universidad de especialidades espíritu santo
advertisement

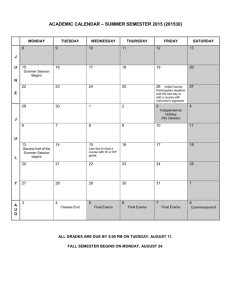
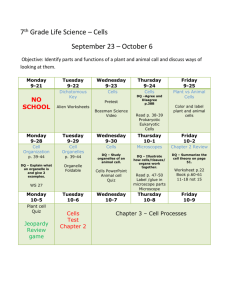
UNIVERSIDAD DE ESPECIALIDADES ESPÍRITU SANTO FACULTAD DE ESTUDIOS INTERNACIONALES SYLLABUS ENGLISH VERSION FOR DAC 11 VER 12 03 09 SUBJECT: Dev & Evaluation of Projects 1 CODE: UGER 280 FACULTY: James Keeley, PhD CREDITS: 3 CONTACT HOURS: 48 NON CONTACT HOURS: 96 YEAR: 2011 PERIOD: May 2 – June 25 DAYS: Monday – Thursday SCHEDULE: 1040 – 1200 pm ROOM: F209 SYLLABUS DATE: Apr 2011 1. COURSE DESCRIPTION This course teaches all the academic theory of project evaluation, development and management. It covers topics such as project concepts, life cycles, time-, qualityand cost management, risk management, project organization and management skills for projects. Students practice the various concepts with case methodology and other exercises. 2. JUSTIFICATION This course enables students to identify, analyze and understand the specific processes involved in the development and sustainment of business, social and governmental projects on both large and small scales. This allows students a better appreciation of the elements involved with project planning, delivery and sustainability. 3. OBJECTIVES a. GENERAL This course examines project management roles and environments, the project life cycle and various techniques of work planning, and control and evaluation to achieve project objectives. The tools currently available to project managers are discussed and presented throughout this course. b. SPECIFIC After completion of this course, students will be able to: 1. Analyze the relationship between organizational continuous improvement and a project's strategic objectives, while continuing to support and assess planning and implementation issues. 2. Defend the need for conformance of project management to organizational culture. 4. COMPETENCIES This course will allow the student to use basic problem solving techniques in order to solve project management issues as they arise; make appropriate decisions based on the requirements of the task and allow for recognition of organizational structure and policy to guide strategic thinking skills in order to complete a project within established time and fiscal parameters. 5. COURSE CONTENT OUTLINE Class Meeting # 1 Monday May 2 Competencies The student defines the salient characteristics of a project and explains the need for project management CONTENT What is the Difference Between a Program and a Project? Project Management Overview Project Conceptualization The student describes the system development cycle 4 Thursday May 5 PERFORMANCE INDICATORS Defines the characteristics of a project Thomsett, R. (ND). Pages 119 Project Scope Wysocki & McGary, (2003) Pages 49 - 72 Explains the need for project management Identifying Project Activities Wysocki & McGary, (2003) Pages 75 - 95 Estimation Duration, Resource Requirements and Cost Wysocki & McGary, (2003) Pages 97 – 116 Compares and contrast the roles of project managers in organizational environments Describes the systems development cycle 2 Tuesday May 3 3 Wednesday May 4 HOMEWORK (96 HRS.) Wysocki & McGary, (2003) Pages 1 – 48 Thomsett, R. (ND). Pages 2136 5 Monday May 9 The student determines roles of systems analysis and systems management within the scope of project management Constructing and Analyzing a Project Network Diagram Finalizing the Schedule; Organizaing and Conducting the Joint Project Planning Session Wysocki & McGary, (2003) Pages 117 - 142 Wysocki & McGary, (2003) Pages 143 – 168 6 Tuesday May 10 Global Project Case Study Student In-Class Discussion Case Presentation 7 Wednesday May 11 Recruiting, Organizing and Wysocki & Managing the Project McGary, (2003) Team Pages 169 – 206 Thomsett, R. (ND). Pages 3744 Explains the roles of systems analysis and systems management in the life cycle of a project Associates the project's information systems with the strategic need to communicate Describes the ways groups are organized into projects 8 Thursday May 12 The student describes the way and manner in which groups are organized into project teams Adaptive Project Framework 9 Monday May 16 10 Tuesday May 17 11 Wednesday May 18 12 Thursday May 19 13 Monday May 23 Monitoring and Controlling Wysocki & Progress; Project McGary, (2003) Management Roles