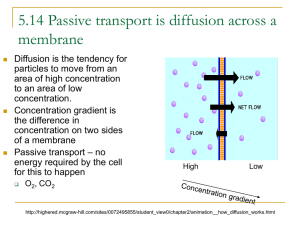
Passive Transport
advertisement

Name: Transport Across A Cell Membrane I. Cell Membrane 1. Play animation to review parts of cell membrane: http://www.susanahalpine.com/anim/Life/memb.htm List main parts: 2. http://www.aber.ac.uk/gwydd-cym/cellbiol/transport/index.htm - Fill in the blanks below: Diffuses easily through lipid bilayer Do not diffuse through lipid bilayer II. Passive Transport http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/Biology1111/animations/transport1.html Click on Passive Transport and answer the following questions: 1. Define Passive Transport: 2. Hit next and go through the slides to give a brief description of each of the following types of diffusion: Main components of cell membrane Integral proteins Job/description Fluid lipid Bilayer 3. Types of Diffusion Simple Diffusion Definition/Description Determinants of diffusion: When does diffusion “end?” Animation of diffusion http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/transport/diffusion.swf Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis For animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/transport/osmosis.swf 4. http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/bloodcells.gif Pictures of Red Blood Cells Identify what type of solution each is placed, what happened and why III. Active Transport http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/Biology1111/animations/transport1.html 1. Define Active Transport 2. Why is it necessary? 3. Types of Active Transport Ion Pumps Definition/Description For animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/transport/atpase.swf Cotransport Endocytosis (Transport of large molecules) ENDO = INSIDE Define: Phagocytosis: For animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/cellstructures/phagocitosis.swf http://student.ccbcmd.edu/~gkaiser/biotutorials/eustruct/phagocyt.html Pinocytosis: For animation: http://student.ccbcmd.edu/~gkaiser/biotutorials/eustruct/pinocyt.html Receptor Mediated Endocytosis: Exocyotosis (EXO = Exit, outside) For animation: http://www.susanahalpine.com/anim/Life/endo.htm Scroll down to “Movement of large molecules across cell membrane http://www.aber.ac.uk/gwydd-cym/cellbiol/transport/index.htm 4. Three different transporters systems are involved in active transport. Use all the websites provide to describe each and to observe the animations. Different Transporter systems Uniport For animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/transport/caryprot.swf Symport For Animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/transport/symport2.swf Antiport For animation: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/transport/antiport.swf 5. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2001_g bio/folder_structure/ce/m3/s5/ Identify and describe what is occurring in the picture using the website above. Active Transport in Paramecium http://www.answers.com/topic/vacuole http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/contractilevac.gif Paramecium Contractile Vacuole: http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/movies/paramecium/para%20cont.mov 6. What is a contractile vacuole? 7. Why does a paramecium living in freshwater need it? IV. Summarize the differences between passive and active transport. Passive Transport Use of ATP With or against concentration gradient Different types Active Transport