FluidMechanics-2 - The University of Jordan
advertisement

The University of Jordan – Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Mechanical Engineering Department
Fluid Mechanics II – Course # ME 0904462
Instructor: Dr. Jamil Al Asfar- Spring, 2012
Time:
8 - 9:30 Monday and Wednesday
Office Hours: Announced on the door of the instructor’s office
I. Course Description 0904462 Fluid Mechanics II [3 Cr. Hrs.]
Review of basic definitions; system and control volume; Foundations
of flow analysis; differential from of the basic laws; general viscous
flow; boundary layer theory, Navier – Stokes equation, Blassius
equation, Von Karman equation, Irrotational flow; stream function,
vorticity and rotationality, Incompressible inviscid frictionless flow, 2D Flow solutions around bodies, compressible flow; adiabatic and
isentropic flow; Normal shock waves; Nozzles; Introduction to
turbomachinery, centrifugal pumps.
II. Required Background or Experience
Prerequisites by course:
1- Fluid Mechanics (1) (0904361)
2- Engineering Mathematics(2)(0901202)
3- Thermodynamics(1) 0904241
Prerequisites by topic:
1- Partial differential equations.
2- Differential equations of mass, momentum, angular
momentum and energy.
3- Viscous fluid motion.
4- Basic thermodynamics of gases.
III. Expected Outcomes
Students will be expected to develop the following skills/understanding upon the
successful completion of 0904462. They will be able to:
1. Identify system vs. control volume approach in various aspects of fluid
mechanics such as momentum and angular momentum equations.
2. Identify stream function, vorticity, irrotationality and frictionless irrotational
flows.
3. Estimate velocity and pressure distribution caused by potential flow around
bodies.
4. Understand viscous flows over surfaces and estimate drag on them.
5. Calculate lift and drag on various streamlined bodies.
6. Calculate forces caused by potential flow around bodies.
7. Analyze wave propagation through compressible flow and identify the effect
of the speed of sound on it.
8. Design a nozzle with compressible flow conditions.
9. Size and select a pump for a given job.
IV. Textbook(s) and Readings
1. Clayton T. Crowe, Donald F. Elger and John A. Roberson., “Engineering Fluid
Mechanics”; 9th Edition, Publisher: Wiley, 2010.
2. Fluid Mechanics, by Frank M. White; McGraw- Hill, 4th Edition, 1999
{reference}.
V. Minimum Student Materials: Text, engineering calculator.
VI. Minimum College Facilities : Classroom with black board.
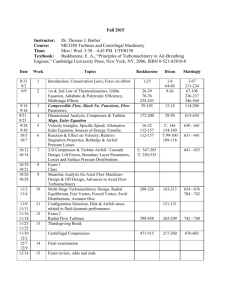
VII. Course Outline
The following topics will be covered in this course:
I.
Differential relations for a fluid particle: A review is made in this
chapter to system versus control volume concept and subsequently to the
differential equations of mass momentum, angular momentum and energy .
Boundary conditions for various flows; The Stream function; Vorticity and
irrationality; Frictionless irrational flows.
II.
Boundary-Layer Flows: Review of the Boundary Layer concept;
momentum integral estimation; B.L. equations; B.L. on a flat plate;
Experimental external flows.
III.
Inviscid Incompressible Flow: Introduction; Elementary plane-flow
solutions; Superposition of plane-flow solutions; Plane flow around bodies;
IV.
Compressible Flow: Introduction; Speed of sound; Adiabatic and
isentropic flow; Isentropic flow with area changes; Normal shock wave;
Converging and diverging nozzles; 2-D supersonic flow;
V.
Turbomachinery: Classification; The centrifugal pump, performance
curves Net Positive Suction Head; Matching pumps to system characteristics.
VIII. Instructional Methods
1. Lecture/Problem solving sessions.
2. Homework.
IX. Evaluation of Outcomes
Evaluation will be done based on the following:
1. Homeworks
: 10%
2. First Exam
:20%
2. Second Exam
:20%
3. Final Exam
: 50%
X. Professional Component Contribution
The student gains the ability to understand and analyze a wide variety of fluid-related
problems in engineering.
XI. Home Work:
Problems 9th ed.
Homework
number
One
Due Date
1.7; 2.18,36; 3.105; 4.7, 24, 63, 100, 101 & 110
Feb 23
Two
Three
Four
Five
Six
Seven
5.19, 33, 37, 39, 46, 75, 96, 105 & 107*
6.9, 36, 56, 80, 92, 98, 16 & 107*
7.9, 13, 30, 32, 36; 9.7, 10, 30, 41 & 54
10.4, 93, 95; 11.6, 11, 31, 41, 55* & 65
12.10, 13, 19, 29, 33, 38 & 59
14.6, 11, 13, 23, 29, 38*, 48, 50, 56; 15.4, & 50
March 1
March 15
April 5
April 26
May 6
May 13