Pages 207 - 241 Technique The student constructs a statement of work (SOW) and decompose overall project goals Closing-Out the Project; Critical Chain Project Management Project Portfolio Management Cycle Build; Client The student Checkpoint; Variations to develops a APF work breakdown structure using established tools and techniques to achieve stated project objectives Earned Value Project Management Explains the roles and responsibilities of project team members Wysocki & Explains the McGary, (2003) relationship Pages 267 - 304 between project managers and line managers, especially in terms of the division of responsibility and authority Wysocki & Identifies McGary, (2003) leadership styles Pages 243 – of project 265 managers Wysocki & McGary, (2003) Pages 351 – 396 Describes techniques used to manage groups and individuals in order to increase Thomsett, R. the effectiveness (ND). Pages 47- of working on a 61 project team Wysocki & McGary, (2003) Pages 306 – 347 Thomsett, R. (ND). Pages 6379 Flemming & Koppelman Pages 1 - 62 Produces a statement of work (SOW) and decompose overall project goals Develops a work breakdown structure (WBS), using established tools and techniques, to achieve stated project objectives Project Management: Innovativeness is the Key (12) Initiates components of the SOW Mid Term Demonstrates knowledge regarding the components of a WBS Project Support; Putting it all Together; Gantt Charting Wysocki & McGary, (2003) Pages 397 – 432 Budget Planning and Scheduling Flemming & Koppelman Pages 63 - 84 Produces a taskflow network, using established tools and techniques, and analyze the contingencies, interrelationships, and critical path(s) of the work elements Identifies cost over-runs and other budget anamolies Innovation 14 Tuesday May 24 MID TERM EXAMINATION 15 The student Wednesday analyzes May 25 optimal labor utilization for cost effectiveness and labor utilization using a resource loading chart 16 Thursday May 26 17 Monday May 30 18 Tuesday May 31 19 Wednesday Jun 1 20 Thursday Jun 2 The student defines the elements of project quality management and applies them to the final project Global Project Case Study Student In-Class Discussion Case Presentation The student Monitoring Performance; identifies risk Forecasting; Final Cost management and Schedule Results activities throughout the project life cycle Project Constraints; Stakeholders Describes how to accomplish project planning with a strategic perspective Flemming & Produces a Gantt Koppelman chart, using Pages 127 - 155 established tools and techniques, to schedule the completion of all work elements Project Management; Challenges and Lessons Learned (12) Lists reasons for using the project management approach to organize work Network Diagraming 21 Monday Jun 6 22 Tuesday Jun 7 25 Monday Jun 13 26 Tuesday Jun 14 27 Wednesday Jun 15 28 Thursday Jun 16 29 Monday Jun 20 30 Tuesday Jun 21 Explains how projects serve as the building blocks in the design and execution of organizational strategies Defends the position that a project's objectives should be integrated with an organization's strategies Identifies a project's key stakeholders Project Management on The student the Web utilizes earnedvalue concepts for project milestone control Mastering the Project Web-Enabled Project Management (16) Constructing a Business Plan Coffee Shop Business Plan Example Constructs a Business Plan for a project Contents of a Business Plan Coffee Shop Business Plan Example Constructs a Business Plan for a project Coffee Shop Business Plan Example Constructs a Business Plan for a project Business Plan Example and Template Demonstrates knowledge related to financial costing Financials; projections and Business Plan Example and the cost of capital Template 23 Wednesday Jun 8 24 Thursday Jun 9 Project Management Network Diagraming (10) The student Business Plan Financial applies project Overview concepts to the business plan Fianancials; the NPV profitability index Project Management: 24-Steps to Mastering Any Project (17) Marketing and Consumer Data Business Plan Example and Template Demonstrates knowledge related to financial projections Applies marketing concepts to the project UEES FERIA CheckList and Prototype Construction FINAL EXAM Feria Checklist and Criteria for entering Applies business components to the business plan 6. METHODOLOGY The methods for learning in this course include classroom lectures and discussions, case studies, small-group sessions, and practical exercises that will expose students to new ideas and increase their knowledge of the role and scope of project design and development. 