Breadboarding Notes - University of Massachusetts Dartmouth
advertisement

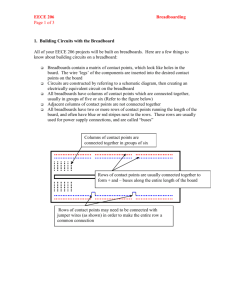
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS DARTMOUTH DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 201 CIRCUIT THEORY I NOTES ON BREADBOARDING THE BREADBOARD LAYOUT Each student will purchase a basic laboratory “kit” consisting of several components, various tools, and a “breadboard” upon which you will construct the circuits to be investigated during the experiments. The layout of a typical breadboard is shown below in Figure 1. Figure 1. A typical breadboard The breadboard which has been included in your kit differs slightly from the illustration shown, but essentially consists of connection points arranged in a “mirror image” about the center line. Of particular importance are the “matrices” formed by the rows labeled A-E and F-J by 64 columns. Notice that the connection points located within one column (either from row A to row E or from row F to row J) are “common” (they are connected together). This will allow you to make up to five connections to the same circuit “node”. From a “row point of view”, the connection points in rows A-E and F-J are isolated from each other (not connected together). The upper and lower “outside edges” of the illustrated breadboard contain 4 groups of connection points arranged in a configuration of 2 rows by 29 columns. The actual breadboard contained in your kit will have the outside 4 rows of connection points arranged as individual rows consisting of 64 common connections. To make this difference more apparent, you will notice that there are red and blue stripes running parallel to the rows, indicating that the connections are common along the entire length of the rows. COMPONENT PLACEMENT AND WIRING Building a circuit on a breadboard can sometimes be challenging. You would like your circuit to work the first time that you try it. Unless you have a faulty component (or components), the circuit should work as long as you have not accidentally mis-wired something. Here are a few suggestions that might make your construction and wiring easier to trace out just in case your circuit doesn’t do what it’s supposed to. 1). When placing components and devices on the breadboard, don’t cram everything close together. Leave a little “working” room around them in case you have to modify the design by either replacing a component or by adding and additional component or two. (If you are building a circuit that must work at high frequencies, this might be poor practice, but for now it’s OK). 2). Be sure to push the component leads far enough into the connection points on the breadboard (until they stop). Failure to do this can result in a poor or loose connection. When installing integrated circuits, try “rocking” the device until the leads properly seat. 3). Use color-coding for your wiring scheme. A common practice is to use red wire for connection to the positive (+) terminal of a voltage source and a black wire for connection to the negative (-) terminal of a voltage source and/or for the ground (0 volt) connections. 4). Consider using the group of connections shown by the red and blue traces as nodes for the power and ground. If your circuit needs both (+) and (-) with respect to ground, you can isolate them on opposite sides of the breadboard. 5). You might consider using other wire colors for connections to external devices (function generator) that might be providing input signals to your circuit, or for connections to either an oscilloscope or meter for measurement purposes. 6). Route your leads around the circuit in such a way as to make it easy to exchange or replace a circuit component that might either be defective or might fail in your circuit. 7). Use wire cutters/strippers to trim leads so that their lengths don’t turn your circuit into “spaghetti”. 8). Think ahead about any measurements that might have to be made, and place your leads so that any scope probes and/or meter leads don’t wind up resting on top of something else, possible causing an accident “short” when you don’t want one. 9). Have a copy of the schematic, or diagram, for the circuit you are building right on the bench top, and check off each connection as it is made.