VHDL Codes for Combinational Devices
advertisement

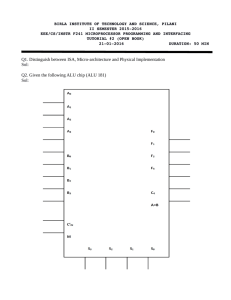
Supplement of Lecture 5: VHDL Codes of some Combinational Devices. VHDL model of comparator (8 bits): library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; use ieee.std_logic_arith.all; use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all; -- 8 Bit Unsigned Comparator entity cmp8 is port ( A,B : in std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); aeqb, altb, agtb : out std_logic ); end cmp8; architecture a of cmp8 is begin aeqb <= '1' when (a = b) else '0'; altb <= '1' when (a < b) else '0'; agtb <= '1' when (a > b) else '0'; end; The operators =, /=, <=, <, >, >= are defined in the std_logic_arith package which is part of the IEEE library. -- vhdl model for the 3 to 8 decoder --************************************************************************* -- IO Interface Declaration --************************************************************************* library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity dec3to8 is port ( -- inputs signal sel: in std_logic_vector(2 downto 0); -- selector signal en: in std_logic; -- enable -- outputs 1 signal y: out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) ); end dec3to8; -- outputs are high true --************************************************************************* -- Architecture body --************************************************************************* architecture behavior of dec3to8 is begin process (sel,en) begin y <= "11111111"; if (en = '1') then case sel is when "000" => y(0) <= '1'; when "001" => y(1) <= '1'; when "010" => y(2) <= '1'; when "011" => y(3) <= '1'; when "100" => y(4) <= '1'; when "101" => y(5) <= '1'; when "110" => y(6) <= '1'; when "111" => y(7) <= '1'; when others => y(7) <= '1'; end case; end if; end process; end behavior; 74LS138 (3 x 8 decoder) VHDL Code: Library ieee Use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; Entity V74x138 is Port (G1, G2A_L, G2B_L: in std_logic; -- enable inputs A: in std_logic_vector (2 downto 0); -- select inputs A= A(2), B= A(1), C = A(0) Y_L: out std_logic_vector (0 to 7)); -- decoded outputs End V74x138; Architecture V74x138_arch of V74x138 is Signal Y_int: std_logic_vector(0 to 7); Begin With A select Y_int <= “01111111” when “000”, “10111111” when “001”, 2 “11011111” when “010”, “11101111” when “011”, “11110111” when “100”, “11111011” when “101”, “11111101” when “110”, “11111110” when “111”, “11111111” when others; Y_L<=Y_L_i when (G1 and not G2A_L and not G2B_L) =’1’ else “11111111”; End V74x138_arch; -- vhdl model for 8 level priority circuit --************************************************************************* -- IO Interface Declaration --************************************************************************* library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; entity priority_new is port ( -- inputs signal y1: in std_logic; signal y2: in std_logic; signal y3: in std_logic; signal y4: in std_logic; signal y5: in std_logic; signal y6: in std_logic; signal y7: in std_logic; -- outputs signal vec: out std_logic_vector(2 downto 0) ); end priority_new; --************************************************************************* -- Architecture body --************************************************************************* architecture behavior of priority_new is begin process (y1,y2,y3,y4,y5,y6,y7) begin vec <= "000"; if (y1 = '1') then vec <= "001"; 3 end if; if (y2 = '1') then vec <= "010"; end if; if (y3 = '1') then vec <= "011"; end if; if (y4 = '1') then vec <= "100"; end if; if (y5 = '1') then vec <= "101"; end