LAB #0
advertisement
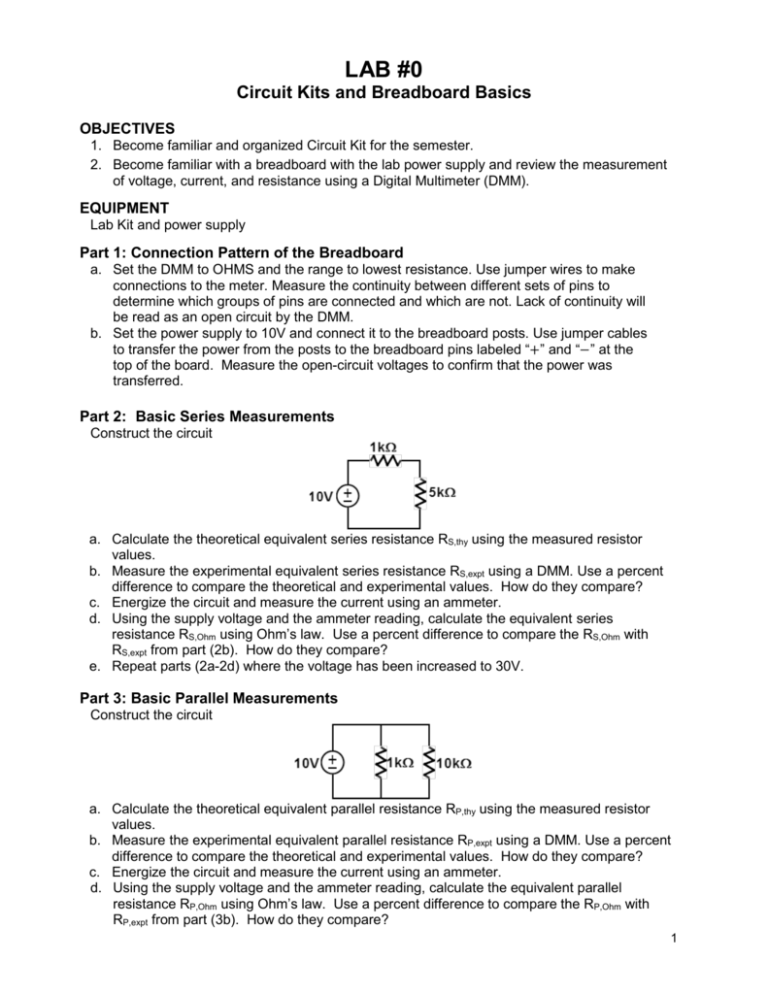
LAB #0 Circuit Kits and Breadboard Basics OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar and organized Circuit Kit for the semester. 2. Become familiar with a breadboard with the lab power supply and review the measurement of voltage, current, and resistance using a Digital Multimeter (DMM). EQUIPMENT Lab Kit and power supply Part 1: Connection Pattern of the Breadboard a. Set the DMM to OHMS and the range to lowest resistance. Use jumper wires to make connections to the meter. Measure the continuity between different sets of pins to determine which groups of pins are connected and which are not. Lack of continuity will be read as an open circuit by the DMM. b. Set the power supply to 10V and connect it to the breadboard posts. Use jumper cables to transfer the power from the posts to the breadboard pins labeled “+” and “−” at the top of the board. Measure the open-circuit voltages to confirm that the power was transferred. Part 2: Basic Series Measurements Construct the circuit a. Calculate the theoretical equivalent series resistance RS,thy using the measured resistor values. b. Measure the experimental equivalent series resistance RS,expt using a DMM. Use a percent difference to compare the theoretical and experimental values. How do they compare? c. Energize the circuit and measure the current using an ammeter. d. Using the supply voltage and the ammeter reading, calculate the equivalent series resistance RS,Ohm using Ohm’s law. Use a percent difference to compare the RS,Ohm with RS,expt from part (2b). How do they compare? e. Repeat parts (2a-2d) where the voltage has been increased to 30V. Part 3: Basic Parallel Measurements Construct the circuit a. Calculate the theoretical equivalent parallel resistance RP,thy using the measured resistor values. b. Measure the experimental equivalent parallel resistance RP,expt using a DMM. Use a percent difference to compare the theoretical and experimental values. How do they compare? c. Energize the circuit and measure the current using an ammeter. d. Using the supply voltage and the ammeter reading, calculate the equivalent parallel resistance RP,Ohm using Ohm’s law. Use a percent difference to compare the RP,Ohm with RP,expt from part (3b). How do they compare? 1