheltered Instruction Observation Protocol, otherwise known as the SIOP model Cognitive Academic Language Learning Approach, otherwise known as the CALLA method Preparation: introducing the lesson objectives. Building Background: help students recognize connections between the new concepts and their existing knowledge and experiences. Comprehensible Input: clarify concepts and modify language to ensure student understanding. Strategies: guide students to use appropriate strategies. Interaction: students collaborate in interactive small groups. Practice and Application: students practice using new strategies or applying new knowledge for learning. Lesson Delivery: adjust the pace of the lesson to meet the needs of the students, guided students through engaging activities. Review and Assessment: assess throughout the lesson to ensure student understanding and to guide future instruction. To begin a social studies SIOP lesson designed to teach students about the southwest region, the teacher would first introduce the language and content objectives. The teacher would connect this lesson with students’ prior experience and knowledge about the southwest, and define key vocabulary words with both words and pictures. Another visual used would be a map to show the region. As the teacher continues with the lesson, she will use guarded vocabulary and scaffolding. She will initiate interactive discussions about the content and lead students through engaging application activities to get students to understand the ways of life in the southwest. The teacher would support students as necessary, review the concepts, and assess students to ensure learning. The Preparation Phase: focuses on prior knowledge and experiences. The Presentation Phase: involves presenting content using visuals, hands-on materials, and guarded vocabulary. The Practice Phase: students are practicing applying the newly taught concepts, language, or strategies using hands-on activities. The Evaluation Phase: students are self-assessing their learning. The Expansion Phase: students are integrating new and existing knowledge. Lessons using the CALLA method involve explicitly teaching students how to use language learning strategies. The beginning of the lesson is similar to the other with the introduction of objectives, building background knowledge, and learning key vocabulary. In a reading comprehension lesson, the teacher would choose one strategy to focus on at a time and utilize guarded vocabulary and hands-on learning strategies to teach it explicitly. She would provide time for students to practice the strategy with texts, and help the students self-assess their ability to use the strategy effectively. Finally, the teacher guides the students through reflection. Herrera, S. G., & Murry, K. G. (2011). Mastering ESL and bilingual methods: Differentiated instruction for culturally and linguistically diverse (CLD) students (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon. 2