Designing an ALU
advertisement
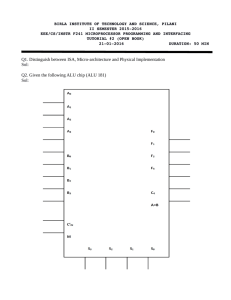
Designing an ALU Taken from various sources Primary source: Digital Design and Computer Architecture by Harris &Harris ALU • An arithmetic logic unit (ALU) – Performs arithmetic and logic operations – A fundamental building block of the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of a computer – Even the simplest microprocessors contain one for purposes such as maintaining timers – A combinational logic circuit Complex ALU Simple ALU The S input is controlled by the processor based on the op code Adder full adder from a previous lecture 5 Adder/Subtractor Textbook ALU Our Target ALU, N=32 The F input is controlled by the processor based on the op code Possible Implementation module alu (input [31:0] A, B, input [2:0] F, output reg [31:0] Y); // implement everything using a case statement??? always @ (*) case (..) … endcase endmodule An Implementation A cover a cover a cover a cover From Harris Text: a simple ALU a cover a cover a cover a cover Test Cases Test the Implementation AA cover a cover a cover a cover simple testbench a cover a cover a cover a cover ALU Enhancements 1. Add a Zero output to the ALU. The output is TRUE when Y==0, otherwise it is FALSE. 1. Add and Overflow output to the ALU. The output is TRUE when the result of the adder overflows, otherwise it is FALSE. An Implementation A cover a cover a cover a cover a From Harris Text: an enhanced ALU cover a cover a cover a cover A Better Testbench • Improved Testbench • Data file