7. EVALUATION The student will be assessed through daily participation and evaluation by written work and testing. By the conclusion of this class the student will be able to recognize and identify key objectives and will be able to fundamentally apply what was learned based upon the information given in this bi-mester of instruction. 7.1 Assessment Criteria Completion and knowledge of the assigned course readings, Consistent use of electronic media, Completion of assigned homework Classroom participation is subjectively considered in final score 7.2 Performance Markers 1. Defines the characteristics of a project, 2. Explains the need for project management, 3. Compares and contrasts the roles of project managers in organizational environments, 4. Describes the systems development cycle, 5. Explains the roles of systems analysis and systems management in the life cycle of a project, 6. Describes the ways groups are organized into projects, 7. Explains the roles and responsibilities of project team members, 8. Completes a business plan 9. Identifies leadership styles of project managers, 10. Describes techniques used to manage groups and individuals in order to increase the effectiveness of working on a project team, 11. Produces a statement of work (SOW) and decompose overall project goals, 12. Develops a work breakdown structure (WBS), using established tools and techniques, to achieve stated project objectives, 13. Produces a task-flow network, using established tools and techniques, and analyze the contingencies, interrelationships, and critical path(s) of the work elements, 14. Produces a Gantt chart, using established tools and techniques, to schedule the completion of all work elements, 15. Lists reasons for using the project management approach to organize work, 16. Explains how projects serve as the building blocks in the design and execution of organizational strategies, 17. Defends the position that a project's objectives should be integrated with an organization's strategies, 18. Identifies a project's key stakeholders, 19. Assesses the strategic issues facing a project team, 20. Analyzes the approaches to managing a project's strategic issues, 21. Describes how to accomplish project planning with a strategic perspective, 22. Associates the project's information systems with the strategic need to communicate. 7.3 Weighting: Homework 50% Exams 50% 8. BIBLIOGRAPHY 8.1 REQUIRED: Flemming, Q. & Koppelman, J. (2000). Earned value project management, 2nd Ed. PMI, Pennsylvania. Wysocki, R. & McGary, R. (2003). Effective project management, 3rd Ed. Wiley Publishng, Indianapolis, IN. Thomsett, R. (ND). The busy person’s project management workbook. This book is in pdf format and will be sent to you for printing. ON ORDER: Kerzner (2009). Project management, a systems approach. 8.2 COMPLIMENTARY: None 8.3 HANDOUTS/READINGS (Given in Class): Project Management; Challenges and Lessons Learned Project Management Network Diagraming Project Management: 24-Steps to Mastering Any Project Web-Enabled Project Management Project Management Explained; A Logical Framework Modeling Project Management Project Management: Innovativeness is the Key Theory of Project Management 8.4WEBLIOGRAPHY: ProQuest Database for Make-up Assignments: Access portal through the UEES homepage at: www.uees.edu.ec The Project Management Center: http://www.infogoal.com/pmc/pmchome.htm The International Research Network on Organizaing by Projects: http://www.irnop.org/ E-Project Central: http://www.eprojectcentral.com/ The Three Little Pigs Project: http://www.eng.uwo.ca/research/ttlpp/overview.htm The Woody 2000 Project: http://www.maxwideman.com/papers/woody2000/intro.htm 9. FACULTY INFORMATION: NAME: E-mail: James W. Keeley, PhD drjwkeeley@yahoo.com jkeeley@uees.edu.ec ACADEMIC CREDENTIALS: B.A.A.S Bachelors of Arts and Sciences GRADUATE: M.Ed. Master of Education M.B.A. Master of Business Administration Ph.D. Doctor of Philosophy Prepared by: James W. Keeley, PhD Date: Apr 15, 2011 Reviewed by: Dean Monica Reynoso Date: April, 2011