if; if (y6 = '1') then vec <= "110"; end if; if (y7 = '1') then vec <= "111"; end if; end process; end behavior; VHDL model of a 4 to 1 multiplexers library ieee; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; -- 4 to 1 mux, 8 bit inputs, using concurrent statements entity mux4to1_8_conc is port ( I0,I1,I2,I3 : in std_logic_vector(7 downto 0); sel : in std_logic_vector(1 downto 0); dout : out std_logic_vector(7 downto 0) ); end mux4to1_8_conc; architecture a of mux4to1_8_conc is begin WITH sel SELECT dout <= I0 when "00", I1 when "01", 4 I2 when "10", I3 when others; end a; Arithmetic and Logic Unit Consider a small 1-bit arithmetic logic unit (ALU) performs the following operations: A+1 A + B + Cin A A-1 Not A A and B A or B A xor B Let us analyze and model the 1-bit ALU using VHDL. We will use the designed 1-bit ALU and the structural-type modeling, to write the VHDL model of a 16-bit ALU. Assume that the arithmetic addition generates the output carry Cout. By analyzing the specification of the problem, we can establish the function table of a 1-bit ALU as follows: FS2 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 FS1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 FS0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Function Implemented A +1 (increment) A + B + Cin (addition) A (identity) A – 1 (decrement) Not A ( complement) A and B (and logic) A or B ( or logic ) A exor B (exclusive or logic) We have to implement two arithmetic operations (+ and - ) plus other logic functions (and, not, identity, or, xor) using basic logic gates. Data involved are of type BIT. The truth Tables for a full adder and full subtractor are given as follows: 5 Subtraction Truth Table: Bin 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 A 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 B 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Diff. = A - B 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 Bout 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 Bin = Borrow in; Bout = Borrow out. Using K-map for minimization, we have : Diff A exor B exor Bin Bout [ Bin and (( not A) or B)] or [( not A) and B] Full Adder Truth Table: Cin 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 A 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 B 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Sum = A + B 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 Cout 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 Cin: carry in; Cout: carry out. Sum A exor B exor Cin Cout [Cin and ( A or B)] or [ A and B] In our design we will use Cin for Borrow in and Carry in; Cout for Carry out and Borrow out depending of the type of operation requested (function selection). This is done at the level of the VHDL code. The VHDL model of a 1-bit ALU is given as: library IEEE; -- File alu_1.vhdl use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; entity alu_1 is port ( a: in BIT; b: in BIT; 6 Cin: in BIT; -- Use for Borrow in or Carry in FS: in BIT_VECTOR(2 downto 0); c: out BIT; Cout: out BIT -- Use for carry out or borrow out ); end alu_1; architecture alu_1_arch of alu_1 is begin -- <<enter your statements here>> process(a,b,FS,Cin) variable v1, v2: BIT; begin case FS is when "000" => -- Increment a by 1 = add 1 to a ( b =1, Cin = 0) v1 := '1'; -- v1 is used for b v2 := '0'; -- is used for Cin c<= a xor v1 xor v2;--addition Cout <= (a and v1) or (v2 and (a or v1)); when "001" => c<= a xor b xor cin;--addition Cout <= (a and b) or (Cin and (a or b)); when "010" => -- Identity c<= a ; Cout <= '0'; when "011" => -- Decrement a by 1 v1 := '1'; -- v1 is used for b = 1 v2 := '0'; -- v2 is used for Bin = 0 c<= a xor v1 xor v2;--addition Cout <= ( (not a) and v1) or (v2 and ((not a) or v1) ); when "100" => -- Not a c<= not a; Cout <= '0'; when "101" => c<= a and b; Cout <='0'; when "110" => c<= a or b; Cout <= '0'; when "111" => c<= a xor b; Cout <= '0'; when others => c<='0'; Cout <='0'; end case; 7 end process; end alu_1_arch; The library xslib that contains alu_1 is built using a package alu_1pckg defined within the file alu_1pck.vhd as follows: library IEEE; use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; PACKAGE alu1_1pckg is COMPONENT alu_1 port ( a: in BIT; b: in BIT; Cin: in BIT; FS: in BIT_VECTOR(2 downto 0); c: out BIT; Cout: out BIT ); end COMPONENT; end alu1_1pckg; library IEEE; -- File alu_1.vhdl use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; entity alu_1 is port ( a: in BIT; b: in BIT; Cin: in BIT; -- Use for Borrow in or Carry in FS: in BIT_VECTOR(2 downto 0); c: out BIT; Cout: out BIT -- Use for carry out or borrow out ); end alu_1; architecture alu_1_arch of alu_1 is begin -- <<enter your statements here>> process(a,b,FS,Cin) variable v1, v2: BIT; begin case FS is when "000" => -- Increment a by 1 = add 1 to a ( b =1, Cin = 0) v1 := '1'; -- v1 is used for b v2 := '0'; -- is used for Cin 8 c<= a xor v1 xor v2;--addition Cout <= (a and v1) or (v2 and (a or v1)); when "001" => c<= a xor b xor cin;--addition Cout <= (a and b) or (Cin and (a or b)); when "010" => -- Identity c<= a ; Cout <= '0'; when "011" => -- Decrement a by 1 v1 := '1'; -- v1 is used for b = 1 v2 := '0'; -- v2 is used for Bin = 0 c<= a xor v1 xor v2;--addition Cout <= ( (not a) and v1) or (v2 and ((not a) or v1) ); when "100" => -- Not a c<= not a; Cout <= '0'; when "101" => c<= a and b; Cout <='0'; when "110" => c<= a or b; Cout <= '0'; when "111" => c<= a xor b; Cout <= '0'; when others => c<='0'; Cout <='0'; end case; end process; end alu_1_arch; Finally the structural model of a 16-bit ALU using 16 1-bit ALUs is given: library IEEE, XSLIB; -- File alu_16b.vhd use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; use XSLIB.alu1_1pckg.all; entity alu_16b is port ( A: in BIT_VECTOR (15 downto 0); B: in BIT_VECTOR (15 downto 0); Cin: in BIT; Sel: in BIT_VECTOR(3 downto 0); 9 C: out BIT_VECTOR (15 downto 0); Cout: out BIT ); end alu_16b; architecture alu_16b_arch of alu_16b is signal C_inout: BIT_VECTOR(14 downto 0); component alu_1 is port ( a: in bit; b: in bit; Cin: in bit; FS: in BIT_VECTOR (3 downto 0); c: out bit; Cout: out bit); end component; begin -- <<enter your statements here>> alu0: alu_1 port map(A(0), B(0),Cin,Sel,C(0), C_inout(0)); alu1:alu_1 port map(A(1), B(1),C_inout(0),Sel,C(1), C_inout(1)); alu2:alu_1 port map(A(2),B(2),C_inout(1),Sel,C(2), C_inout(2)); alu3:alu_1 port map(A(3), B(3),C_inout(2),Sel,C(3), C_inout(3)); alu4:alu_1 port map(A(4), B(4),C_inout(3),Sel,C(4), C_inout(4)); alu5:alu_1 port map(A(5), B(5),C_inout(4),Sel,C(5), C_inout(5)); alu6:alu_1 port map(A(6), B(6),C_inout(5),Sel,C(6), C_inout(6)); alu7:alu_1 port map(A(7), B(7),C_inout(6),Sel,C(7), C_inout(7)); alu8:alu_1 port map(A(8), B(8),C_inout(7),Sel,C(8), C_inout(8)); alu9:alu_1 port map(A(9), B(9),C_inout(8),Sel,C(9), C_inout(9)); alu10:alu_1 port map(A(10), B(10),C_inout(9),Sel,C(10), C_inout(10)); alu11:alu_1 port map(A(11), B(11),C_inout(10),Sel,C(11), C_inout(11)); alu12:alu_1 port map(A(12), B(12),C_inout(11),Sel,C(12), C_inout(12)); alu13:alu_1 port map(A(13), B(13),C_inout(12),Sel,C(13), C_inout(13)); alu14:alu_1 port map(A(14), B(14),C_inout(13),Sel,C(14), C_inout(14)); alu15:alu_1 port map(A(15), B(15),C_inout(14),Sel,C(15), Cout); end alu_16b_arch; 10