Advanced Biology Chapter 1 Test Study Guide - DC
advertisement

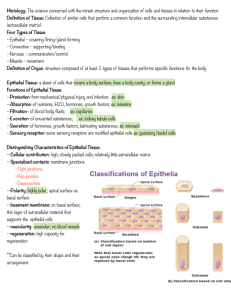
Anatomy/Physiology Chapter 4 Test Study Guide You will be expected to know and be able to do the following things. The Tissue Level of Organization, pages 109-146 Student will be able to: Name and briefly describe the four types of tissues in the body. Name and describe the five types of cell junction. Give 1 or 2 locations or situations where each type of cell junction occurs. Describe characteristics of epithelial tissue. Describe and label the sides of an epithelial tissue cell. Compare and contrast covering and lining epithelial tissue with glandular epithelial tissue. Describe and identify the three arrangements epithelial cells can be found in within the body. Describe and identify the four shapes that epithelial tissue cells can have. Briefly identify, describe, give an example, and give a function of the different types of covering and lining epithelial tissues. Explain the function of glandular epithelial tissue. Compare and contrast endocrine gland and exocrine glands and give examples of each. Describe how multicellular glands are categorized. Identify the various types (pictures) of multicellular exocrine glands. Compare and contrast merocrine, apocrine, and holocrine glands and give examples of each. Give several functions of connective tissue. Describe the general features of connective tissue. Describe and identify the six types of connective tissue cells. Briefly describe ground substance and fibers that are found in connective tissue. Contrast the three types of fibers in connective tissue. Compare and contrast embryonic connective tissue and mature connective tissue. Describe the five categories of mature connective tissue and give examples/functions of each. Briefly describe how cartilage is repaired. Describe and compare/contrast the types of membranes in your body including examples and functions of each. Describe the functions and unique characteristics of muscular tissue. Compare and contrast the three types of muscular tissue. Describe the functions and unique characteristics of nervous tissue. Label and describe the parts of a nervous cell. Explain what it means to be an excitable cell and give some examples. Describe how tissues are repaired and how they maintain homeostasis. Explain how tissues are affected by a person getting older. Vocabulary Tissue Histology Pathologist Cell junction Plaque Adhesion belt Connexins Apical surface Lateral surface Basal surface Basement membrane Avascular Secretion Absorption Squamous cells Cuboidal cells Columnar cells Transitional cells Goblet cells Keratin Gland Endocrine gland Exocrine gland Unicellular gland Multicellular gland Simple gland Compound gland Tubular gland Acinar gland Tubuloacinar gland Merocrine gland Apocrine gland Holocrine gland Extracellular matrix Fibroblasts Adipocytes Mast cells White blood cells Macrophages Plasma cells Ground substance Fiber Collagen fibers Elastic fibers Reticular fibers Stroma Mesenchyme Loose connective tissue Dense connective tissue Interstitial growth Appositional growth Osseous tissue Osteons Compact bone Spongy bone Blood tissue Blood plasma Red blood cells Platelets Lymph Membranes Epithelial membrane Synovial membrane Mucous membrane/Mucosa Serous membrane/Serosa Parietal layer Visceral layer Serous fluid Pleura Pericardium Peritoneum Cutaneous membrane/skin Synovial fluid Muscular tissue Skeletal muscular tissue Cardiac muscular tissue Smooth muscle tissue Neurons Action potentials Neuroglia Excitable cells Electrical excitability Stroma Parenchyma Tissue regeneration Cartilage