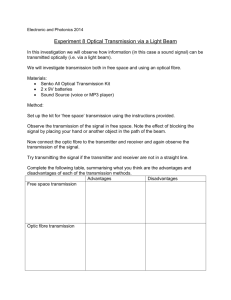
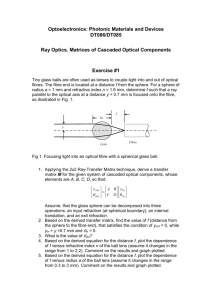
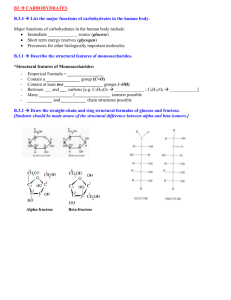
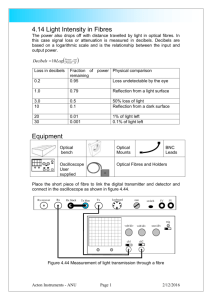
Dietary Fibre
advertisement

NAME:_____________ FORM: ______ What’s for breakfast? At the end of this unit you should be able to:1. Be aware of the importance of breakfast and healthy breakfast choice 2. Understand the source and functions of dietary fibre (N.S.P.) in the body. 3. Understand the structure of the wheat grain. 4. Interpret nutritional information on breakfast cereal packets. 5. Make a healthy fruit yogurt muesli stack! Dietary Fibre What people eat affects their health in some way, this is particularly so if you are eating too much of one thing and not enough of another. What we eat is only one factor affecting our health but it is a very important one. An unhealthy diet can lead to certain health problems and diseases such as : – Obesity Coronary Heart Disease Tooth decay Upset stomachs, and even cancer of the digestive system High blood pressure What’s wrong with the food we eat? In the U.K. eating habits are changing. We eat more readymade foods and restaurants more often. In my family How often do you? (Tick the box) Weekly 1. Eat out in cafe or restaurant 2. Have take-away food e.g chinese 3. Eat ready made meals Monthly Occasionally Dietary Fibre Dietary fibre is also known as non-starch polysaccharide (NSP). Dietary fibre is the outer part of plant cells and is found in cereal grains and in fruit and vegetables. Dietary fibre cannot be digested. As it passes through the body it absorbs water, increases bulk and helps the muscles of the intestine to push out the undigested food. This removal of waste should be regular; otherwise toxins may build up in the body. Fibre acts like a sponge absorbing water. If insufficient amounts are eaten, then the body becomes constipated. HIGH FIBRE – muscles in the wall of the large intestine. Soft and bulky food helps to keep the muscles healthy. LOW FIBRE – The muscles do not work properly when there is very little fibre. DIVERTICULITIS – This is caused by a low fibre diet. The wall of the large intestine is pushed out and becomes painful. Problems associated with a low fibre diet. Constipation - a condition where bowel movements are irregular and uncomfortable because bowel waste is hard and slow moving. Diverticulitis – a condition where the bowel wall has been damaged and distorted with pockets where bacteria can gather. Dietary Fibre in cereal grains A wheat grain is divided into three parts: Outside bran (source of dietary fibre) Endosperm (makes the flour) Germ (source of protein) where the seed grows from. What happens inside our digestive system? An experiment! 1. Measure 2 tablespoons of wholemeal flour. 2. Sieve into bowl. 3. Identify what is left in the sieve. __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ 4. Now measure 2 tablespoons of cold water into a small bowl. 5. Empty the contents of the sieve into the water and stir. Describe what happens. Result: ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Fill in the missing words: 1. D _______ f _________ is the _____________ part of all __________ cells and is therefore found in c____________ g_________ and f__________ and v_____________. 2. How does dietary fibre work? (a) Acts like a ________________ (pnsoeg) (b) __________(ksaos) up water and forms a _________ ________ (garle kblu) (c) This helps push ________ (estwa) out of the body. 3. I need _______ dietary fibre every day. (a) 15g (b) 40g (c) 80g (d) 25-30g 4. Four types of food that contain dietary fibre are: (i) F ________________ (ii) V _______________ (iii) C ________________ (iv) N _______________ Look at the cereal packets Write down the name of each cereal below From the information on the packet find how much dietary fibre there would be in a serving of approximately 30g. Name of cereal Quantity of dietary fibre in a 30g portion 1. Which cereal is highest in dietary fibre? ________________________ 2. Which cereal is lowest in dietary fibre? _________________________ 3. What is your favourite cereal? ________________________________ INCREASE FIBRE IN THE DIET Using the 123 HE book 2 (page 13) list the 9 simple ways to increase fibre in the diet. 1. _________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________ 4. _________________________________________________________ 5. _________________________________________________________ 6. _________________________________________________________ 7. _________________________________________________________ 8. _________________________________________________________ 9. _________________________________________________________ Foods high in fibre Foods lower in fibre Peas, Sweetcorn, lentils, wholemeal bread, dried fruit, leafy vegetables, brown rice, wholemeal pasta, apples with skin, muesli, potatoes with skin, some breakfast cereals. White rice, cornflakes, white bread, cucumber, watery vegetables, tinned fruit, white pasta, tomatoes, peeled potatoes, white flour Foods with no fibre Eggs, butter, cheese, milk, meat, fish, yogurt. Where is our fibre? Cereals: grams of fibre Bread: grams of fibre 10g (2tblsp) bran 4.4 50g (2tblsp) All bran 13.4 25g (4tblsp) Cornflakes 0.28 200g porridge (made with 2 tblsp oats) 1.6 2 Shredded wheat 6.8 2 Weetabix 4.4 2 slices med. cut white loaf 2 slices med. cut wholemeal loaf 4 sm slices sunblest hi-bran Nuts: fruit: 25g Almonds 25g Brazil nuts 25g peanuts 25g peanut butter 25g walnuts Vegetables: 150g baked beans 75g cabbage 75g carrots 75g cauliflower 15g lettuce 50g mushrooms 75g onions 75g peas 120g baked potato 60g tomato 25g(1pkt) crisps grams of fibre 3.6 2.3 2.0 1.9 1.2 2.2 6.8 8.3 grams of fibre 1 apple 1 banana 1 orange 1 pear 2 sticks rhubarb 75g strawberries 1 tblsp sultanas grams of fibre 11.0 1.9 2.3 1.4 0.2 2.0 1.0 3.9 2.5 0.9 3.0 Highlight those foods that are particularly high in dietary fibre 2.3 2.0 3.4 3.0 2.4 1.7 1.8